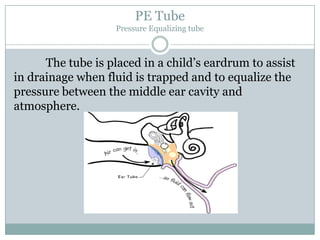
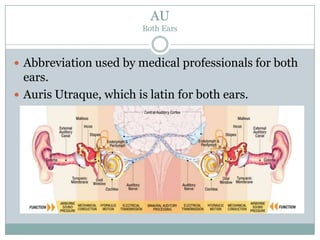
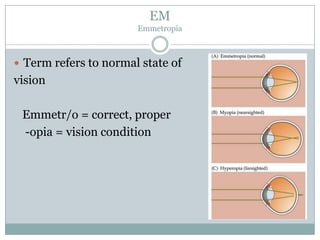
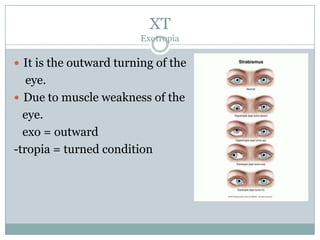
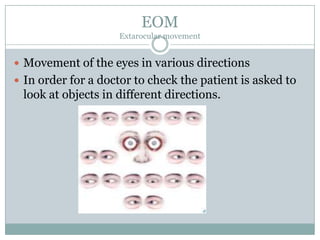
The document defines various medical abbreviations and terms related to the special senses of the eye and ear. It provides descriptions of terms like PE tube, EENT, BC, AU, OM, EM, XT, OS, EOM, and VA. PE tube refers to a pressure equalizing tube placed in a child's eardrum. EENT is an abbreviation for eyes, ears, nose and throat. BC refers to bone conduction of sound through the skull. AU abbreviates both ears. OM describes otitis media, or middle ear inflammation. EM, XT, OS, and VA define eye and vision related terms like emmetropia, exotropia, the left eye, and visual acuity