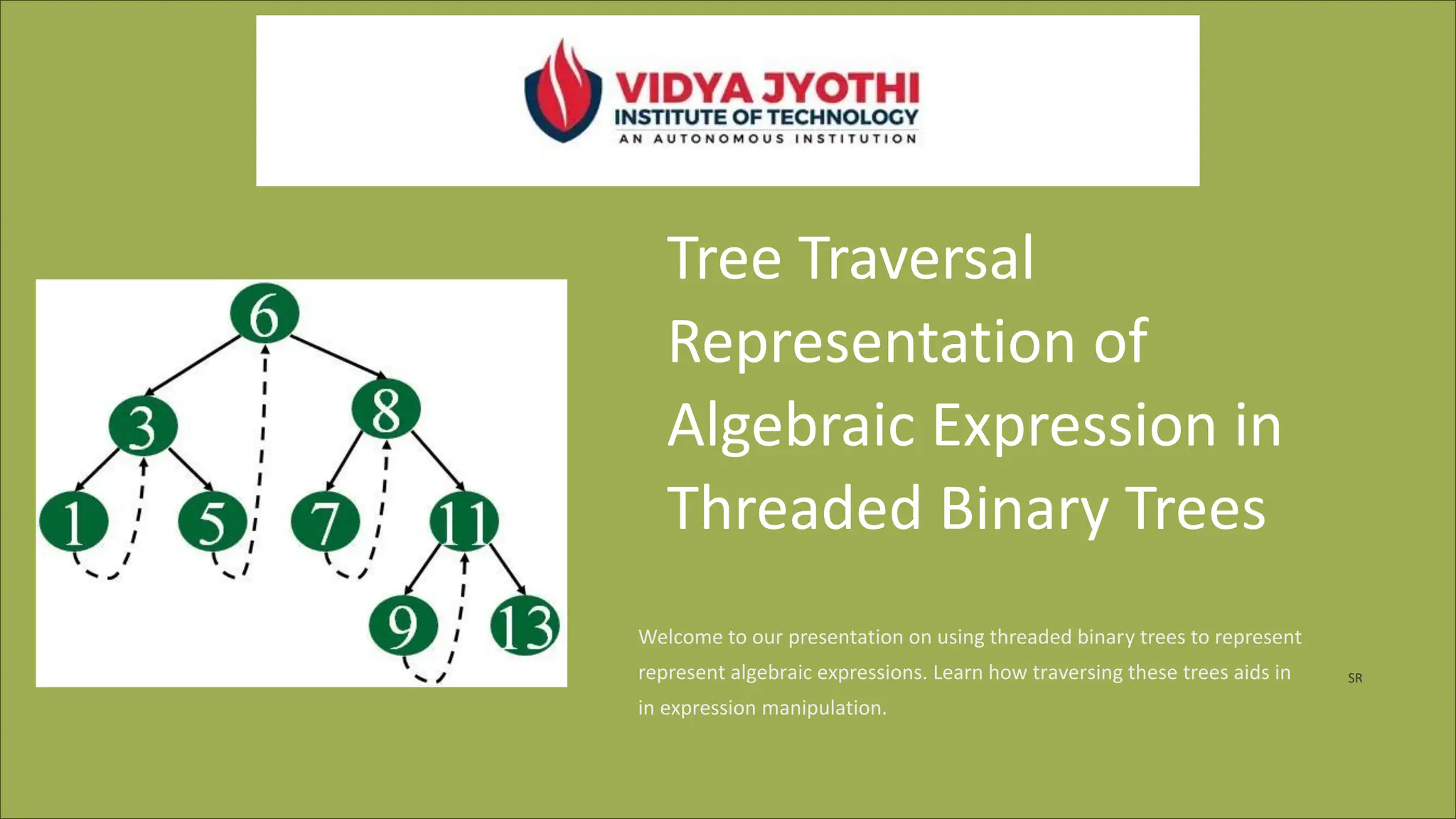
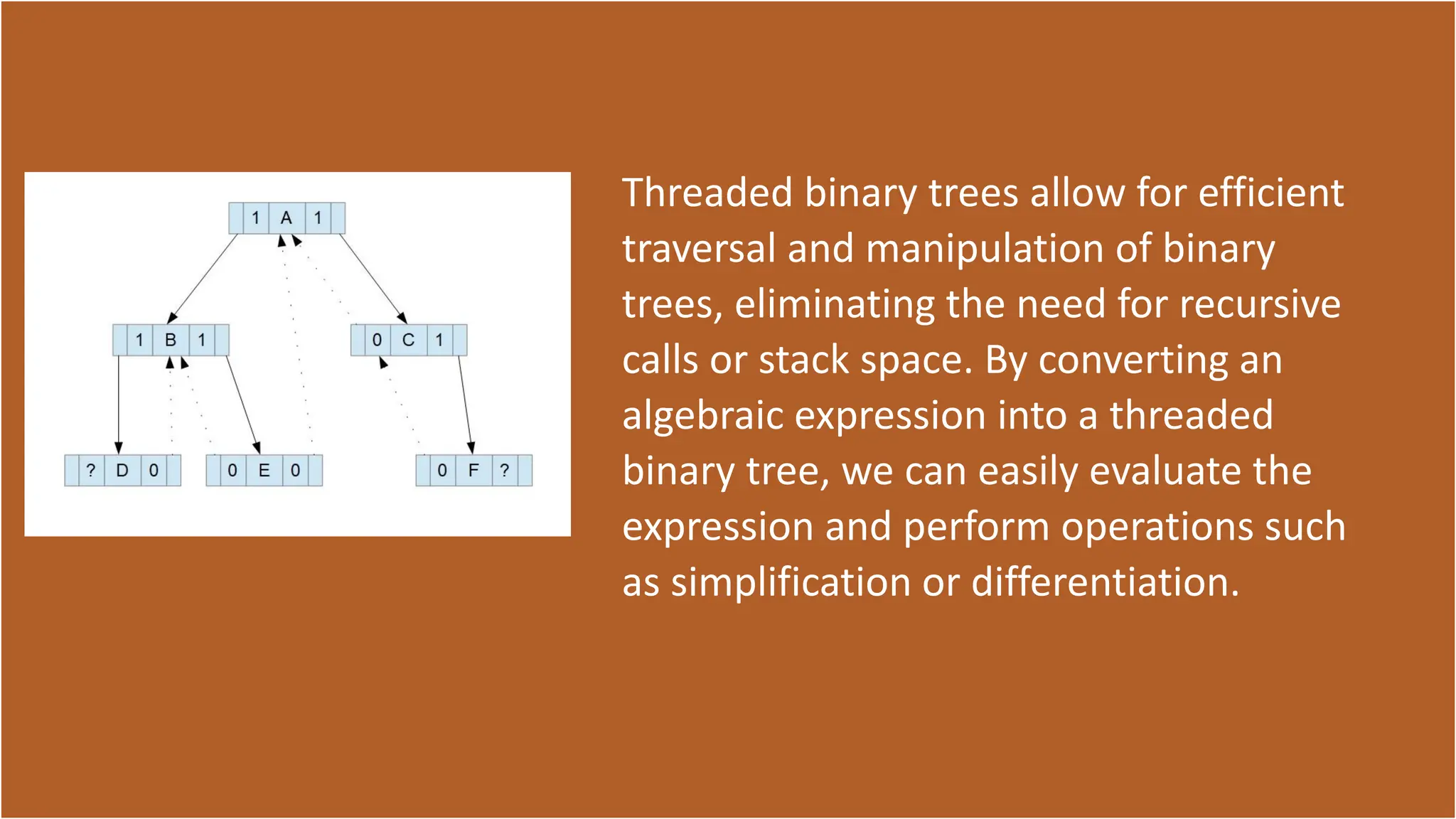
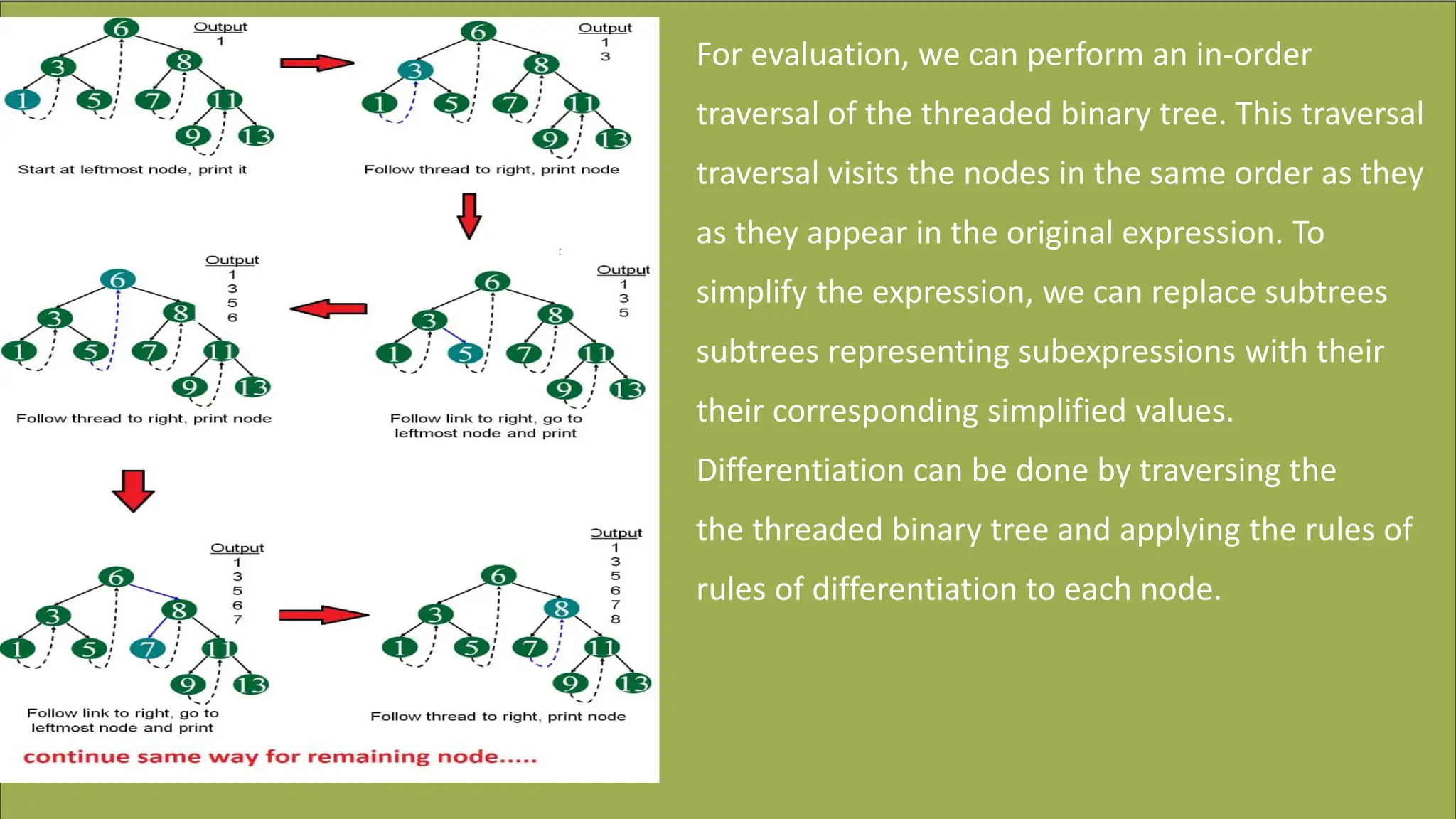
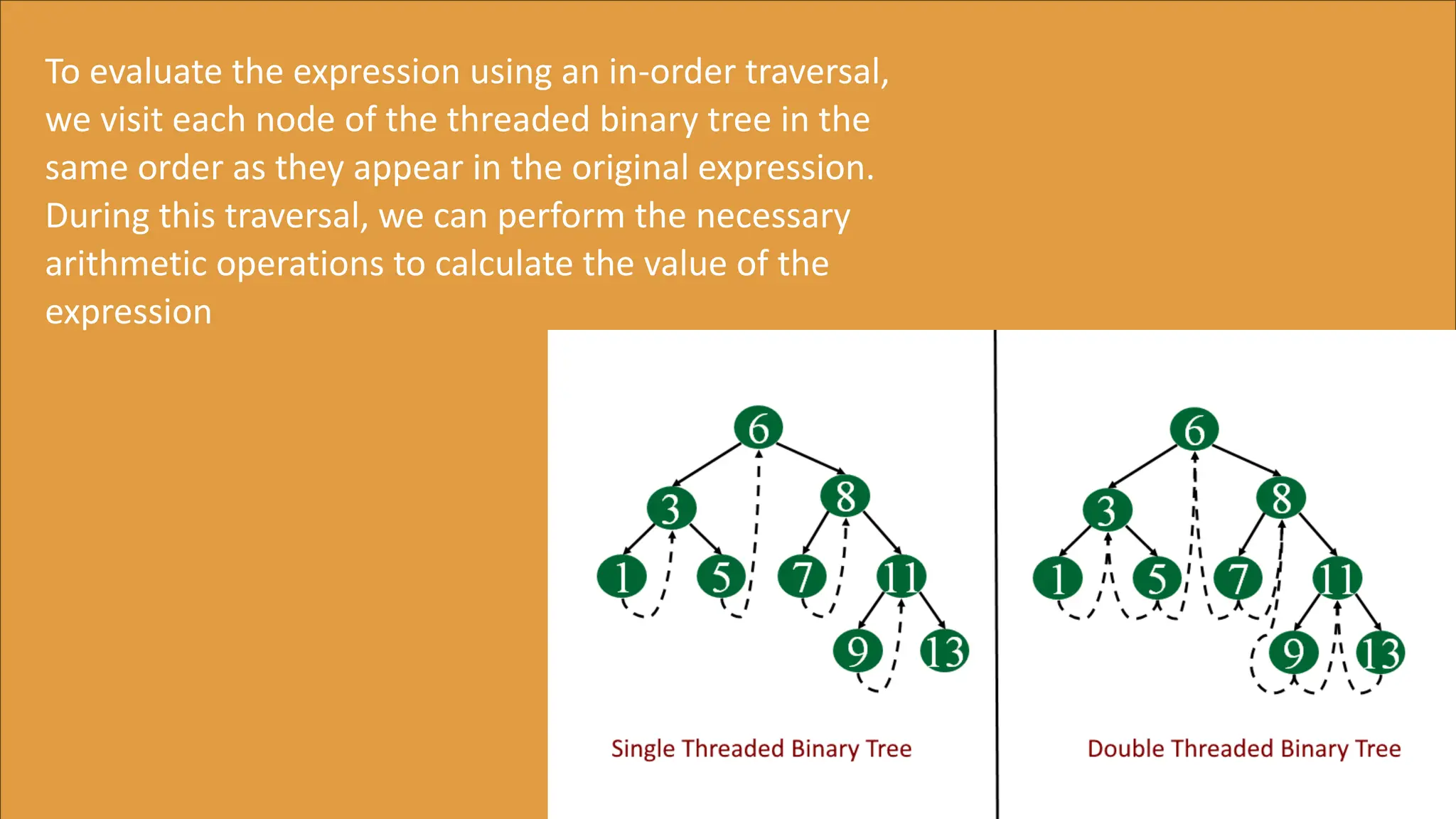
The document discusses the use of threaded binary trees for representing and manipulating algebraic expressions. It explains the definition and purpose of threaded binary trees, describes the conversion of infix expressions to these trees, and outlines methods for evaluation and manipulation, including simplification and differentiation. Potential limitations of this approach are also mentioned, noting that while efficient, threaded binary trees may lack intuitiveness and can struggle with complex expressions.