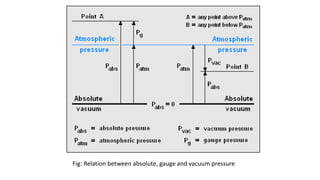
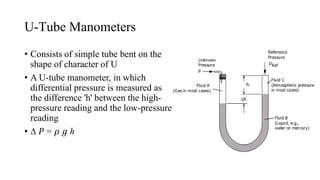
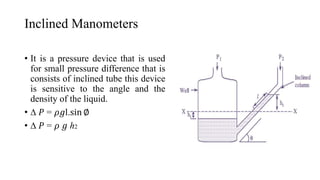
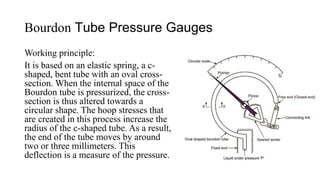
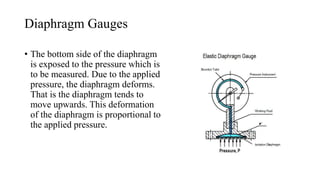
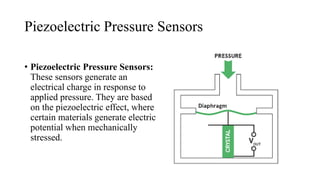
Pressure can be measured using various instruments that operate based on different principles. Manometers like U-tube and inclined manometers measure pressure using the height of liquid columns. Bourdon tube, diaphragm, and bellows gauges use mechanical elements that deform under pressure. Piezoelectric sensors generate electrical signals in response to applied pressure. Proper instrument selection depends on the type of pressure (absolute, gauge, or vacuum), required accuracy, and application. Common applications include fluid system monitoring, HVAC, boilers, and automotive/medical uses.