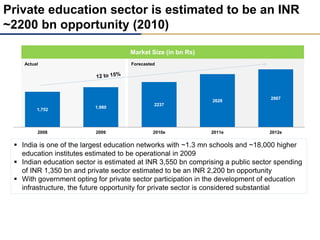
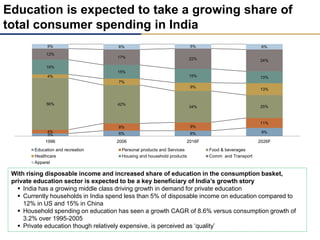
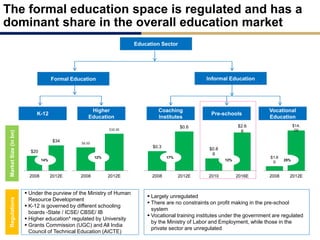
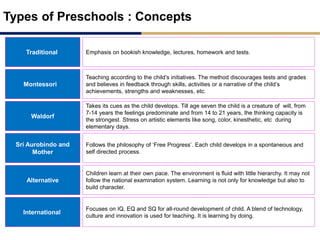
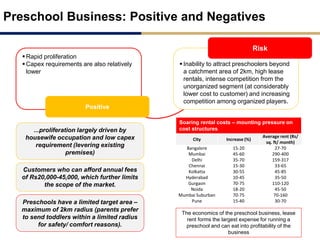
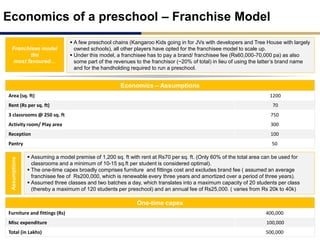
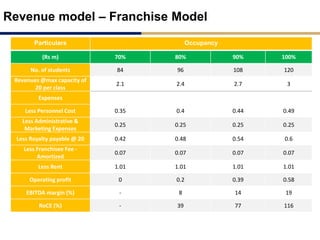
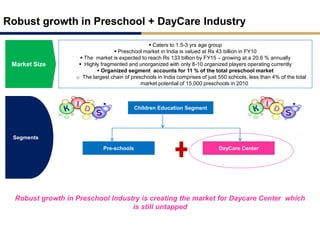
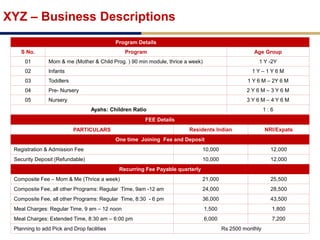
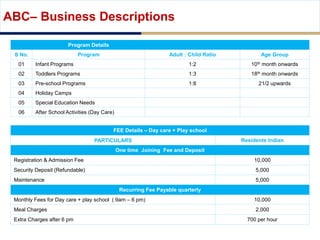
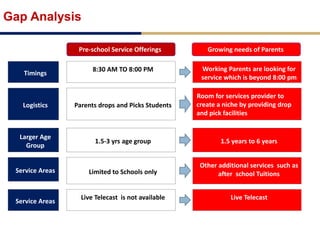
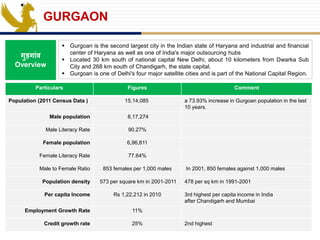
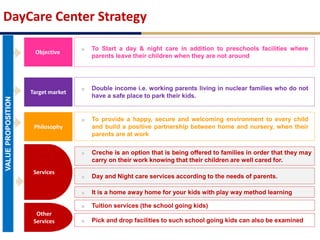
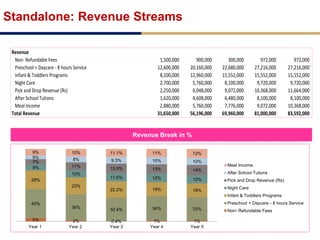
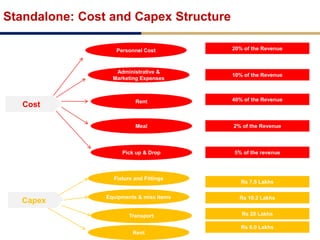
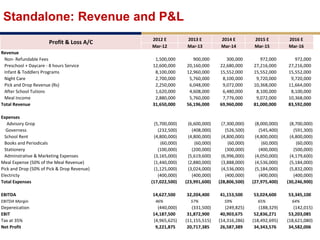
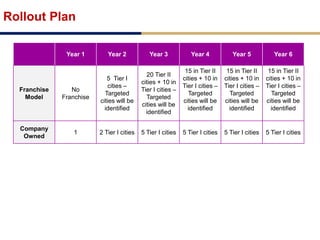
Day care centers are gaining importance in India as more parents work. The day care market is highly fragmented and untapped, with only 1% of preschoolers currently enrolled. Running a successful day care center requires factors like appropriate staffing ratios, suitable neighborhood location, educational activities, teacher training, brand awareness, and standardized infrastructure across franchises. XYZ and ABC are two business descriptions of existing day care center models in India, with details on their programs, fees, and service offerings. A strategic gap analysis identifies opportunities to expand service areas, age groups covered, and offer additional services like transportation, tutoring, and live streaming. Gurgaon is highlighted as a potential market for new day care centers given its growing population, economic