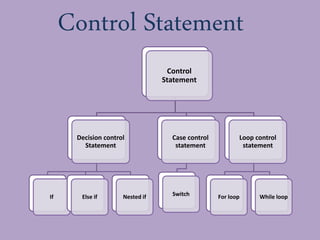
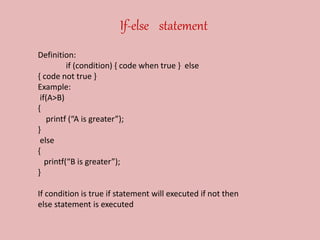
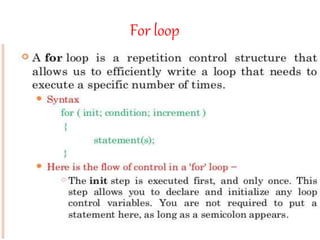
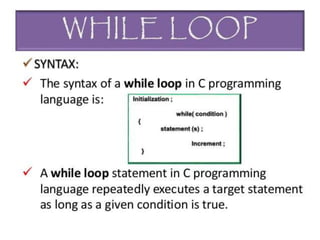
This presentation provides an introduction to programming in C language. It covers key topics such as control statements like if-else and switch statements, functions, arrays, and strings. Control statements allow for decision making and loops in a program. Functions are blocks of code that perform tasks and can return values. Arrays are collections of similar data types, while strings are character arrays that end with a null character. The presentation defines each concept and provides examples to illustrate their usage in C programming.










![String
String are group of arrays also
called character array strings
always ends with null character.
Syntax of string:-
Data Type variable name [ size];
ex:- int a[20];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptonc-180108111427/85/Presentation-on-C-language-By-Kirtika-thakur-20-320.jpg)
