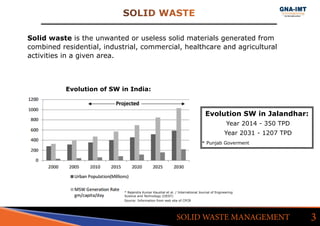
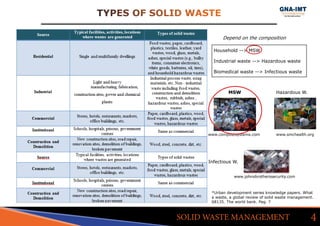
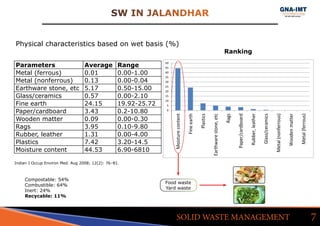
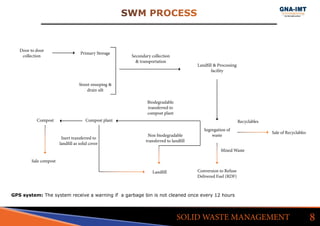
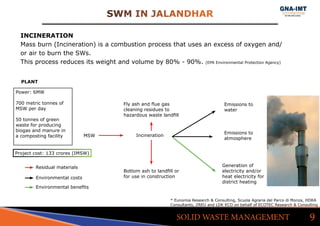
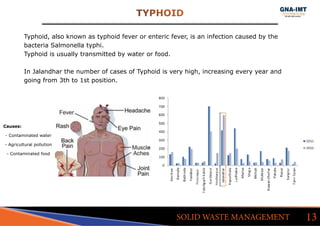
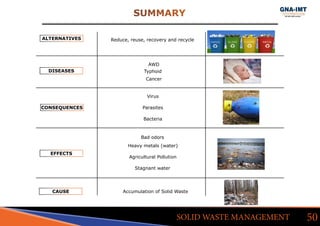
The document discusses solid waste management in Jalandhar City, India and its impact on community health. It notes that diseases like acute watery diarrhea, typhoid, and cancer have been on the rise in the city. To address this, actions taken in other cities like Ludhiana are discussed, such as door-to-door waste collection and construction of waste stabilization ponds. Reducing, reusing, recycling, and proper waste disposal methods are recommended to improve solid waste management and reduce pollution and disease in Jalandhar.