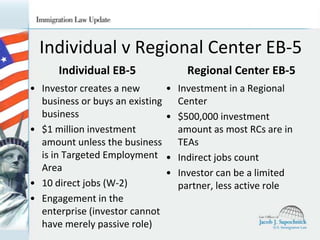
This document summarizes the EB-5 immigrant investor visa program. It outlines the two types of EB-5 cases (individual and regional center), requirements for family immigration, the four-step process to become a lawful permanent resident, details about regional centers and how they work, differences between individual and regional center EB-5 cases, general requirements around investing capital in a new commercial enterprise and creating jobs, lawful source of investment capital, and considerations for removing conditional status.