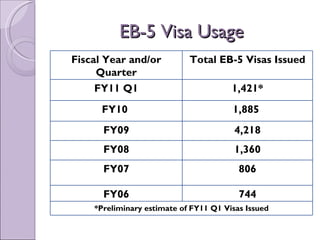
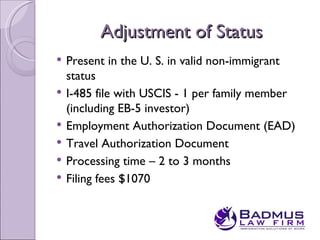
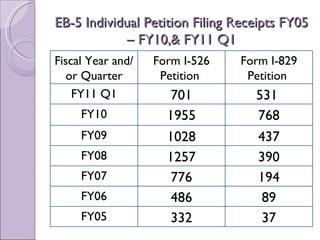
The document provides an overview of the EB-5 immigrant investor visa program. It discusses that EB-5 visas allow foreign investors to obtain permanent residence in the US by investing a minimum of $1 million or $500,000 in a targeted employment area. Investors can invest through a traditional business or regional center program. If requirements are met, investors can obtain conditional permanent residence for 2 years and then remove conditions to become lawful permanent residents.