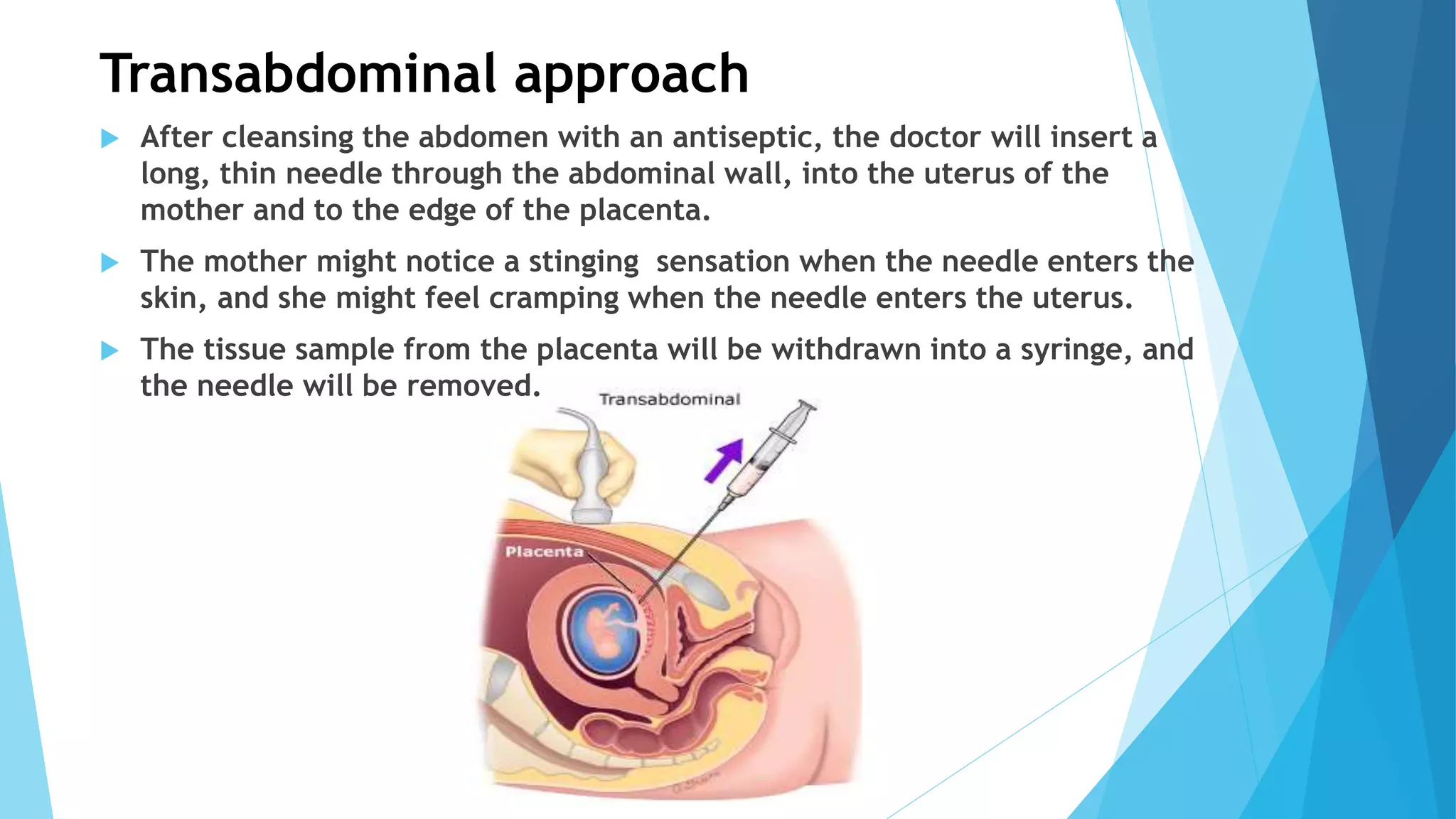
Prenatal diagnosis refers to the identification of potential genetic disorders in an unborn baby, often performed on women over 35 or those with a family history of genetic issues. Techniques include invasive procedures like amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS), both aimed at detecting chromosomal abnormalities with varying degrees of risk and accuracy. These procedures also raise ethical concerns regarding gender determination and potential misuse, prompting regulatory measures in countries like India.