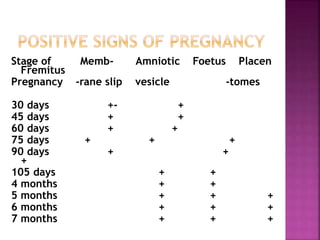
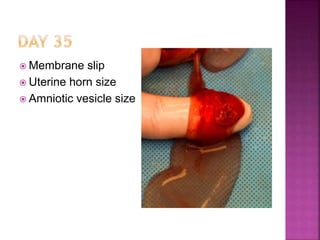
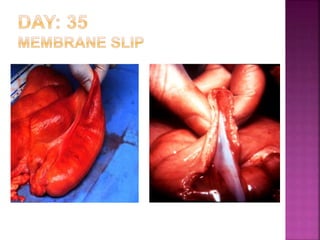
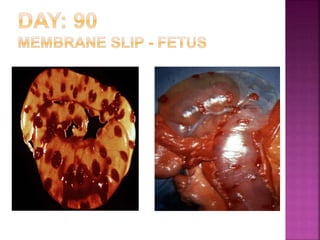
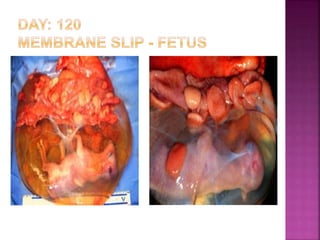
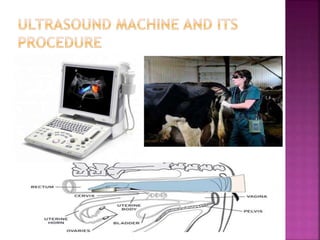
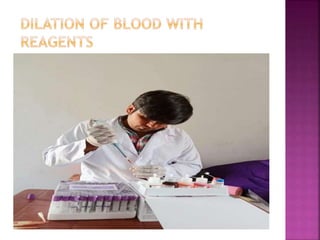
This document discusses various techniques for diagnosing pregnancy in cattle, including rectal palpation, ultrasonography, and biochemical tests. Rectal palpation allows manual examination of the reproductive tract but requires experience. Ultrasonography uses ultrasound imaging to view reproductive organs and fetuses from 30 days of pregnancy onward. Biochemical tests detect pregnancy-associated proteins in milk or blood samples to determine pregnancy status. Together, these modern diagnostic methods allow identifying pregnant cattle for strategic management decisions.