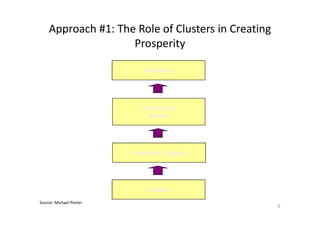
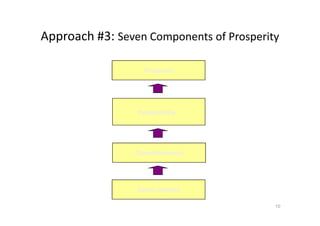
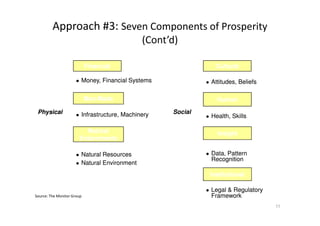
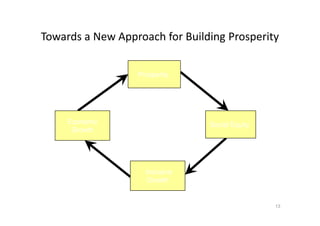
This document discusses different approaches to creating prosperity, and argues that a new approach called "inclusive growth" is needed. It defines inclusive growth as economic growth that is shared fairly among citizens. The document outlines traditional government roles in macroeconomics, microeconomics, and regulation, but argues these are not sufficient. Additional roles for government include education, moral and infrastructure leadership, empowering citizens, and considering more than just GDP growth. The conclusion is that both established and new approaches are needed, and approaches must address inclusive growth to ensure everyone benefits and experiences prosperity.