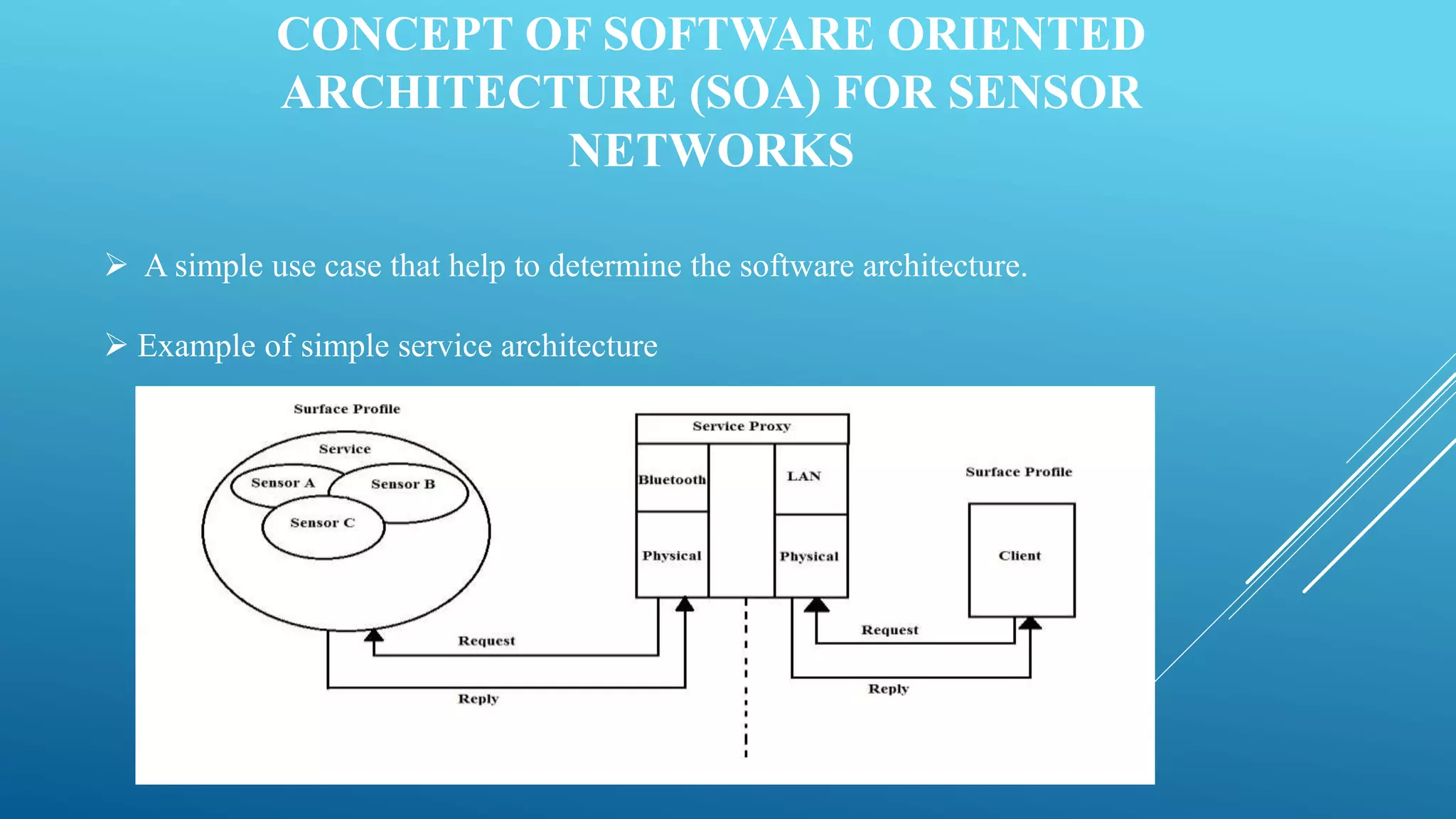
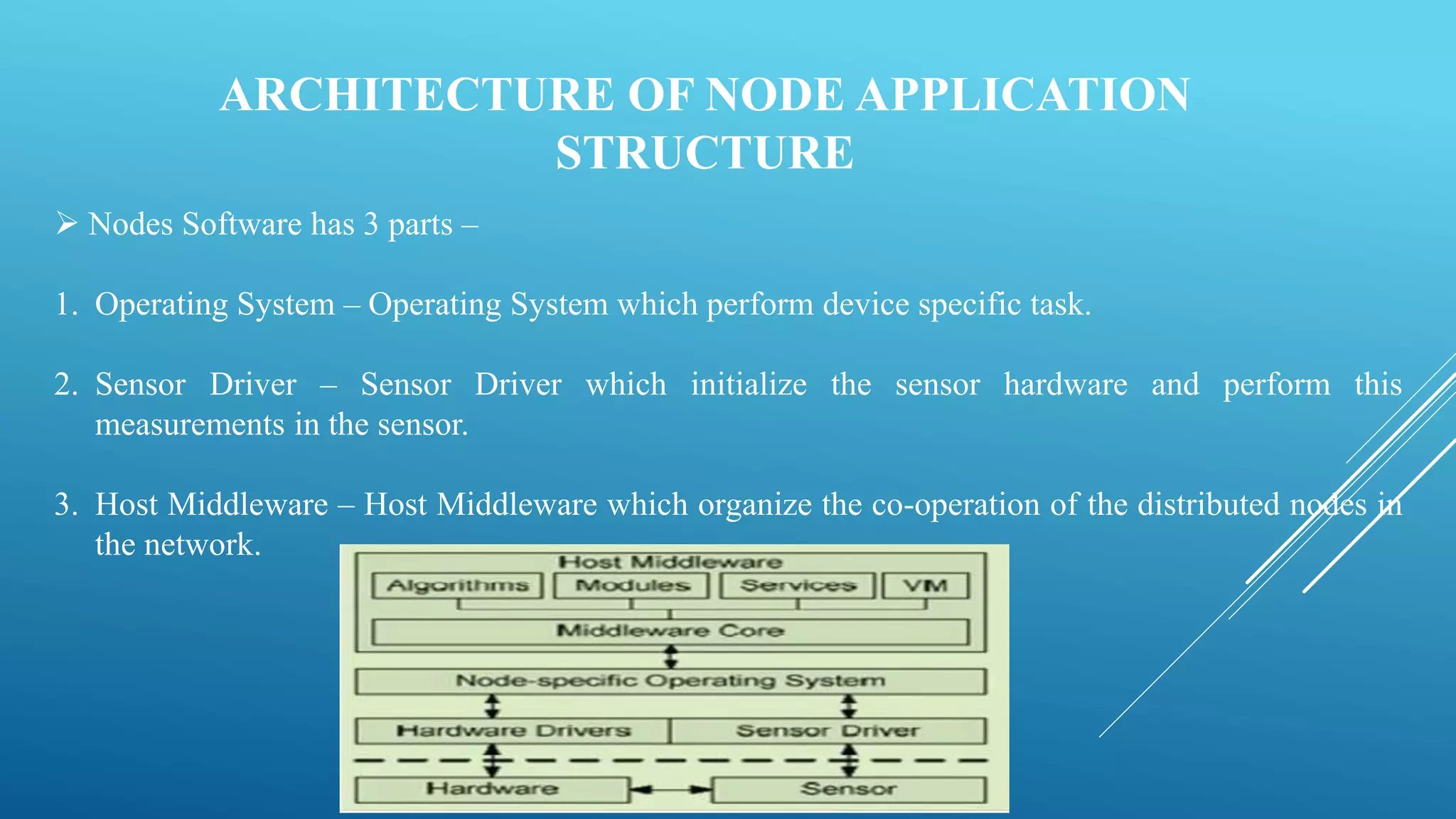
This presentation provides an overview of sensor networks. It discusses the introduction and types of sensor networks, as well as the characteristics of sensor networks which include being self-organizing, having concurrent processing, and low-cost with restricted energy resources. The presentation also outlines the software engineering aspects including sensor applications, node applications, and sensor network applications. It describes some architectural issues and standards/specifications for sensor networks. Finally, it discusses advantages and applications of sensor networks.