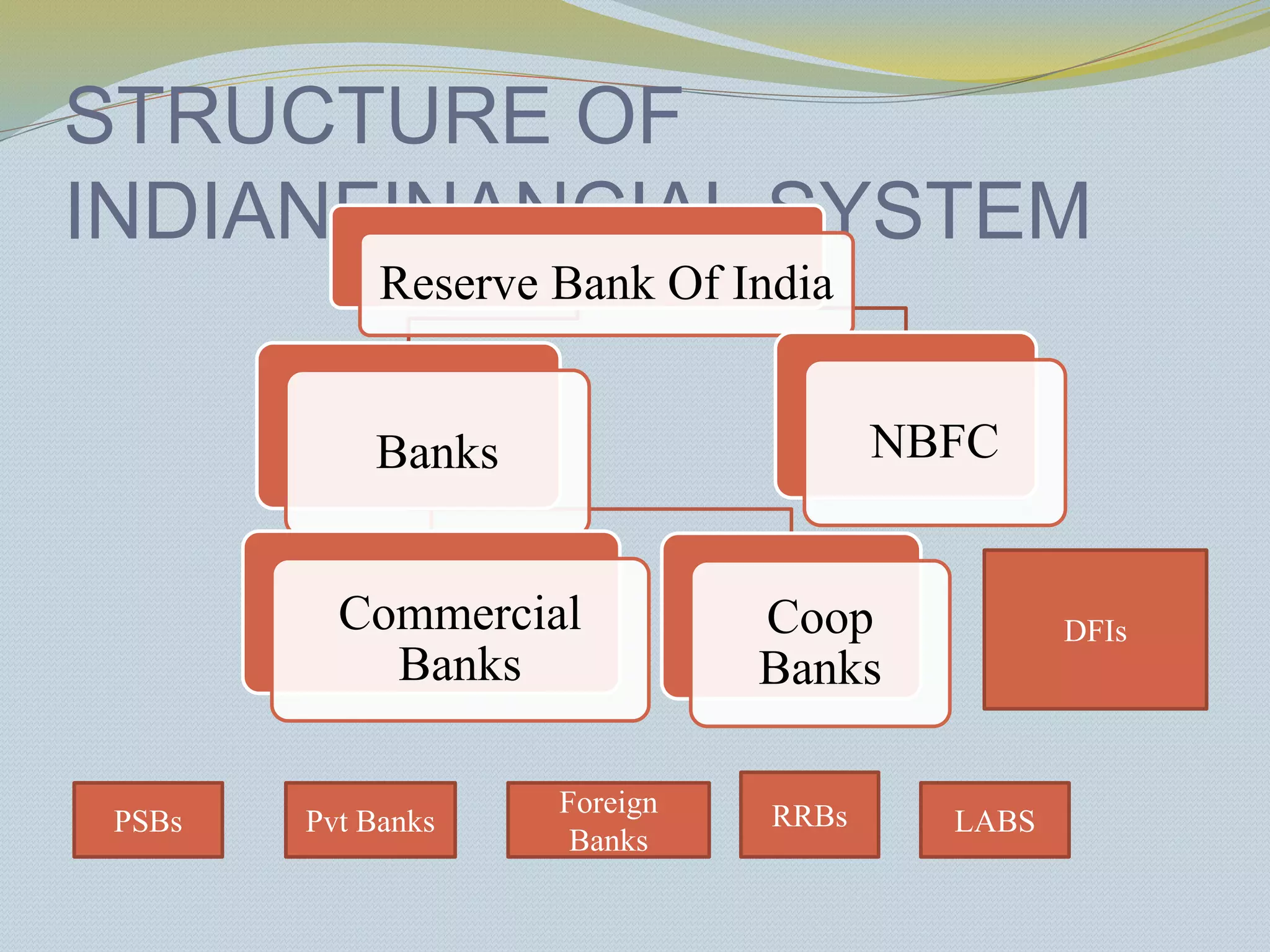
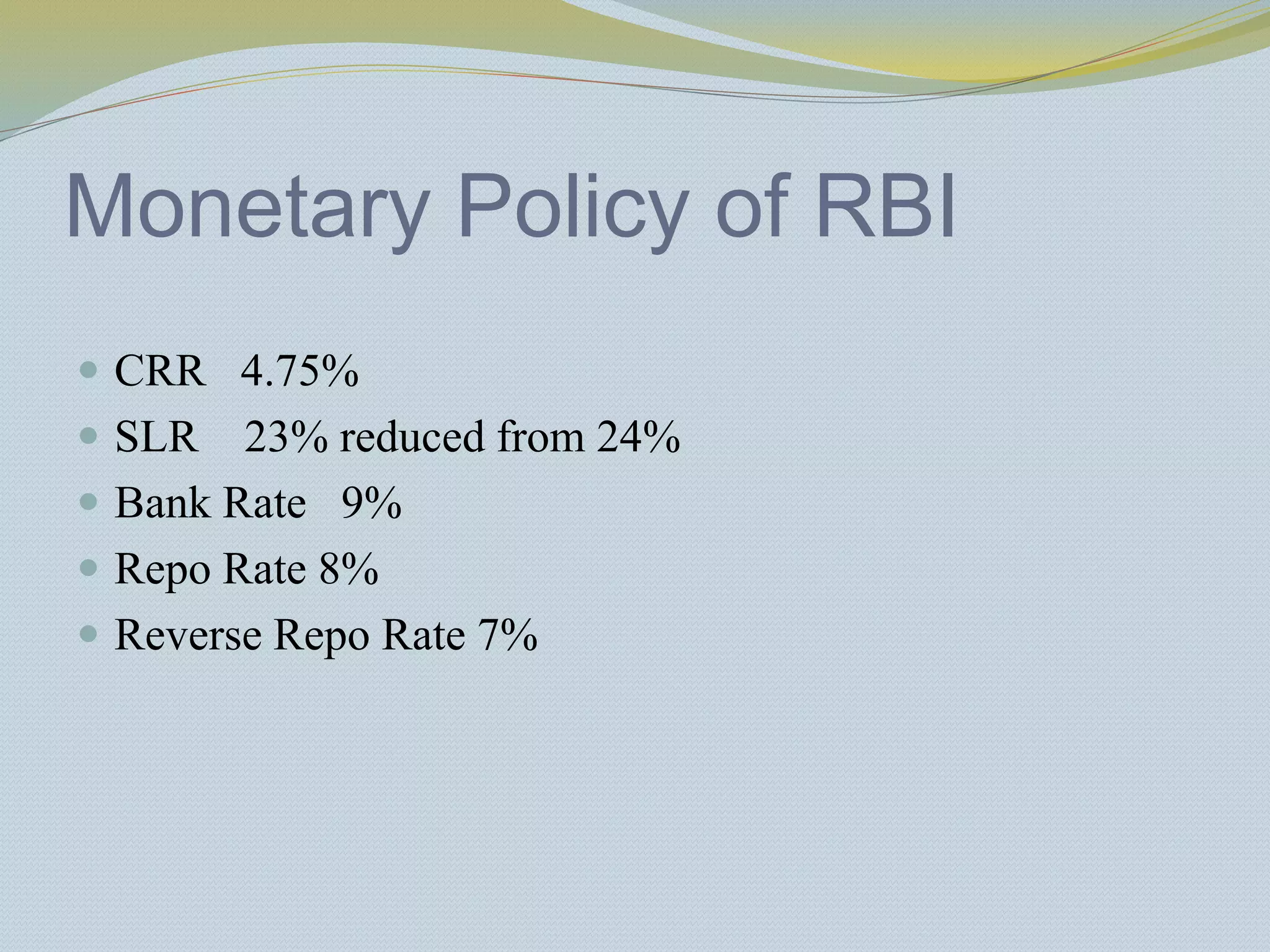
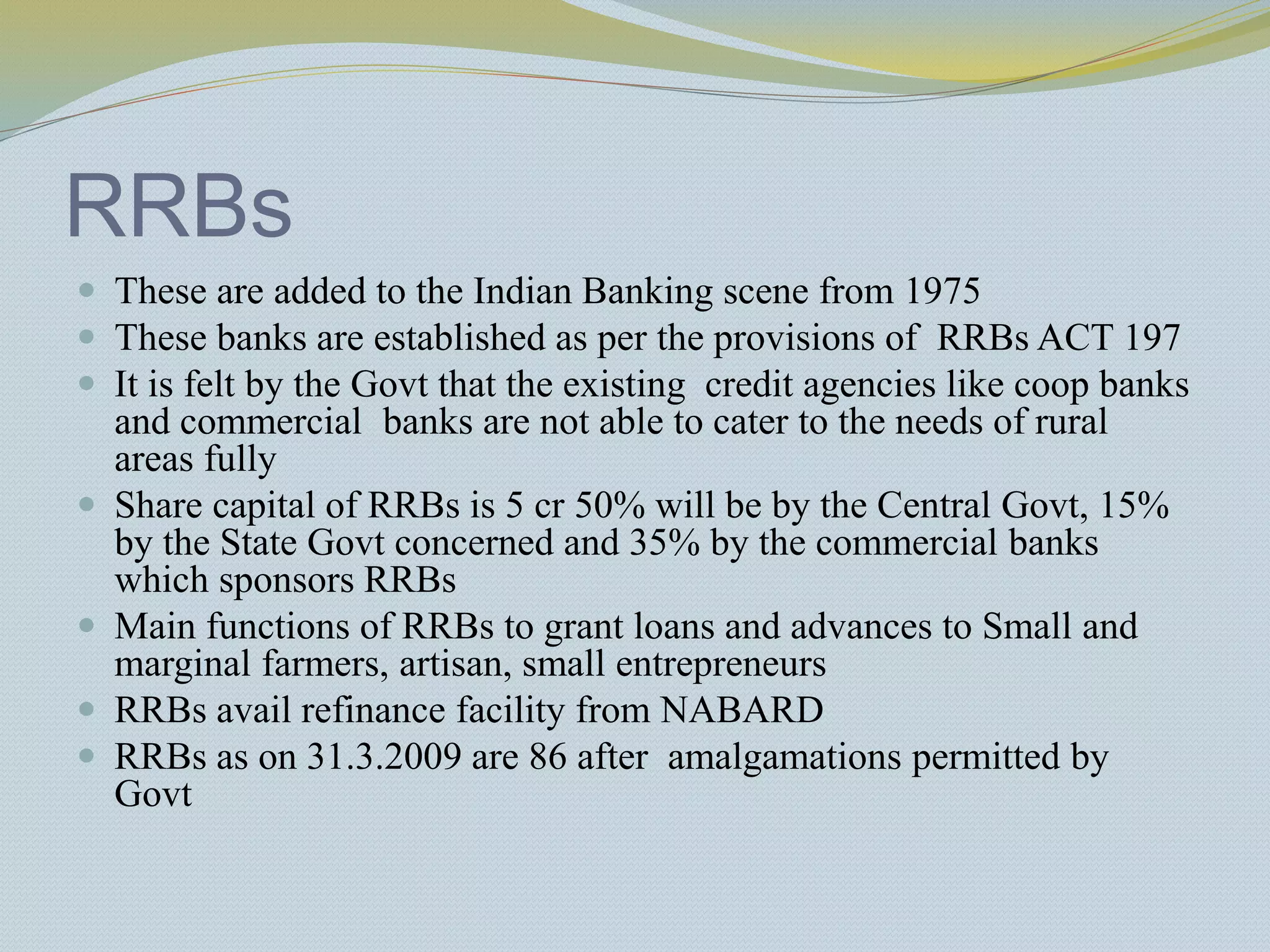
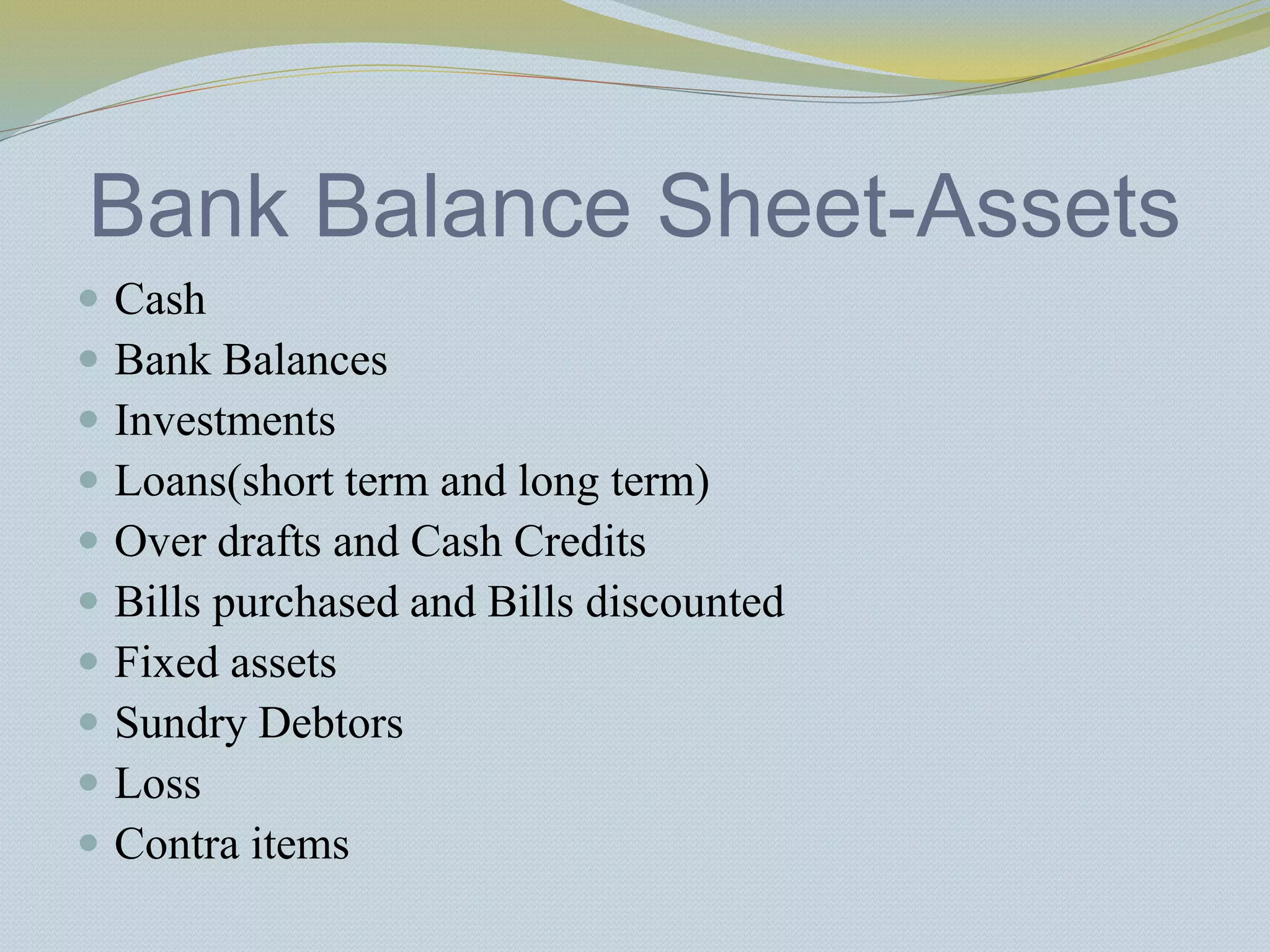
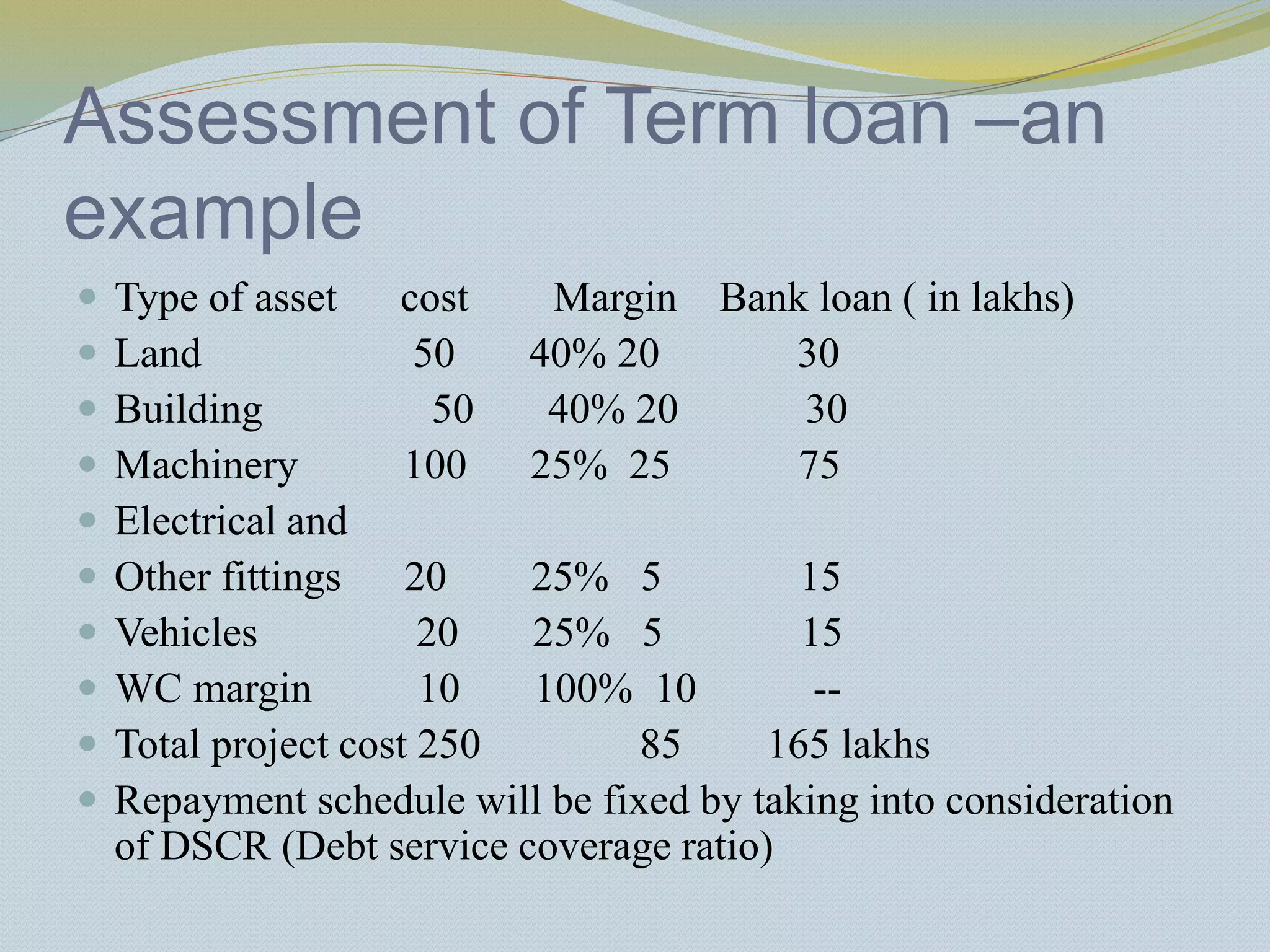
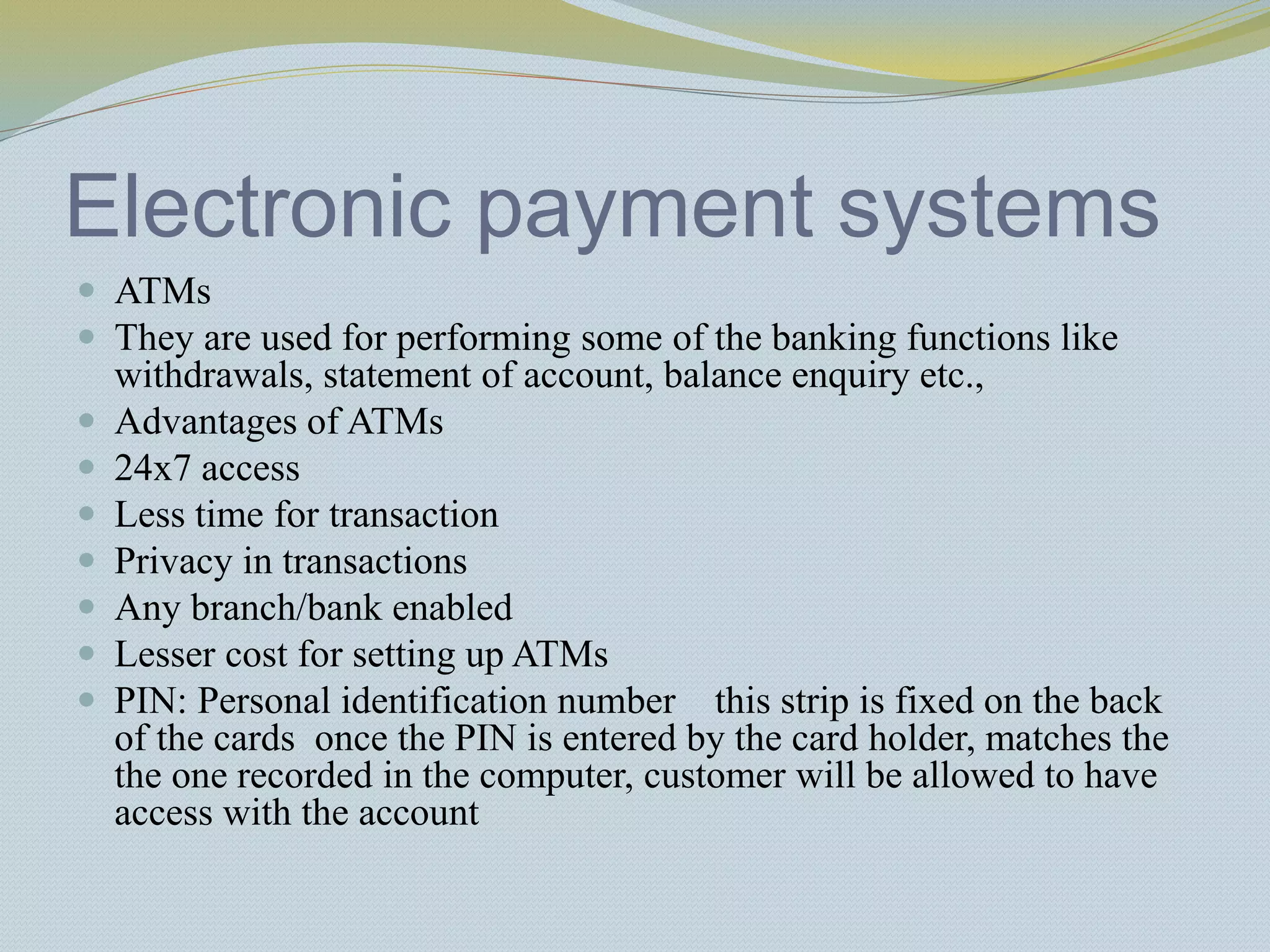
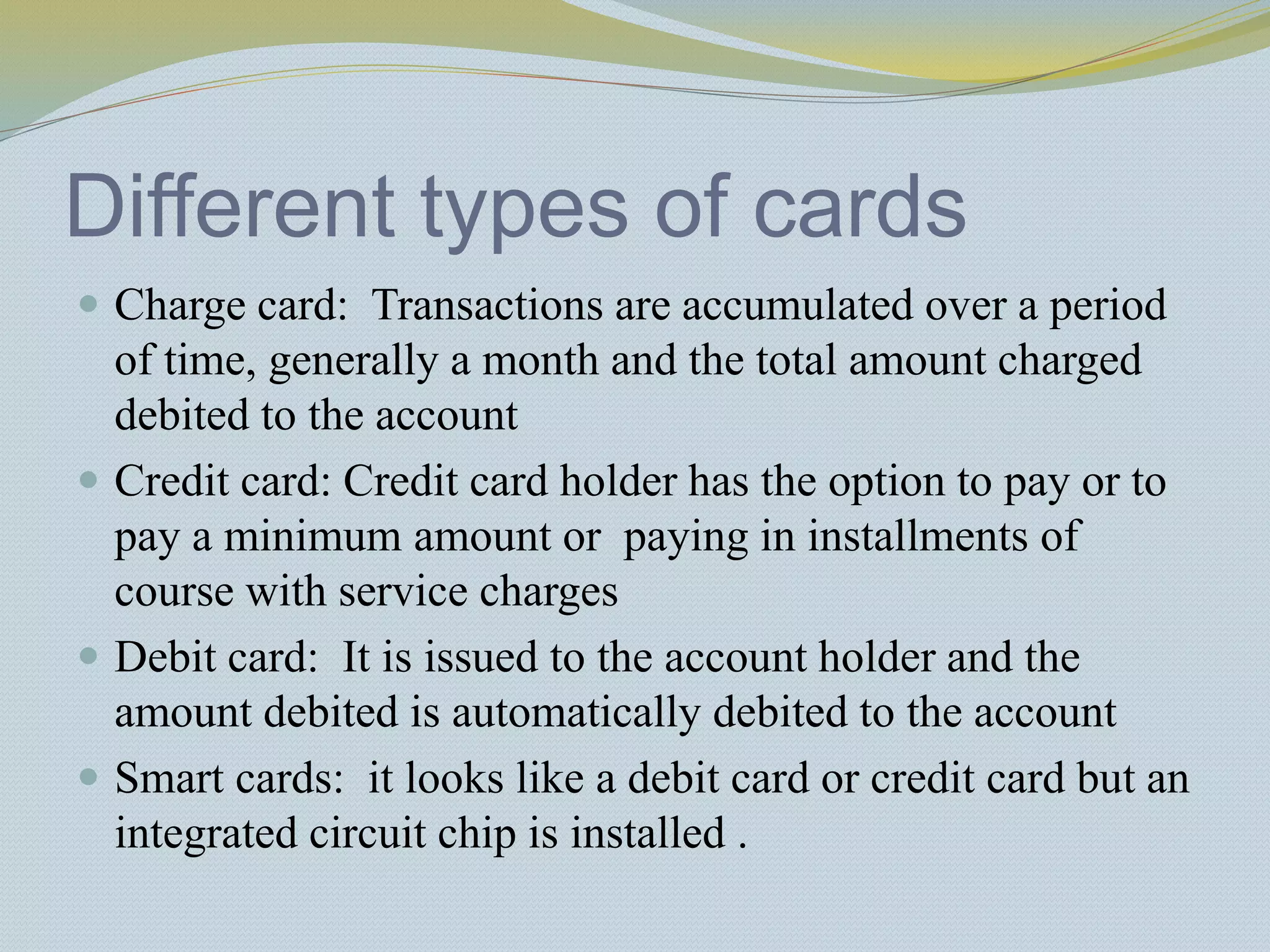
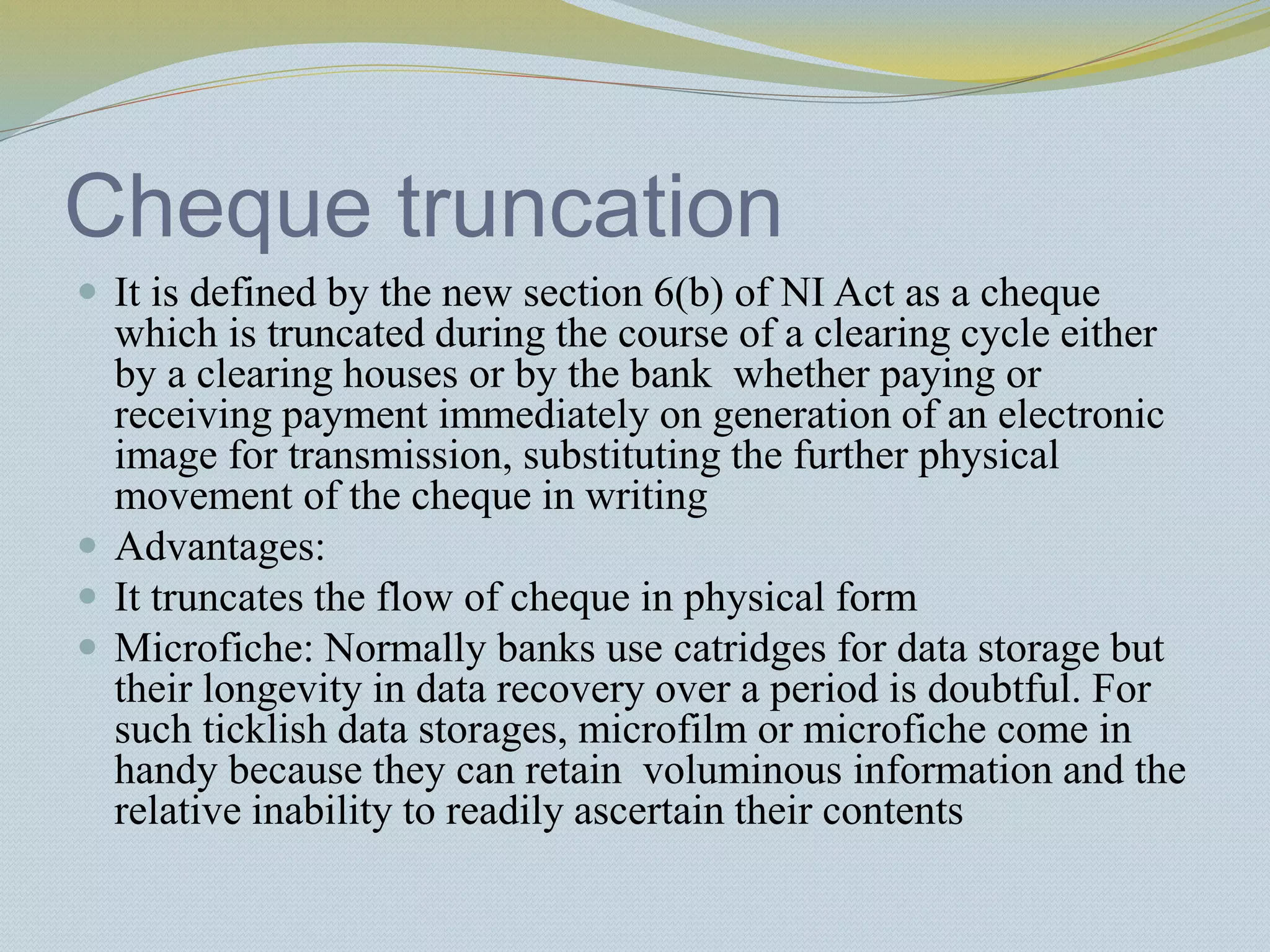
The document provides a history of banking in India from the establishment of the earliest banks in the late 19th century through nationalization efforts in the 20th century. It discusses key events and institutions including:
1) The establishment of early presidency banks in the 1870s which laid the foundations for modern banking. These were later amalgamated into the Imperial Bank of India in 1921.
2) The passage of the Reserve Bank of India Act in 1934 which established RBI as the central bank and the Banking Regulation Act of 1949 which brought banks under greater government control and empowered RBI for regulation and supervision.
3) The nationalization of the State Bank of India in 1955 and additional nationalization efforts of 14