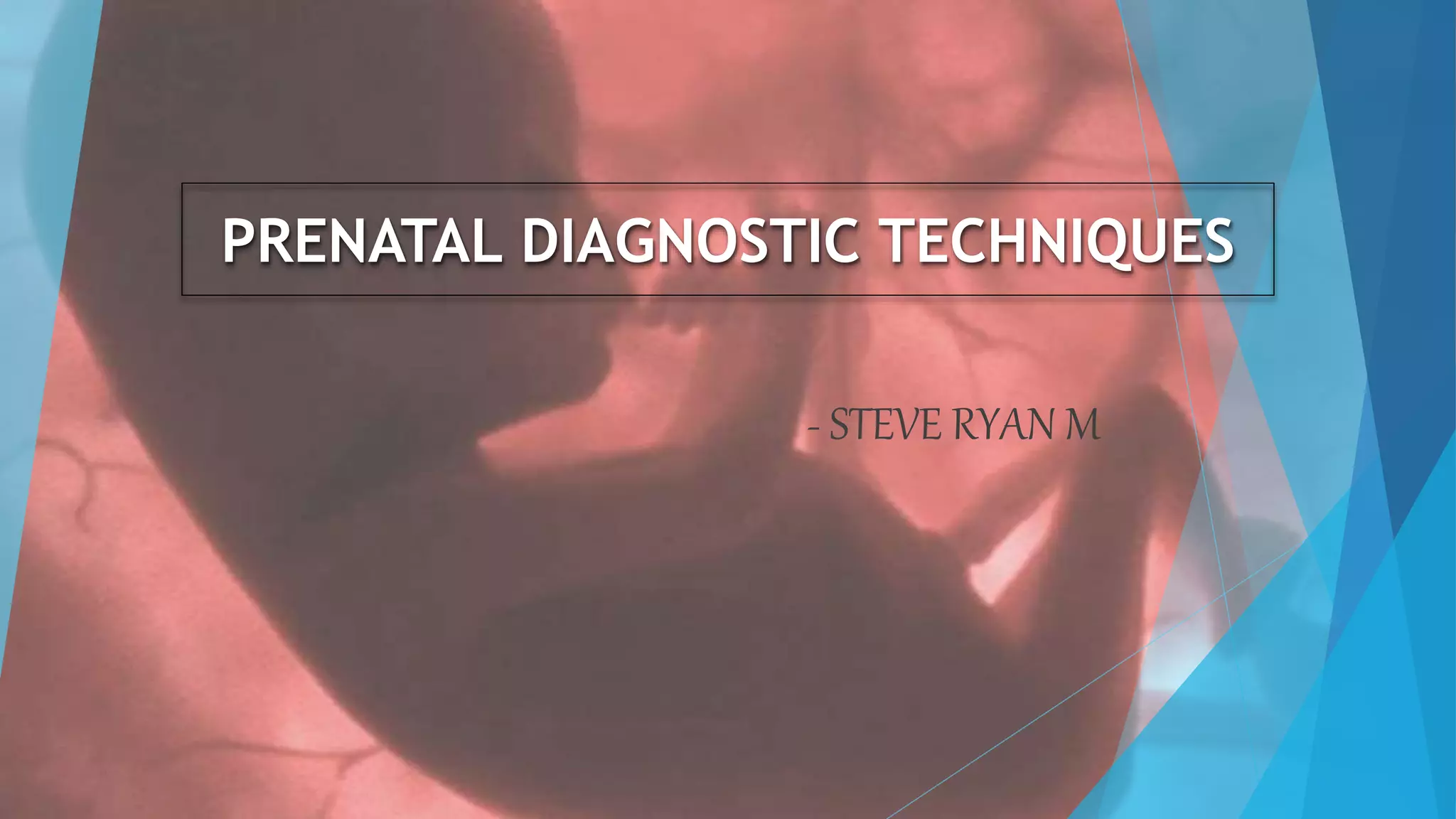
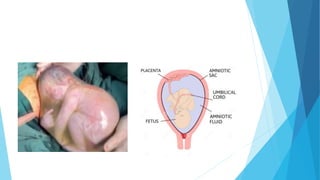
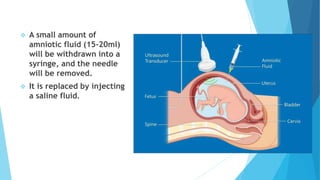
Prenatal diagnostic techniques allow for the diagnosis of genetic disorders in unborn babies. The two main invasive techniques are amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling. Amniocentesis involves extracting amniotic fluid from the amniotic sac between 15-17 weeks using ultrasound guidance. Chorionic villus sampling involves sampling placental tissue between 10-12 weeks either through the abdomen or cervix. Both techniques carry risks of miscarriage but can detect chromosomal abnormalities with high accuracy.