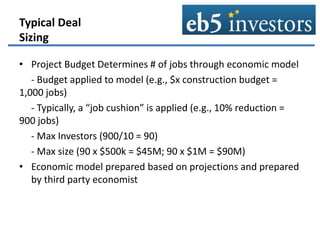
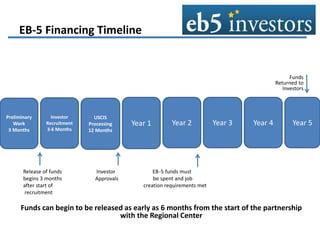
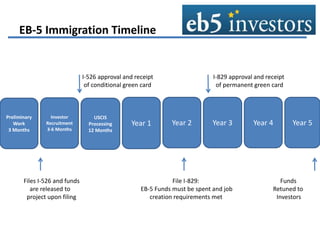
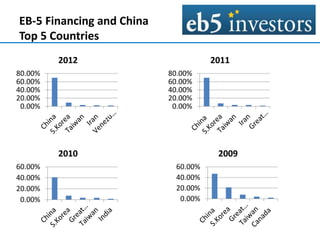
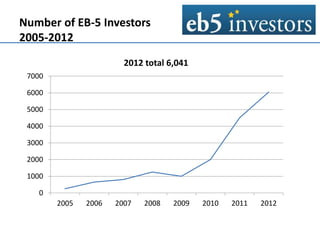
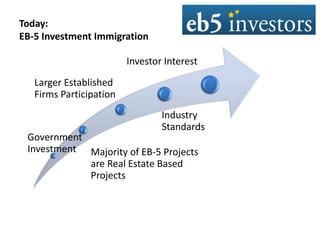
This document summarizes an agenda for an EB-5 financing forum. It provides background on the EB-5 visa program, including its history, investment requirements, and the typical structure of EB-5 deals. EB-5 visas allow foreign nationals to obtain permanent residency by investing in job-creating US businesses. Typical EB-5 deals are arranged through regional centers and involve debt or preferred equity investments of $500k-$1M. Funds are released from escrow once certain approvals are received. Regional centers facilitate EB-5 investments and compliance, while project partners work with regional centers on fundraising and job creation requirements. The majority of EB-5 investors are high-net-worth individuals from China seeking education