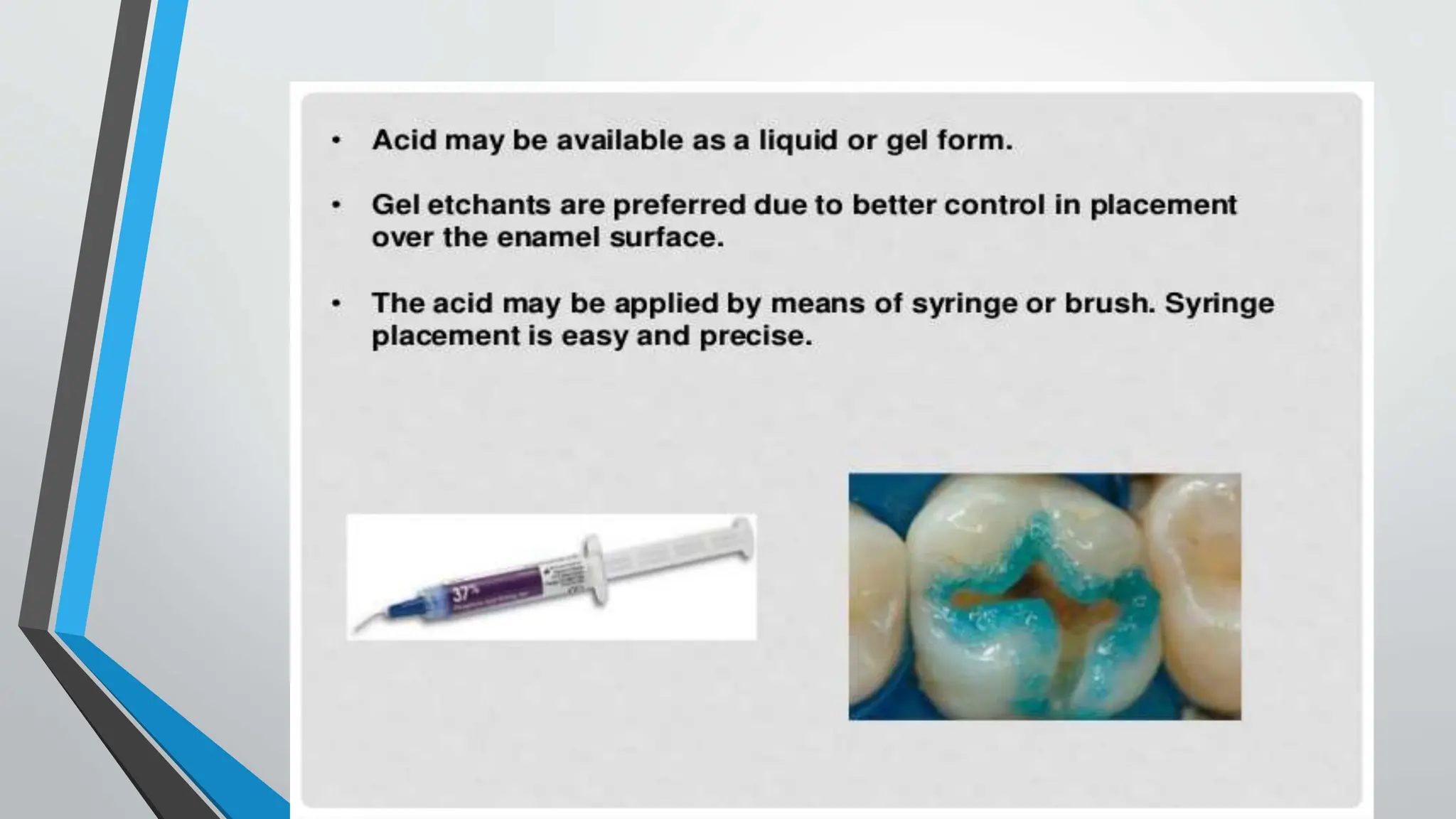
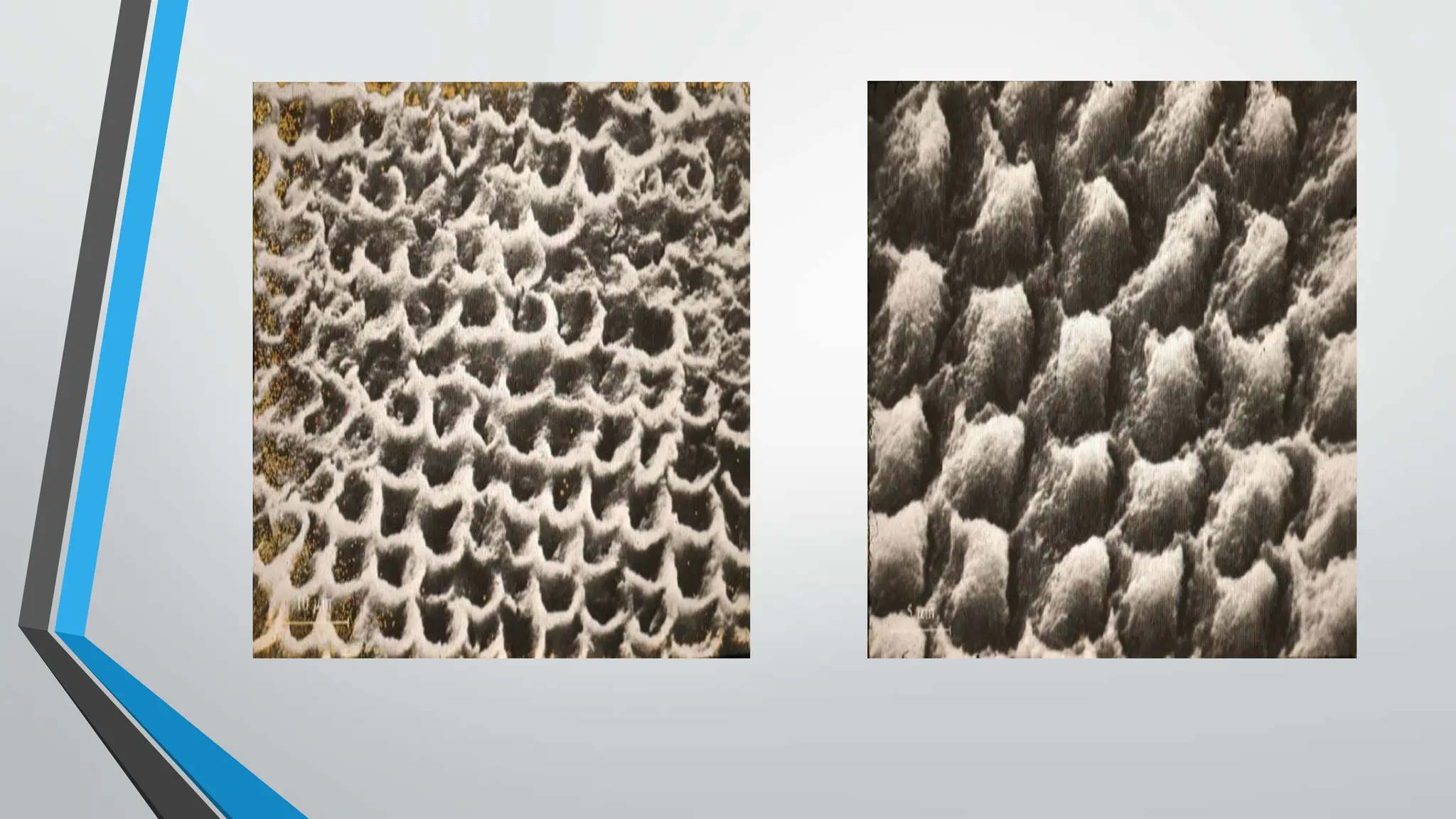
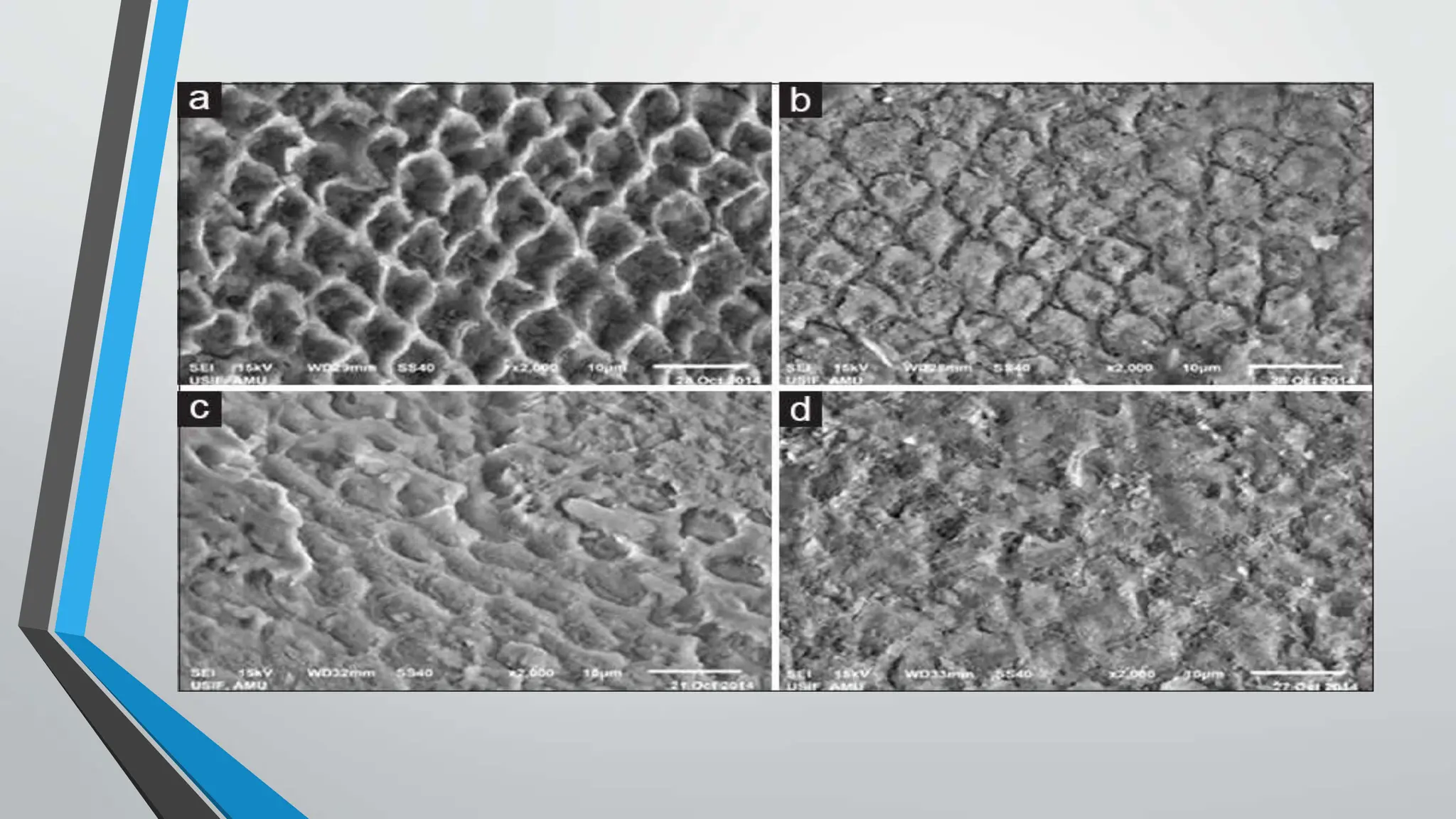
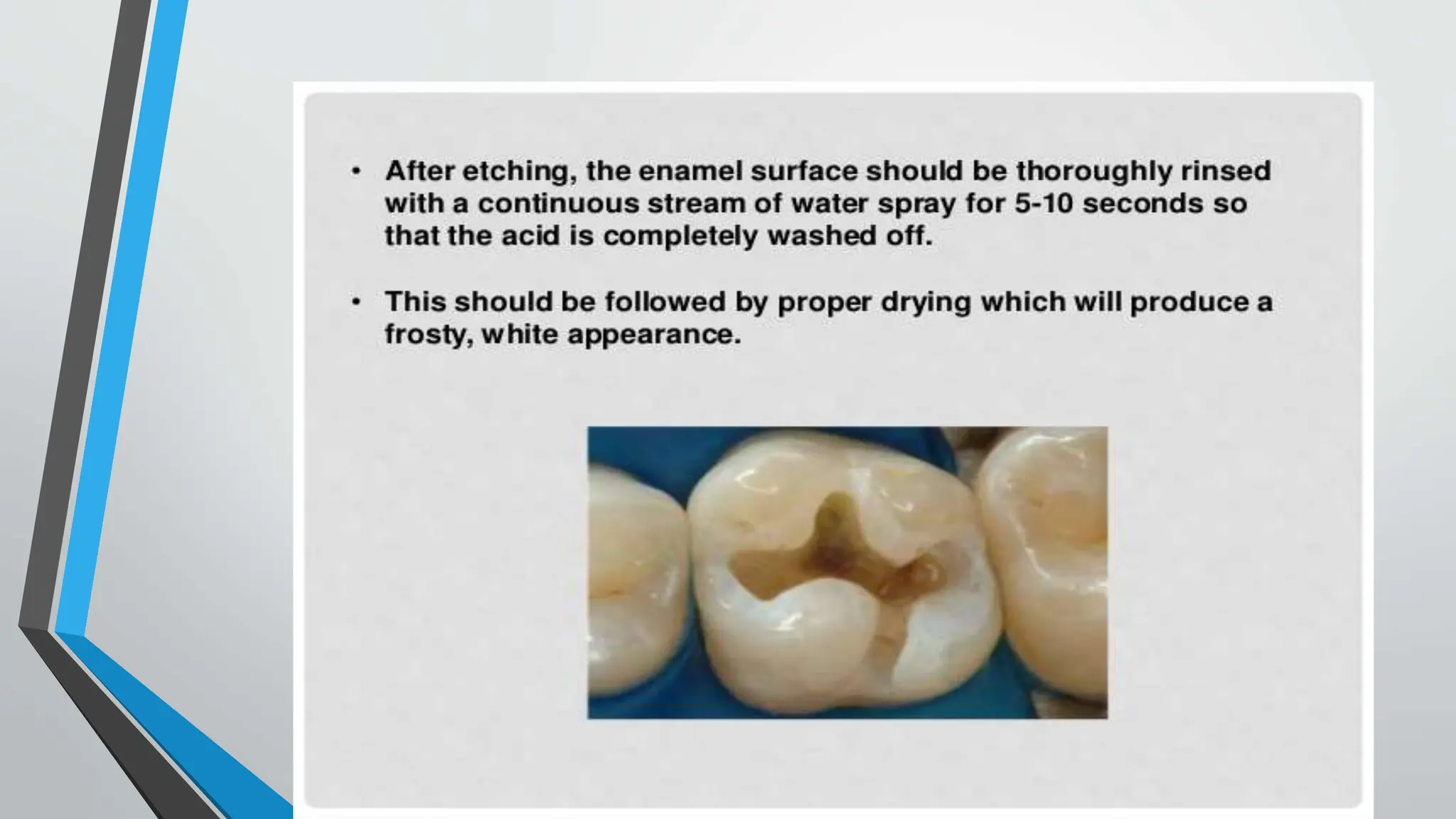
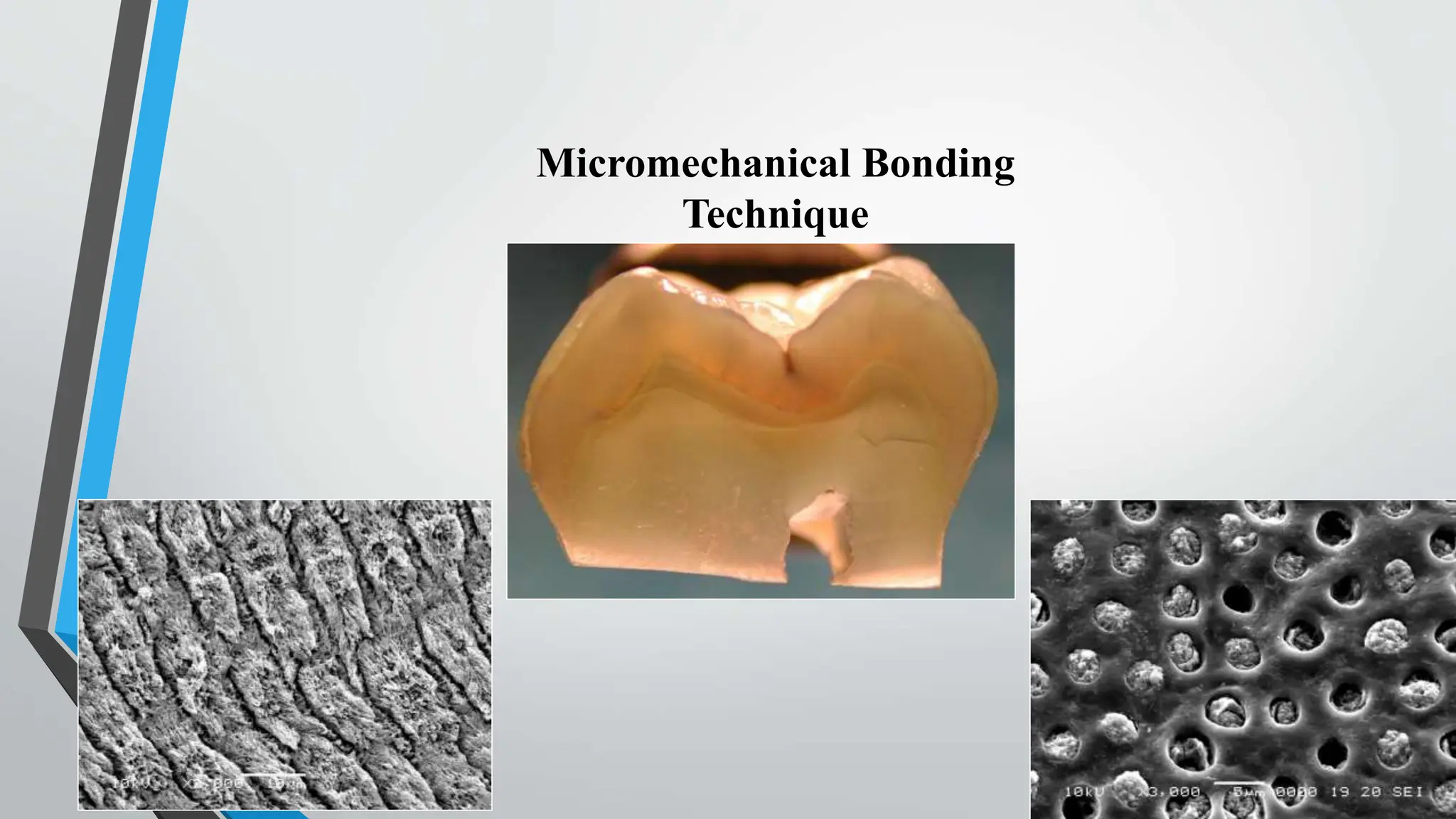
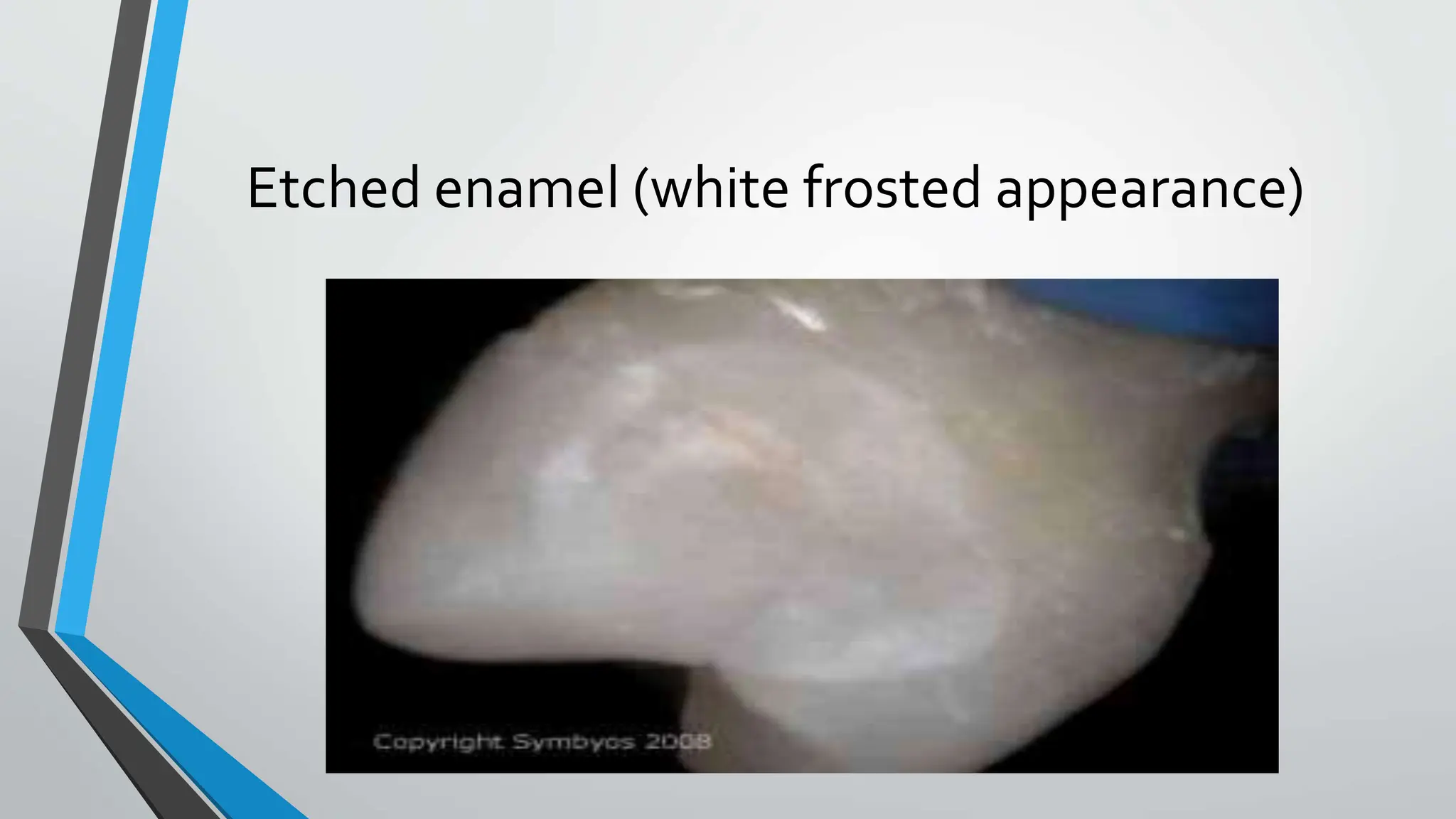
The document discusses the acid etching process used for bonding resin-based materials to tooth enamel, highlighting its role in creating micro-mechanical adhesion. Key factors for successful bonding include etching time, washing, and drying stages, while the presence of the smear layer on freshly cut dentine affects bonding efficacy. Dentine conditioning with acid helps remove the smear layer and facilitate the formation of a hybrid layer critical for effective bonding.