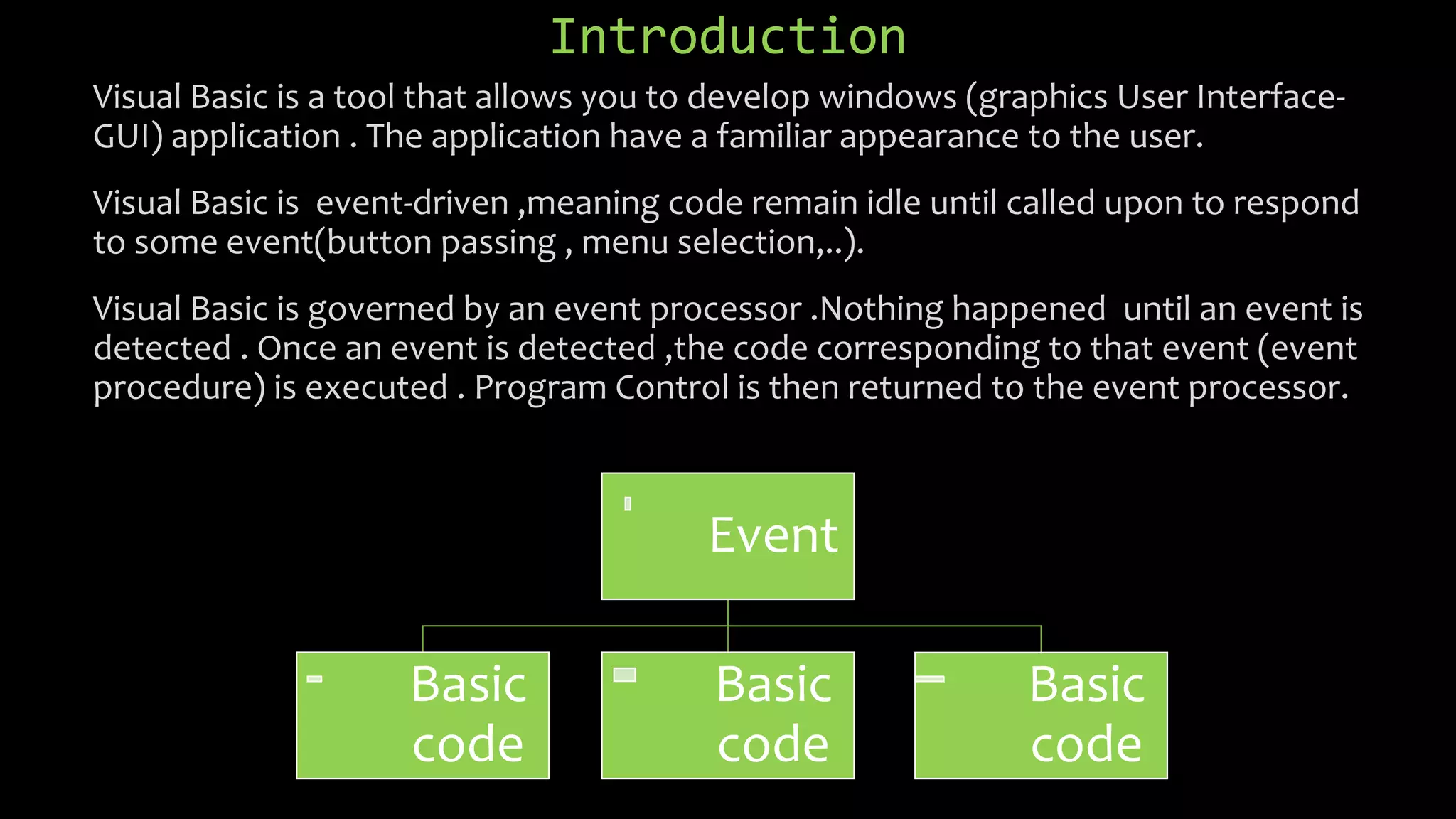
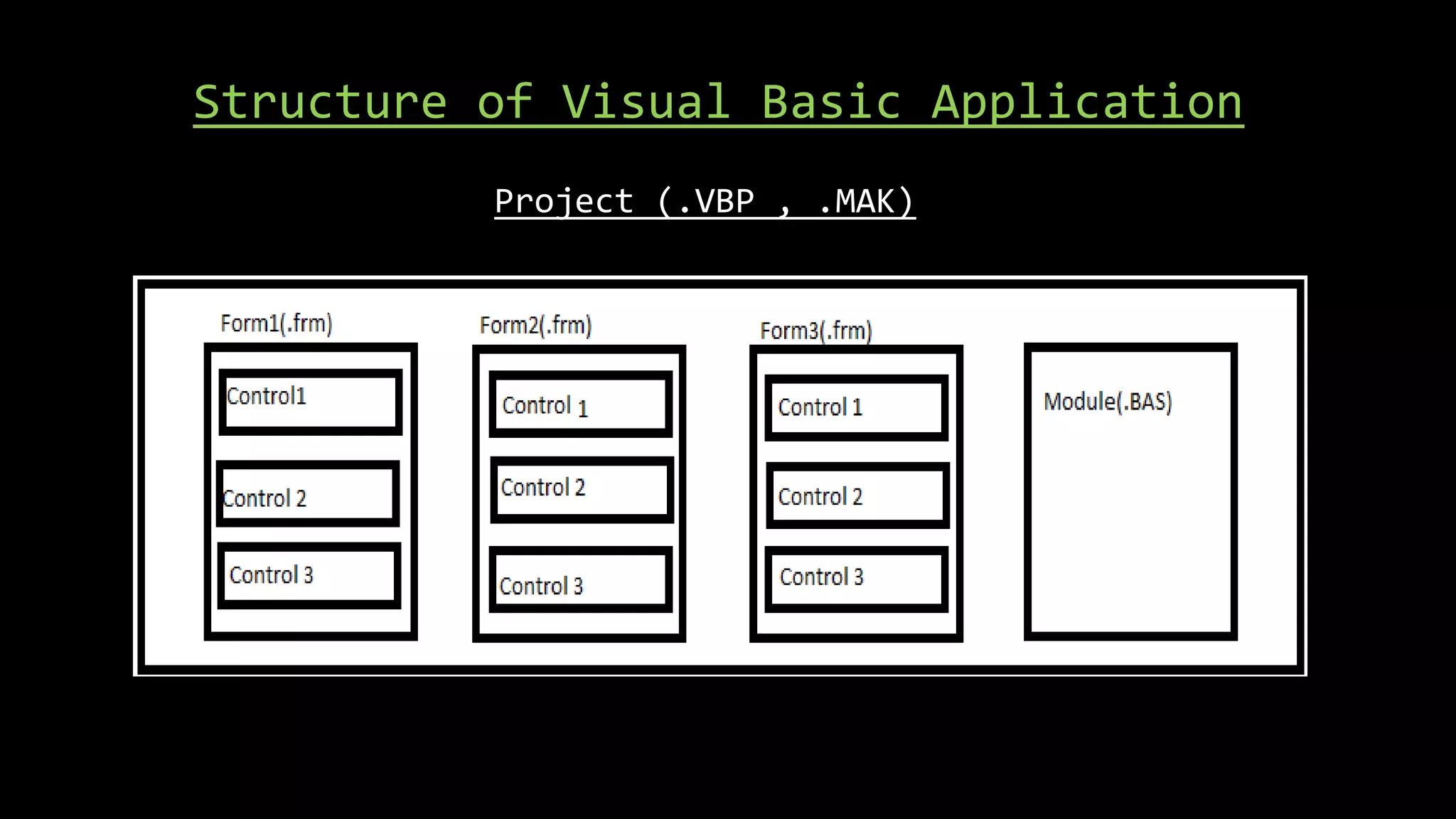
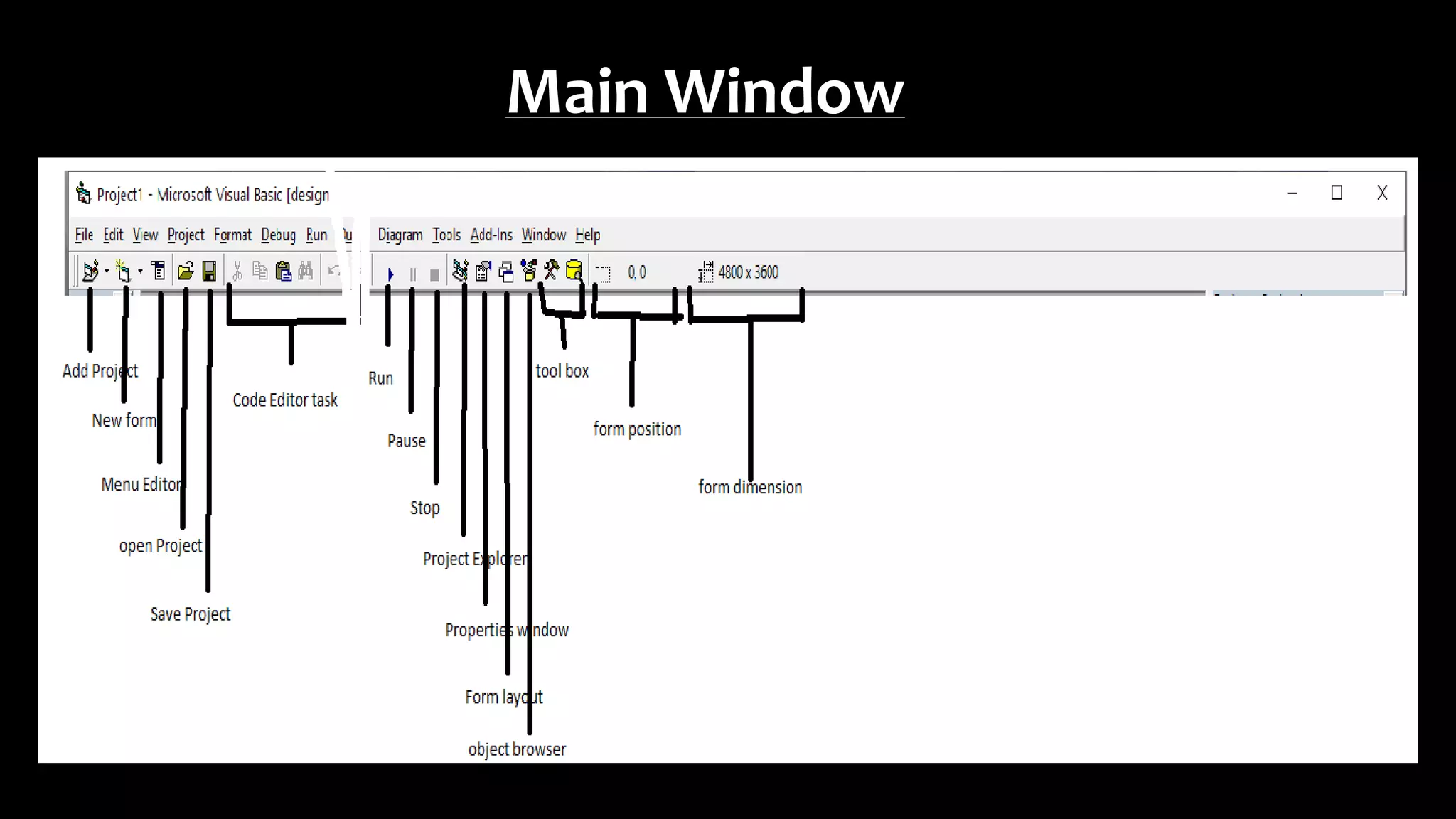
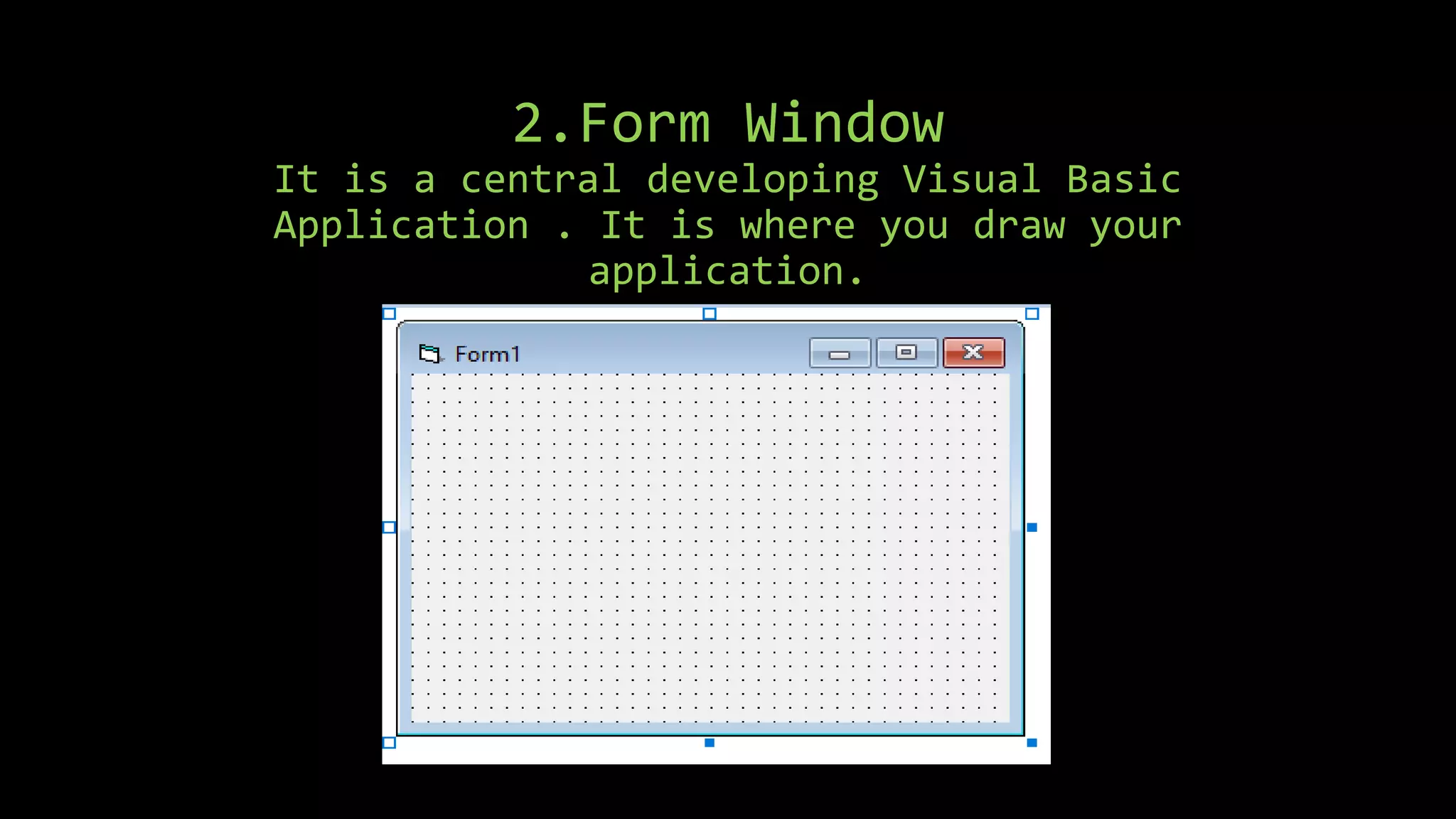
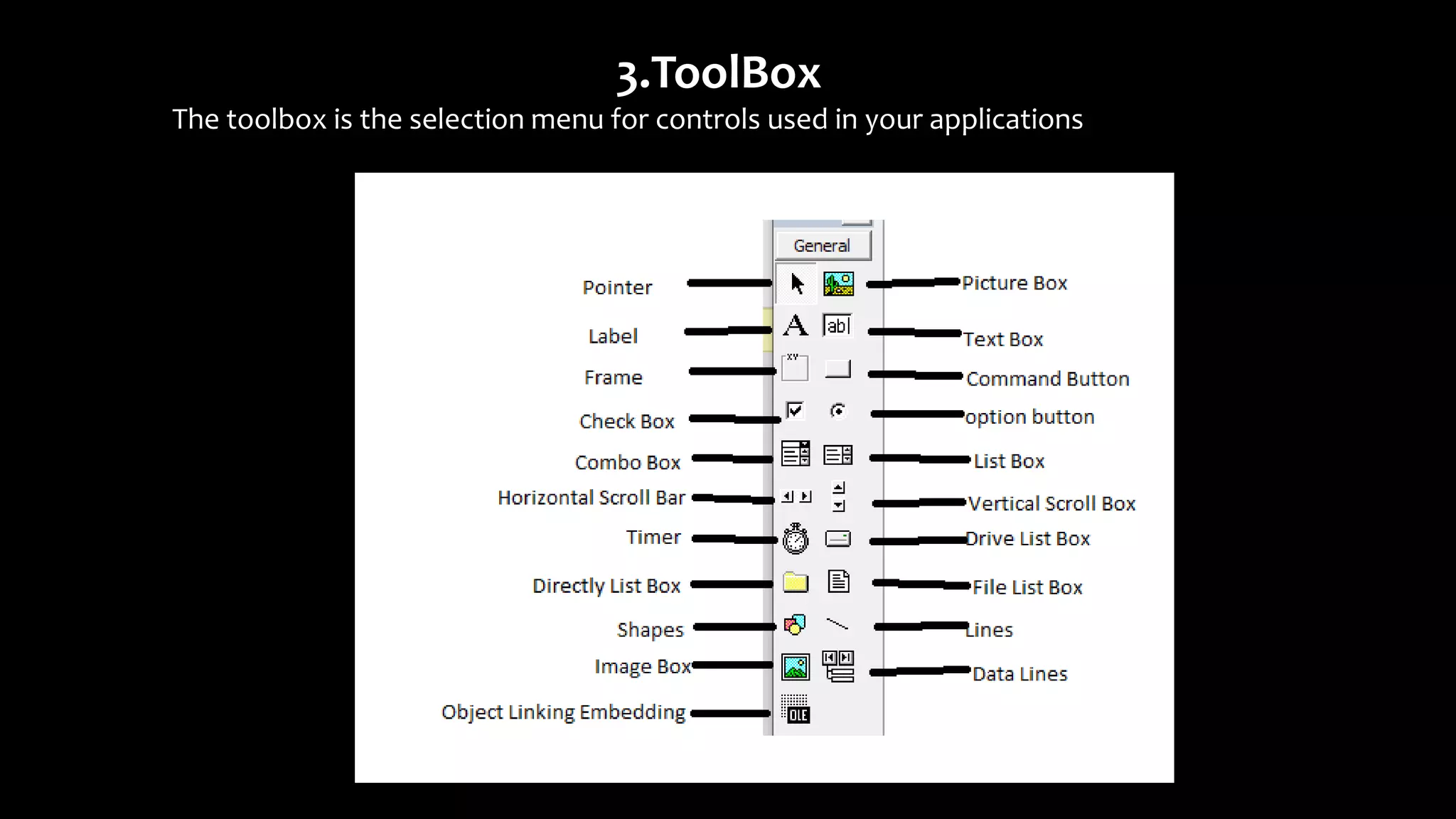
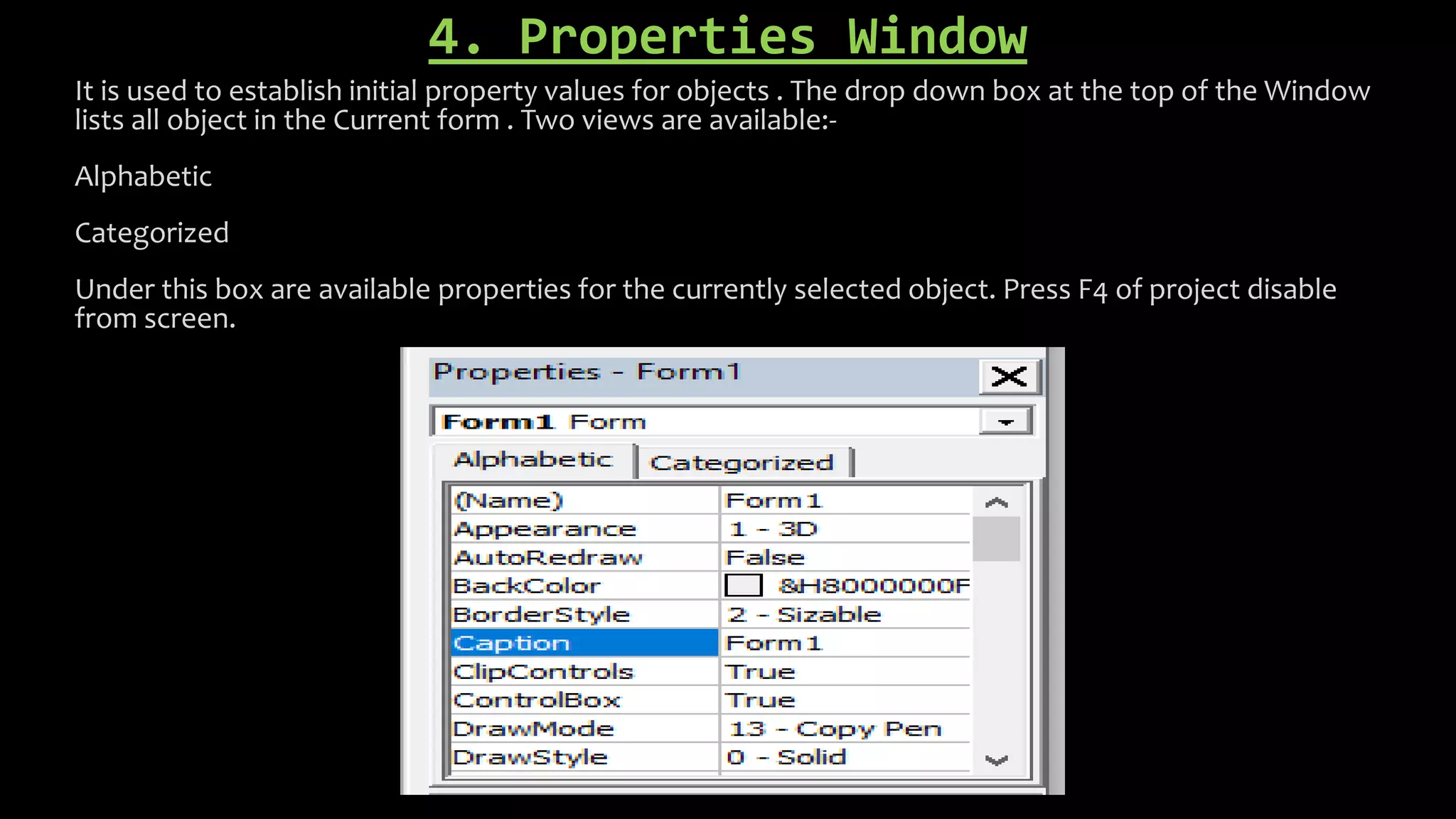
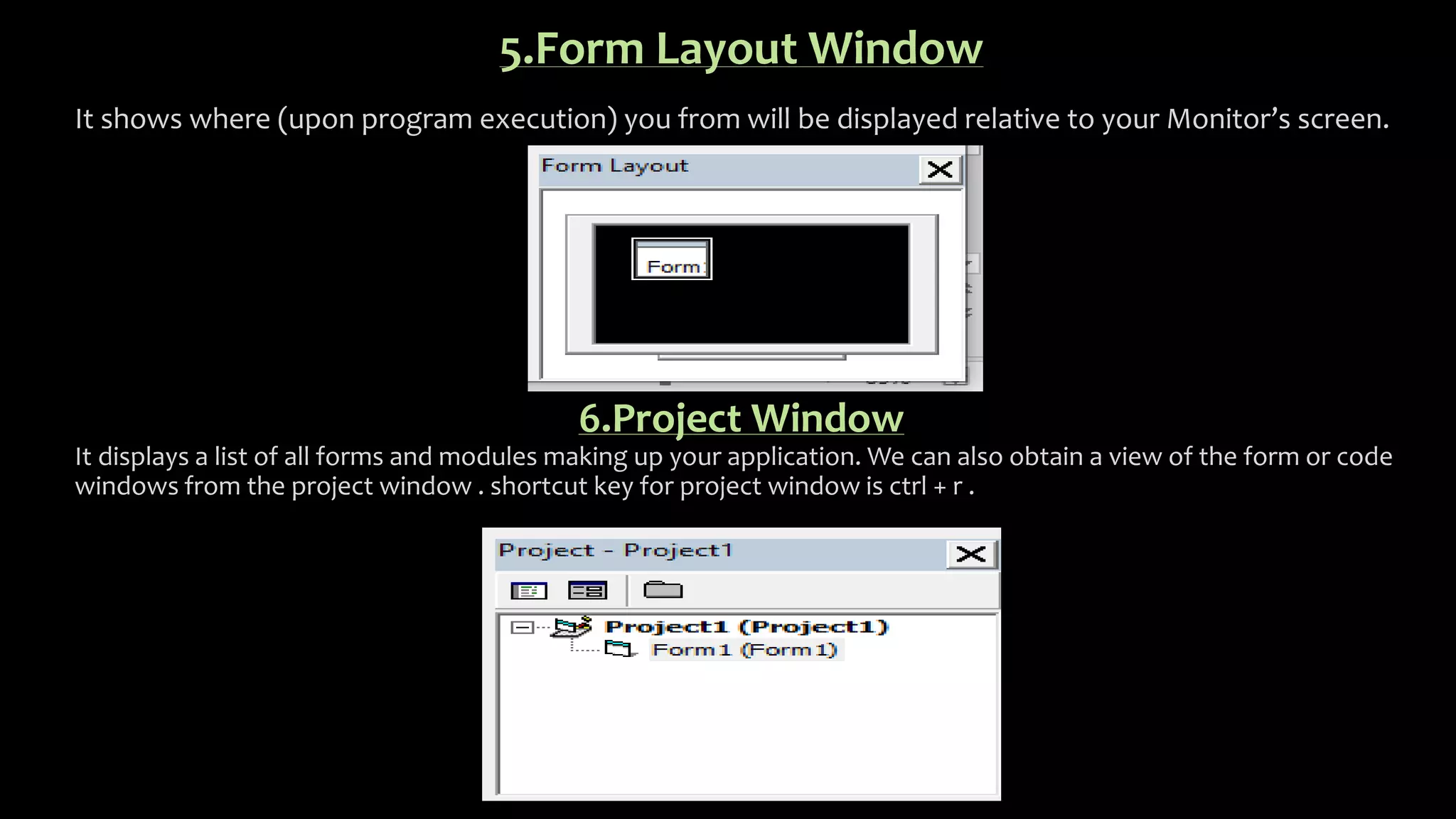
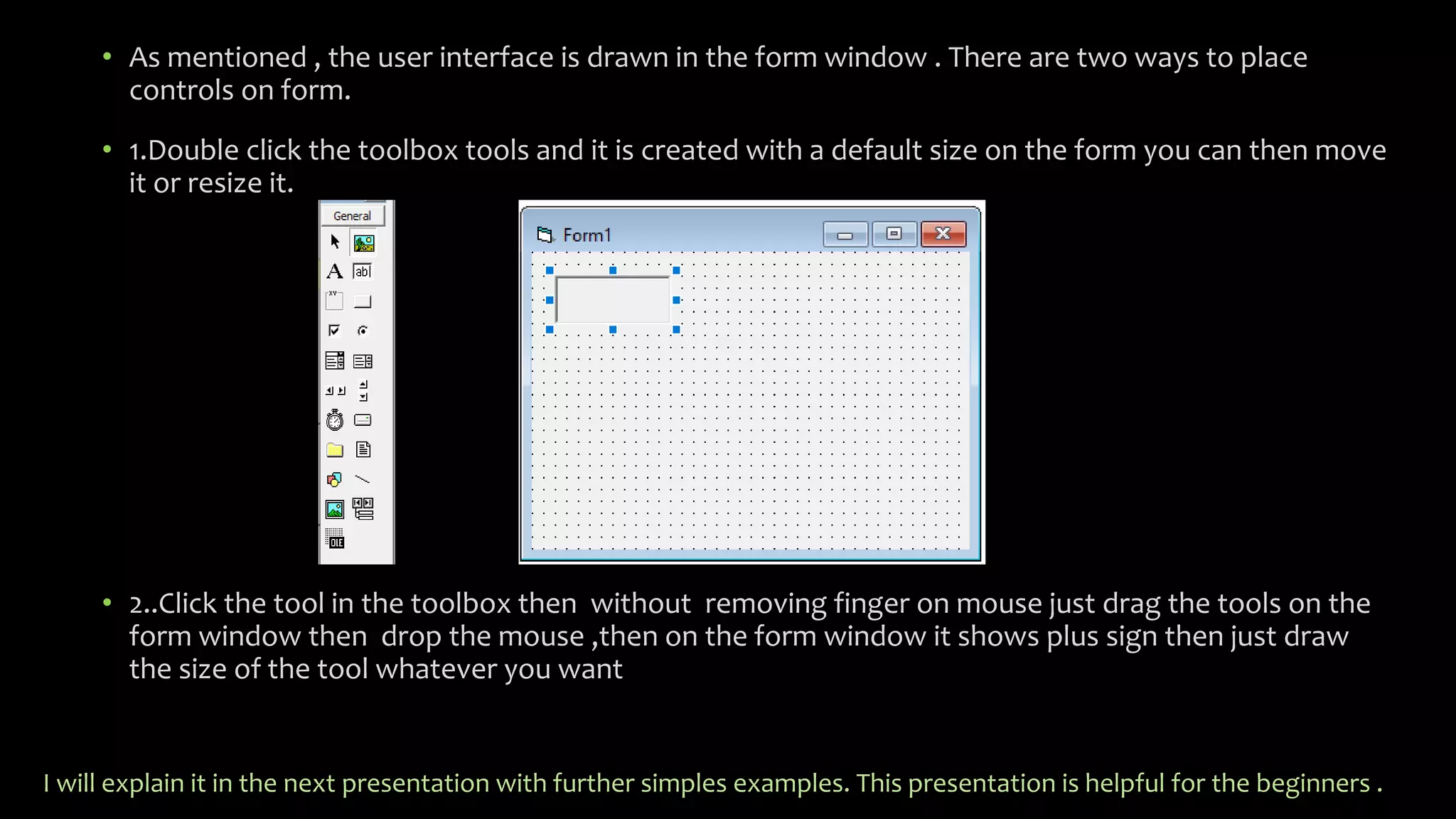
Visual Basic is an event-driven programming language that allows developers to build graphical user interface (GUI) applications. It uses forms to create windows for the user interface. Controls like text boxes, labels, and buttons are placed on the forms to allow user interaction. When an event like a button click occurs, the corresponding event procedure code is executed. The user interface is designed using forms, and properties are assigned to controls to determine characteristics like names, sizes, and positions. Code is attached to controls using event procedures to determine what happens when events occur.