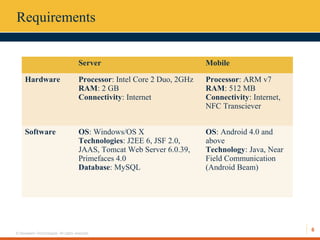
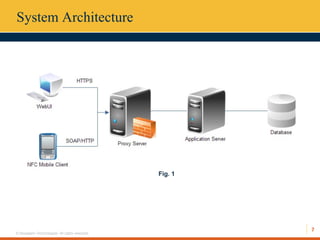
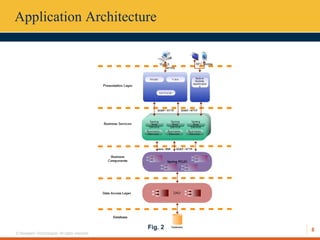
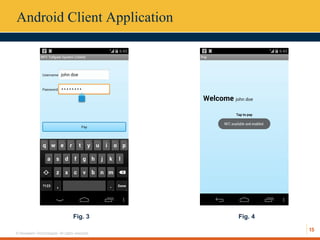
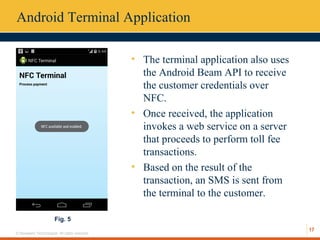
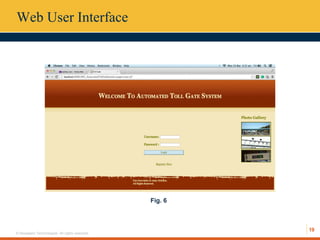
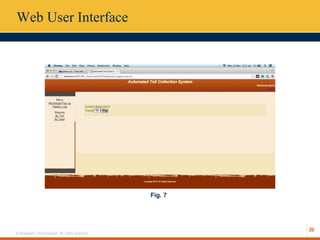
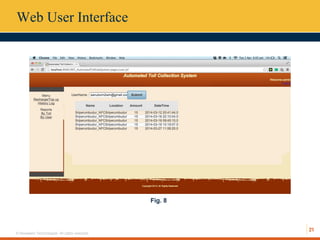
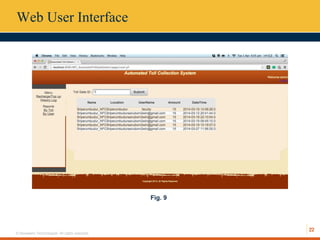
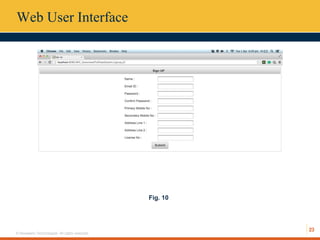
This document describes an automated toll collection system using near-field communication (NFC) technology. The system aims to reduce toll transaction processing times and provide receipts and usage logs to customers. It uses an Android mobile application to transmit encrypted credentials from an NFC-enabled device to a tollgate terminal. A web service validates the credentials against a database and confirms sufficient account balances for toll payments. If valid, an SMS is sent to the customer as a receipt. The system architecture includes a web interface for account management and administration reports. Literature on NFC systems integration and security was also reviewed.













![24
© Hexaware Technologies. All rights reserved.
References
• [1]Widmann, R.; Grunbeger , S.; Stadlmann, B.; Langer , J., “System Integration of
NFC Ticketing into an Existing Public Transport Infrastructure,” Near Field
Communication (NFC) 2012
• [2]E. Haselsteiner and K. Breitfuß, “Security in Near Field Communication (NFC) –
Strengths and Weaknesses”, RFIDSec 2006, Jul. 2006
• [3]Madlmayr, G.; Langer, J.; Scharinger, J. “Managing an NFC Ecosystem,” 7th
International Conference on NFC Mobile Business (ICMB), 2008
• [4]Eun, Hasoo; Lee, Hoonjung; Oh, Heekuck. “Conditional Privacy Preserving
Security Protocol for NFC Applications,” IEEE Transactions on Consumer
Electronics, Vol. 59, No. 1, February 2013
• [5]Nosowitz, Dan (1 March 2011). "Everything You Need to Know About Near Field
Communication". Popular Science Magazine. Popular Science.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bc18aab8-df92-4b7c-add8-814cb382ea76-161001060942/85/Presentation-24-320.jpg)