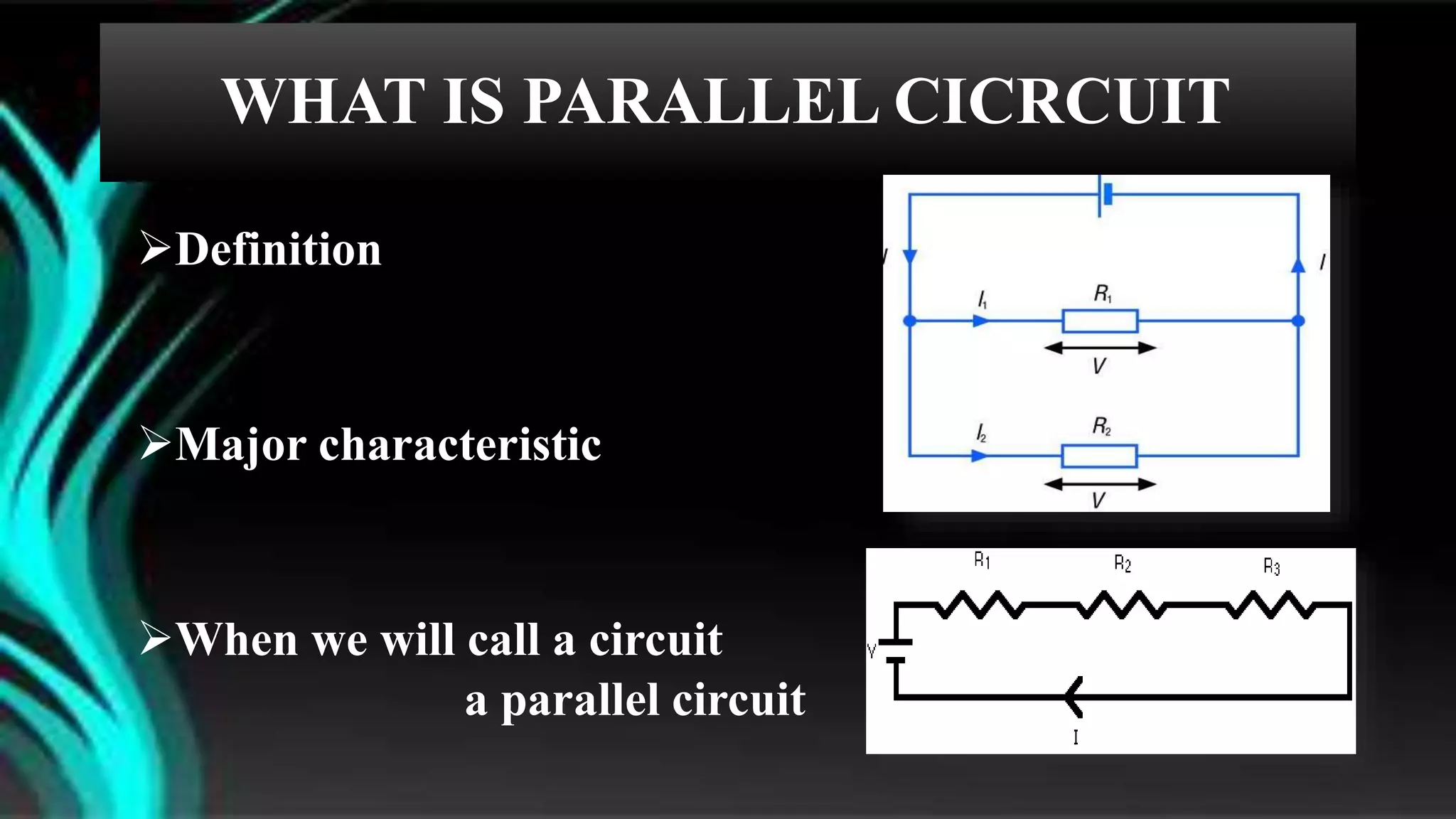
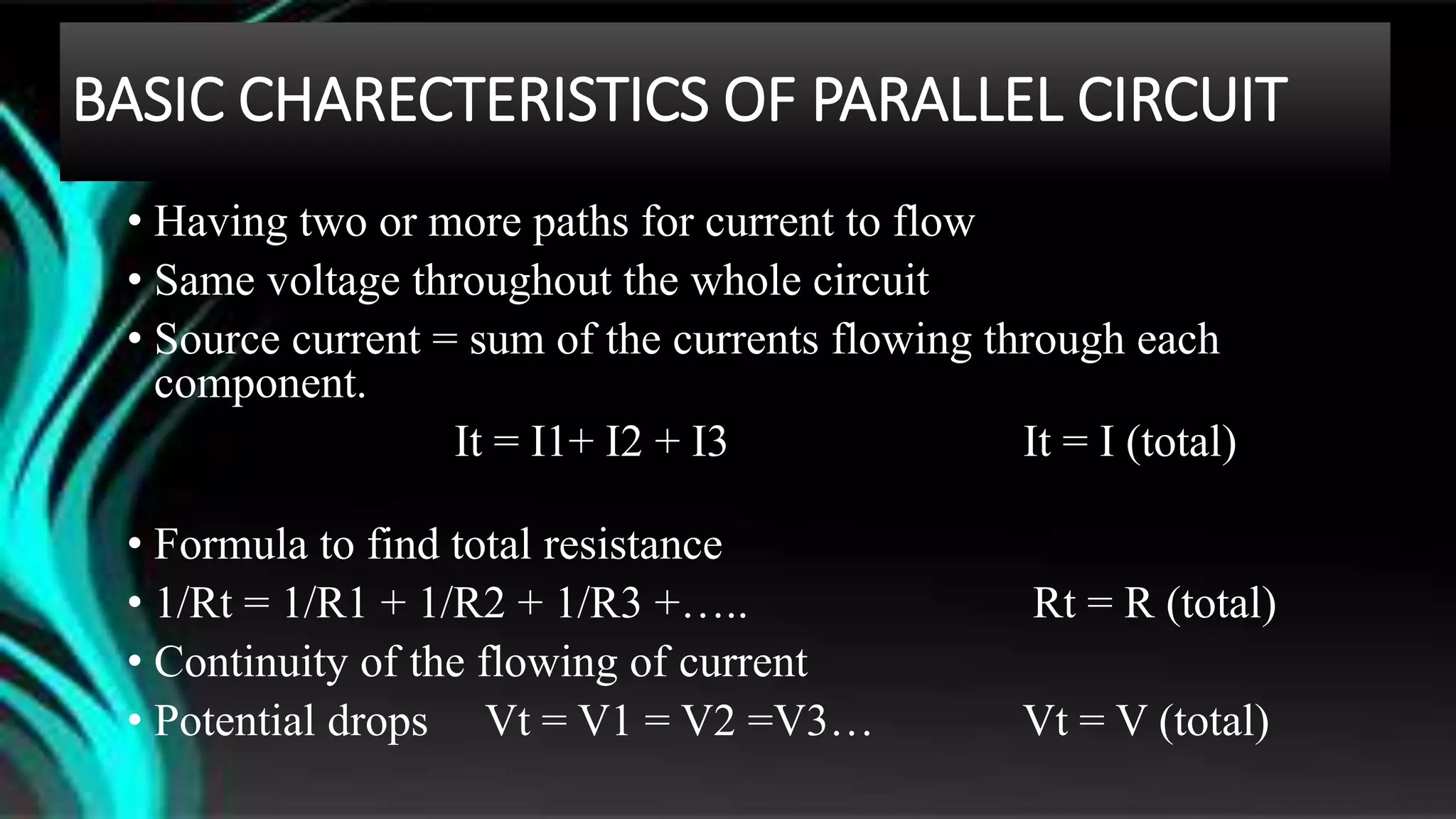
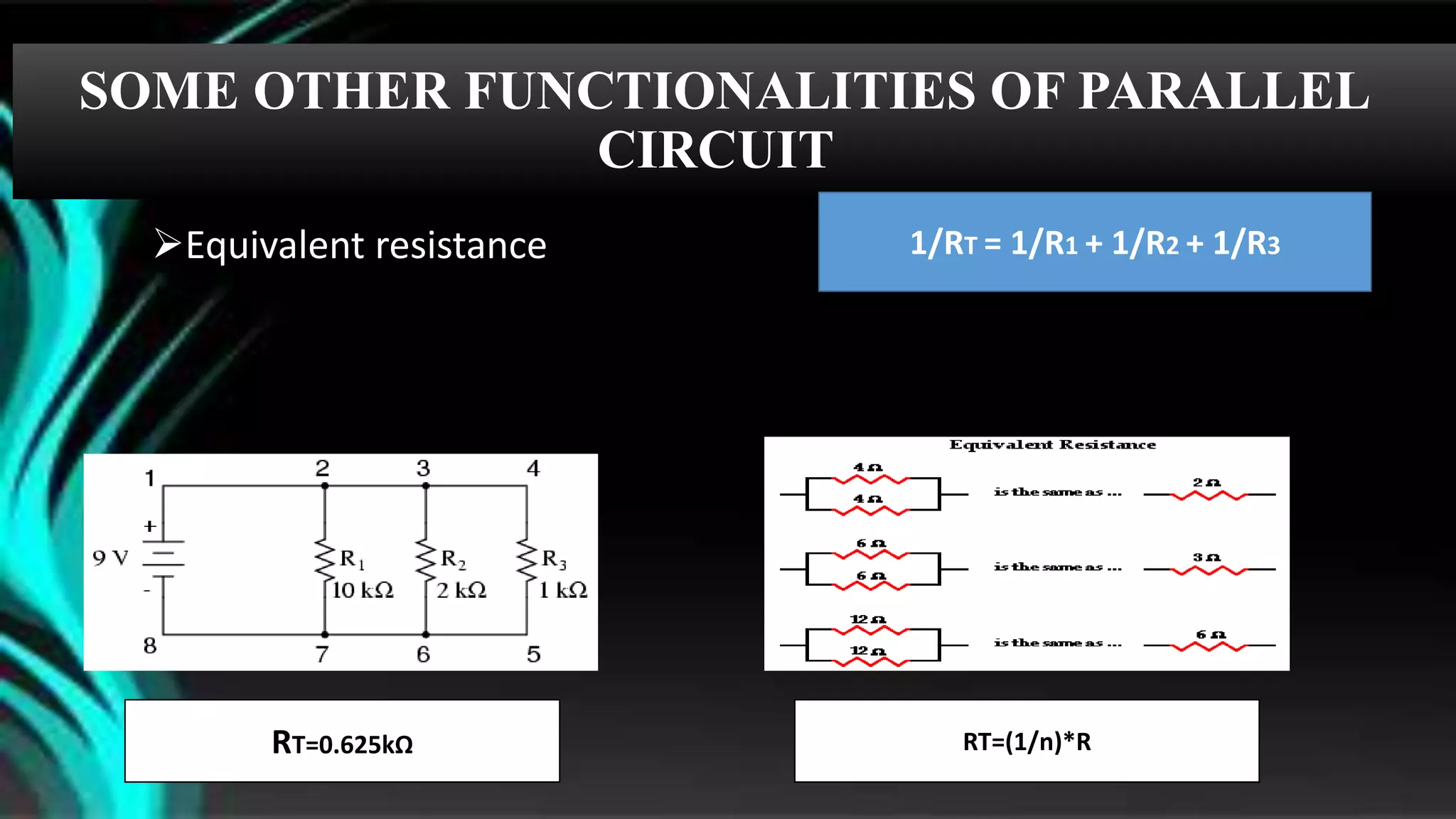
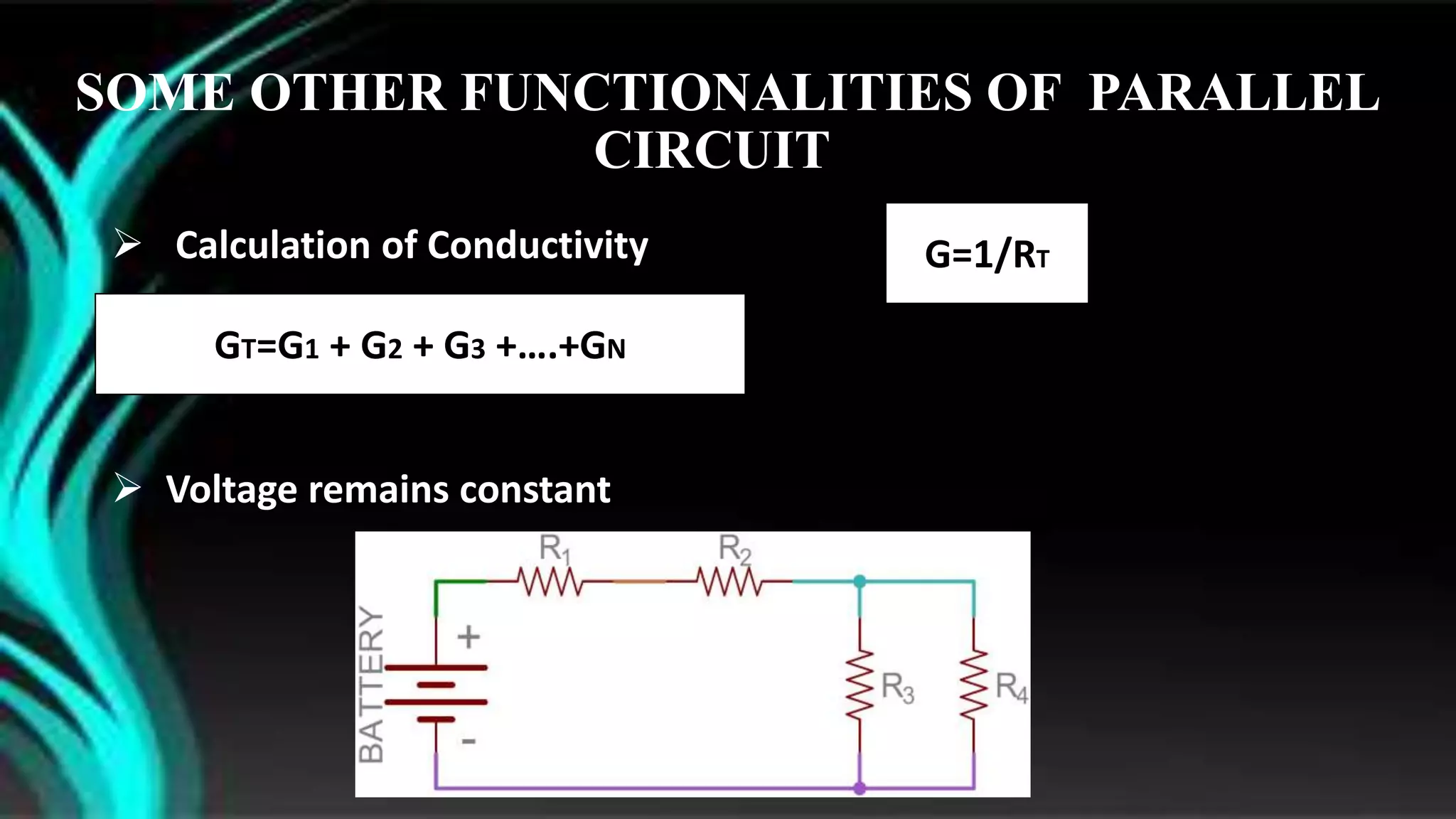
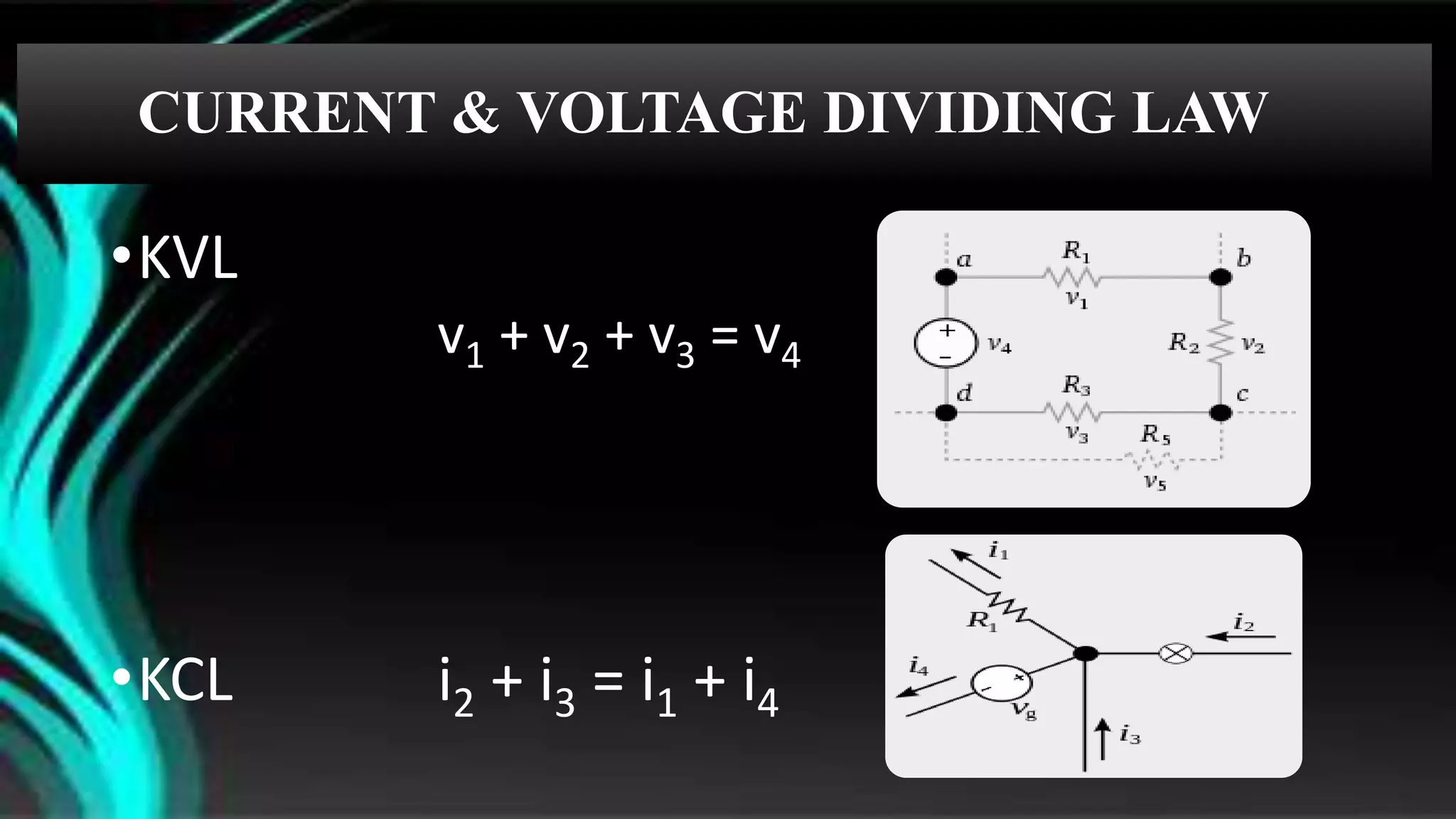
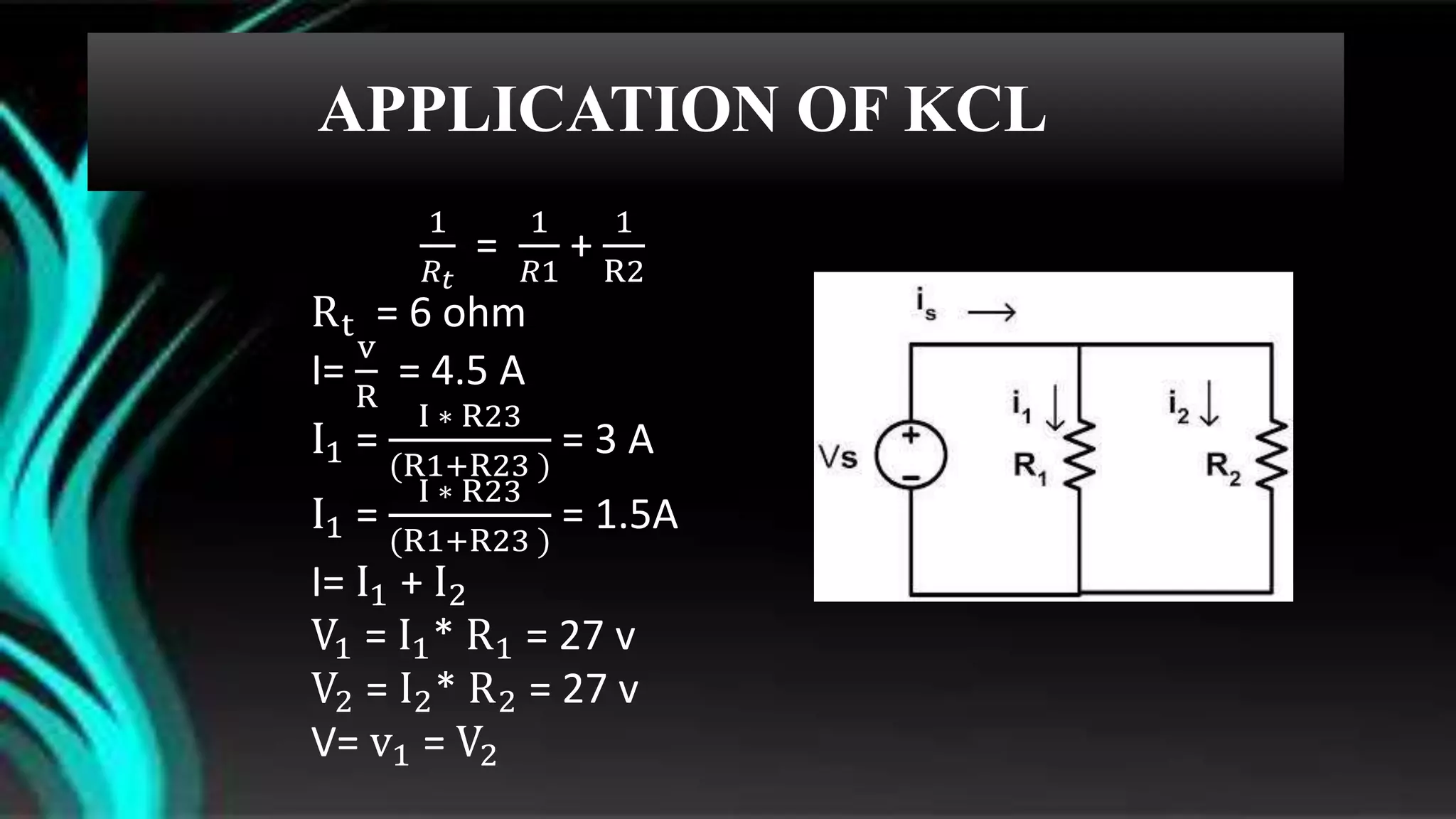
The document discusses parallel circuits, detailing their definition, characteristics, and formulas for calculating total resistance and current. It explains Kirchhoff's laws as they apply to parallel circuits and provides examples of calculations involving current and voltage. Additionally, it highlights the practical applications of parallel circuits in everyday life such as electrical connections and devices.