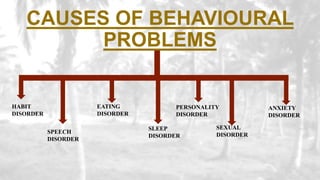
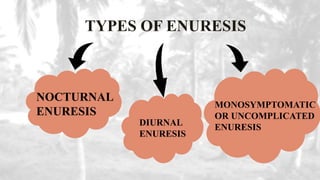
This document provides an overview of behavioral disorders in children. It begins with an introduction stating that normal children are well-adjusted when their emotional, physical and psychological needs are met. It then defines behavioral problems as significant deviations from socially accepted norms. The main causes and various types of behavioral disorders are discussed, including habit disorders, speech disorders, eating disorders, sleep disorders, personality disorders, and anxiety disorders. Specific behavioral disorders like enuresis, encopresis, nail biting, thumb sucking, pica, anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, somnambulism, sleep talking, nightmares, stuttering, and school phobia are then defined and their causes, signs/symptoms