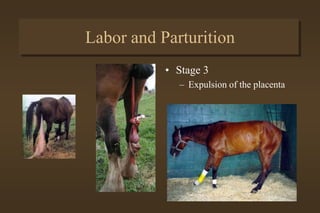
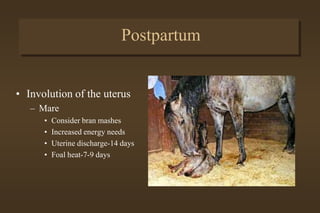
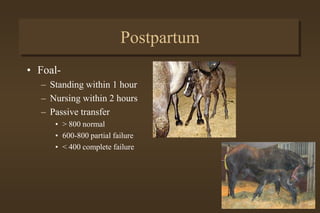
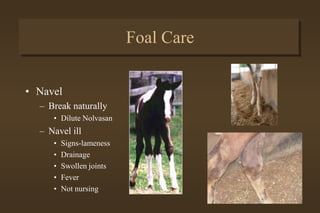
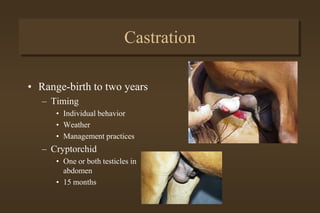
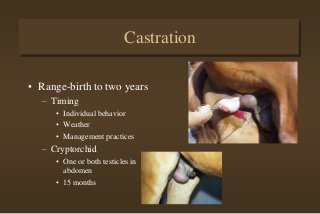
This document discusses equine medicine related to foaling and foal care. It covers the signs of impending foaling in mares, necessary foaling equipment, the three stages of labor and birth including normal birthing position, postpartum care for mares and foals including colostrum transfer, care of newborn foals such as navel treatment and passing meconium. It also discusses exercise, handling, weaning at 4-6 months, and castration timing ranging from birth to two years old.