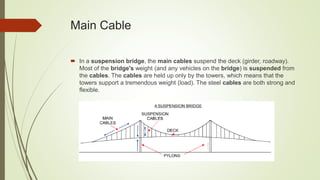
The document discusses the proposed design of a cable suspension bridge connecting Haldia Dock Complex to Kalitala, West Bengal, India. The 3,310 meter long bridge would cross the busy Hooghly River. Key components of the bridge design include the deck, stiffening girder, pylons, suspension cables, and foundations. Loads such as dead load, live load, wind load, and seismic load will be considered in the structural analysis. The objectives are to design and analyze the bridge using STAAD Pro software and assess the environmental impact using Simapro.