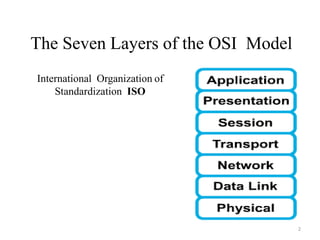
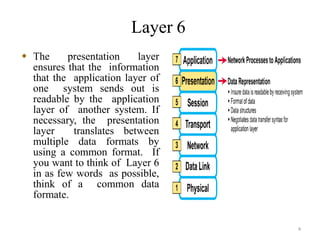
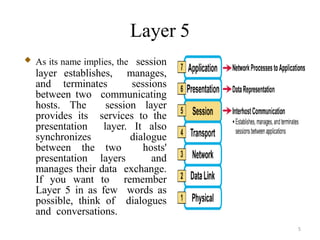
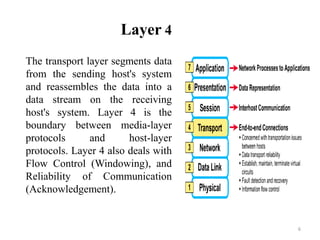
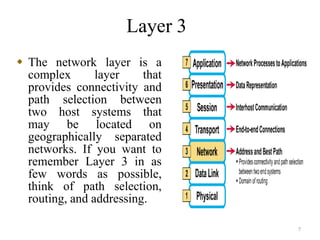
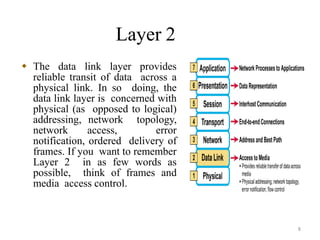
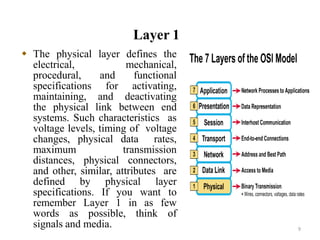
The presentation summarizes the seven layers of the OSI model. Layer 7 is the application layer, which provides network services to user applications like web browsers. Layer 6 is the presentation layer, which ensures information can be read by translating between data formats into a common format. Layer 5 is the session layer, which establishes and manages sessions and data exchange between communicating hosts, like dialogues. Layer 4 is the transport layer, which segments and reassembles data streams between hosts, dealing with flow control and reliability. Layer 3 is the network layer, which provides path selection and routing between networks. Layer 2 is the data link layer, which provides reliable data transmission across physical links using frames and media access control. Layer 1 is the physical layer