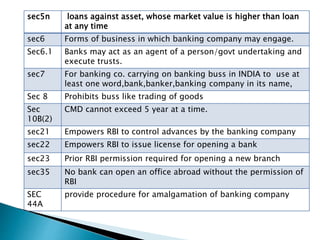
The Banking Regulation Act of 1949 regulates banking firms in India and gives powers to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to license and supervise banks. It defines banking and imposes requirements on transactions, management, and penalties for non-compliance. The RBI Act of 1934 established the RBI and provides the framework for RBI to conduct monetary policy and supervise scheduled banks. Key powers include issuing currency, setting reserve ratios, lending to banks and governments, and collecting credit information. Both acts work to create transparency, protect depositors, and ensure smooth functioning of the banking system.