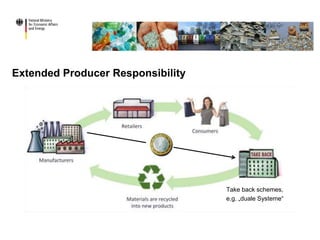
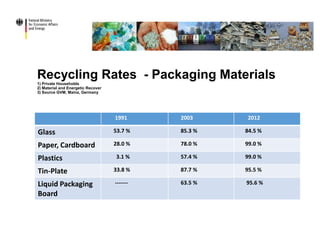
The document discusses the evolution and current state of waste management in Germany, highlighting its challenges like overfilled dumpsites and insufficient incineration facilities, as well as the success factors including strong legal frameworks and high public awareness. It emphasizes the economic benefits, such as reduced CO2 emissions, job creation, and increased recycling rates driven by regulations like the German Closed Cycle Management Act. Future goals include advancements in packaging legislation and enhanced recycling efforts both in Germany and the European Union.