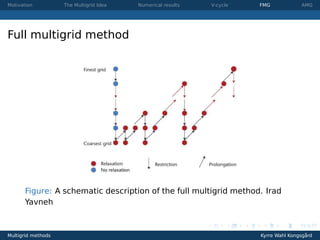
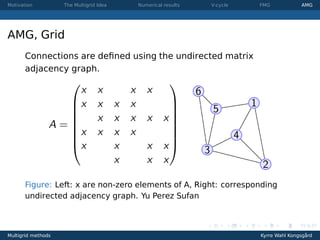
This document provides an overview of multigrid methods for solving elliptic PDEs such as Poisson's equation. It discusses the motivation for multigrid methods based on the error behavior of iterative methods like Jacobi. The core idea of multigrid is to introduce coarser grids where low-frequency errors become high-frequency, improving convergence. Details are provided on V-cycles and full multigrid methods for geometric problems, as well as algebraic multigrid which extends the approach to general matrices. Coarsening, interpolation, restriction, and the coarse-grid operator are defined algebraically.


![Motivation The Multigrid Idea Numerical results V-cycle FMG AMG
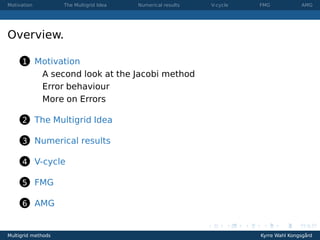
Jacobi method
To solve Au = f we use the Jacobi method.
um+1 = D−1 (f − (L + U)um )
Eigenvalues λµ of the iteration matrix G = I − D−1 A.
µπ h
λµ = 1 − 2sin2 ( ) = cos(µπ h), µ = 1, 2, ..., n
2
with corresponding eigenvectors
√
vµ = 2h [sin(µπ h), sin(µπ 2h), ..., sin(µπ nh)]T (1)
Multigrid methods Kyrre Wahl Kongsgård](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-130204040214-phpapp02/85/Multigrid-Methods-4-320.jpg)









![Motivation The Multigrid Idea Numerical results V-cycle FMG AMG
Acknowledgements
This lecture is copy-paste compilation of several similar
introductions to geometric and algebraic multi grid methods,
[1], [2], [3]
Gilbert Strang.
Computational Science and Engineering.
Wellesley-Cambridge Press, 1st edition, 2007.
Irad Yavneh.
Why multigrid methods are so efficient.
Computing in Science and Engineering, 8:12–22, 2006.
Robert D. Falgout.
An introduction to algebraic multigrid.
Computing in Science and Engineering, 8:24–33, 2006.
Multigrid methods Kyrre Wahl Kongsgård](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-130204040214-phpapp02/85/Multigrid-Methods-19-320.jpg)