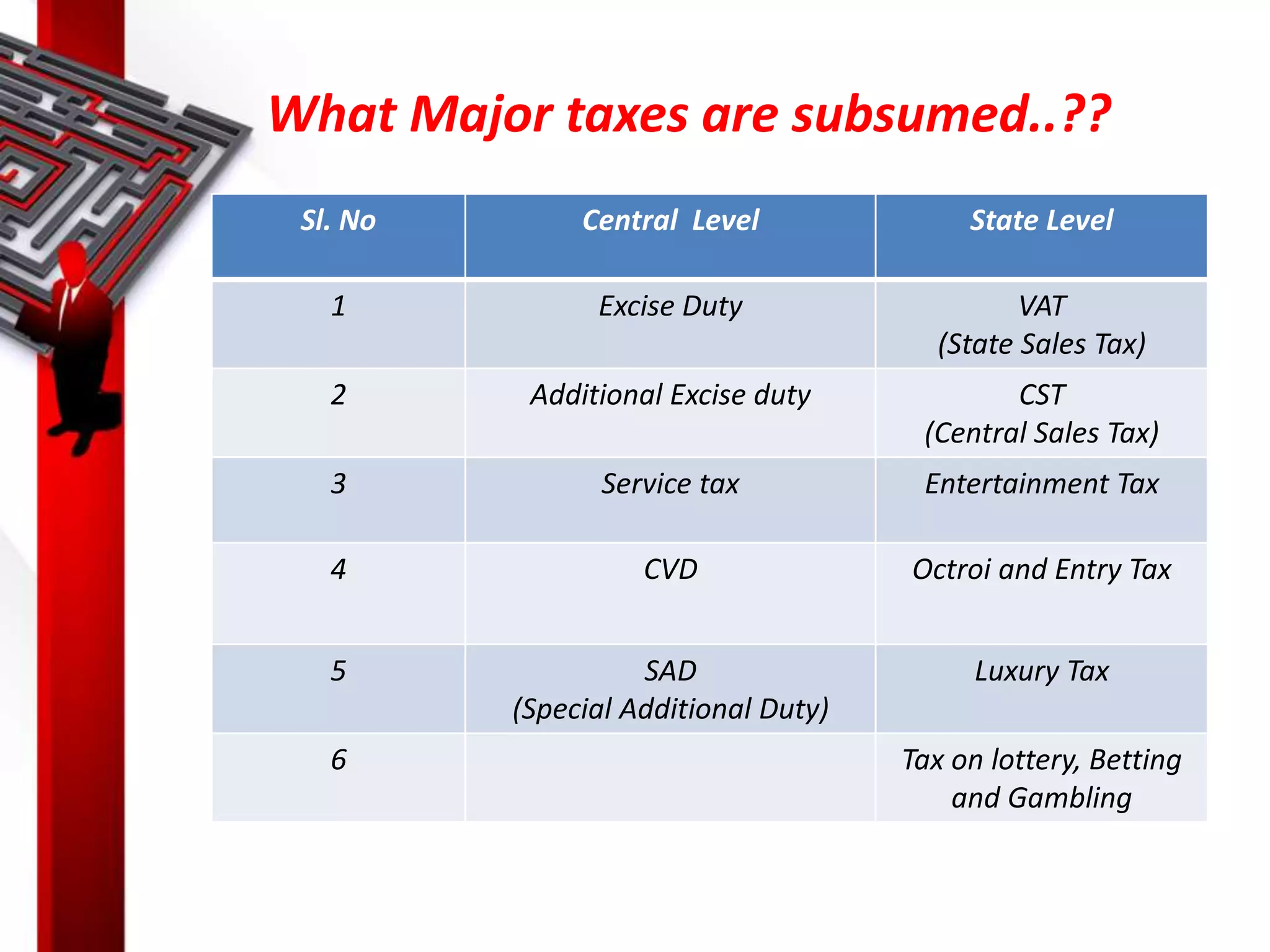
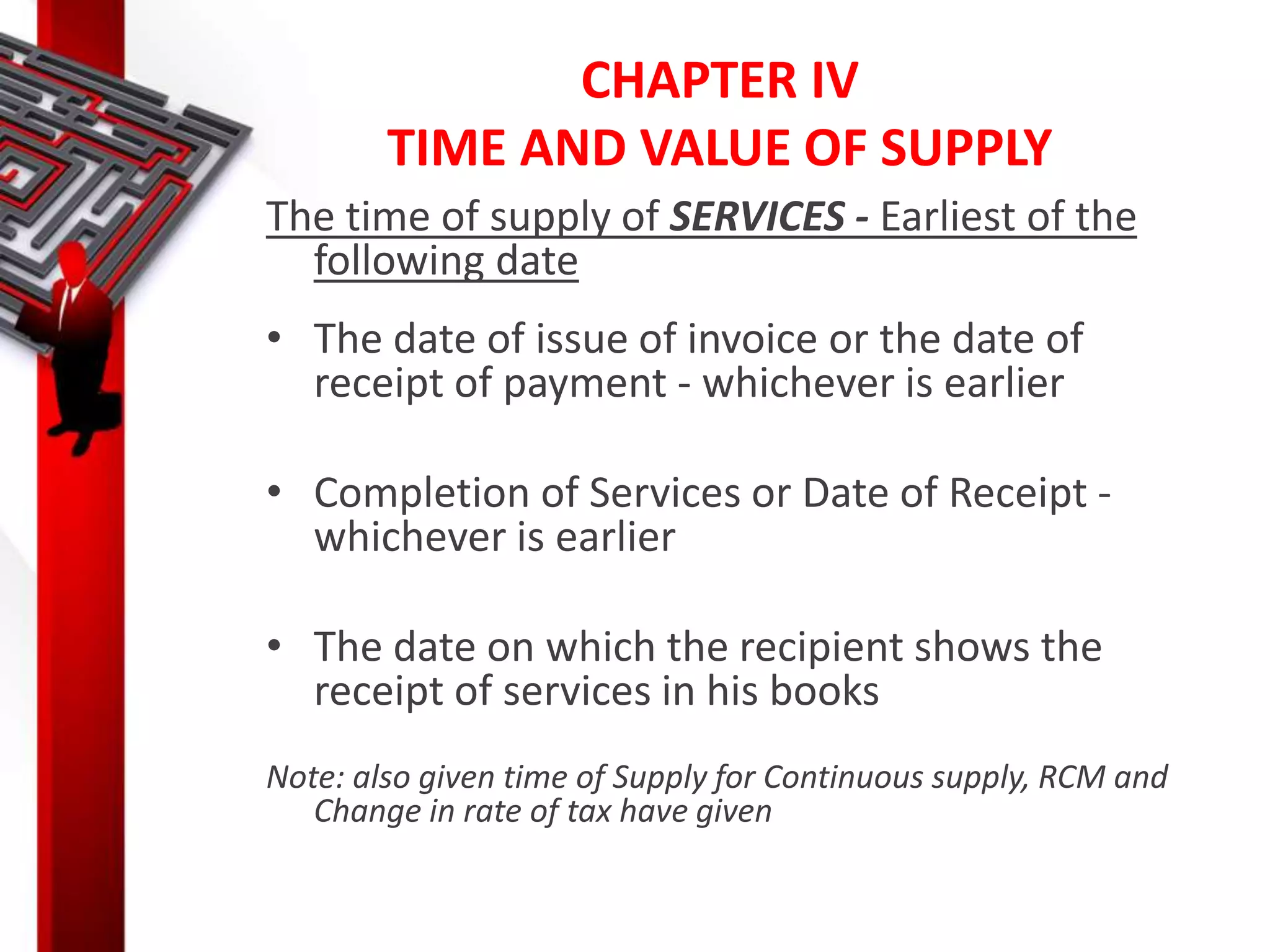
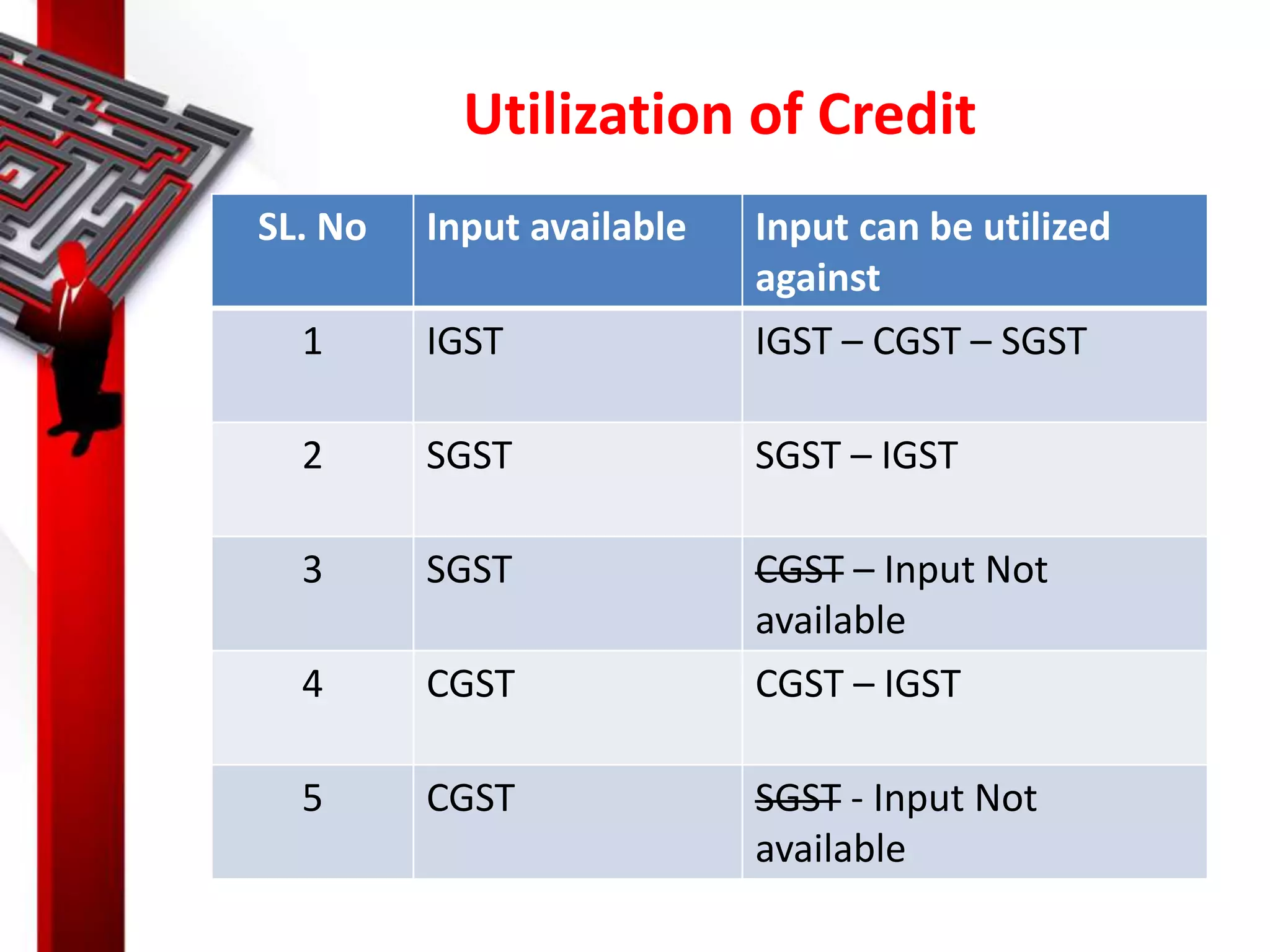
The document discusses the Goods and Services Tax (GST), including its background, implementation, working mechanism, and major taxes that it replaces. It provides detailed information on various aspects of GST, such as the definitions, time and value of supply, exemptions, input tax credit, registration, returns, penalties, and the benefits of GST for businesses and governments. The conclusion emphasizes GST's goal of creating a fair and transparent tax system while reducing compliance burdens.