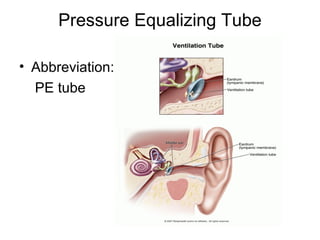
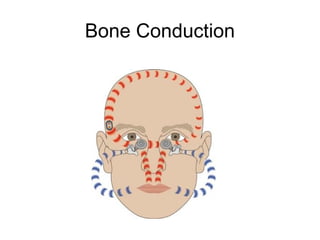
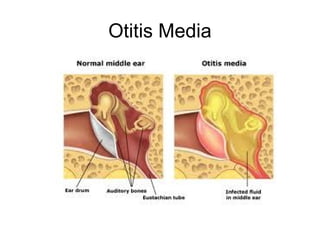
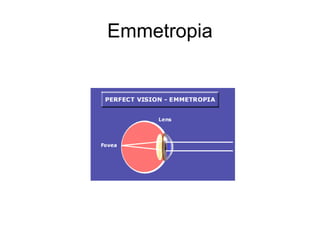
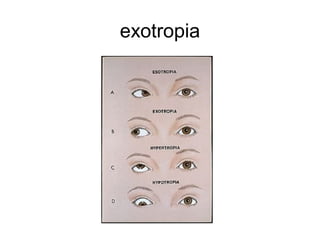
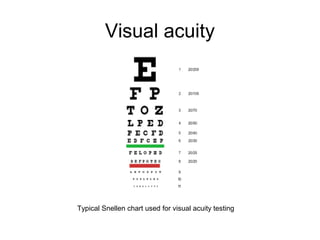
This document provides medical terminology definitions and abbreviations for terms related to the special senses (eyes, ears, nose, and throat). It defines terms such as pressure equalizing tube (PE tube), which is a small tube surgically inserted into the eardrum; eye, ear, nose, and throat (EENT), which refers to the medical specialty; and bone conduction, which is the conduction of sound to the inner ear through the skull bones. Other terms defined include otitis media (OM), inflammation of the middle ear; emmetropia (EM), the condition of normal vision; exotropia (XT), an outward deviation of the eyes; and visual acuity (VA), the clearness or