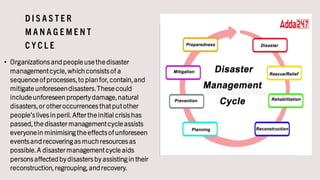
The document discusses disaster management in India. It defines disaster management and outlines the disaster management cycle. It describes different types of disasters including natural disasters like floods and earthquakes, and human-caused disasters such as industrial accidents. The Disaster Management Act of 2005 established agencies responsible for disaster management in India at the national, state, and local levels, including the National Disaster Management Authority. The agencies work to prevent, mitigate and respond to disasters in India.