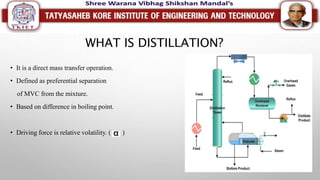
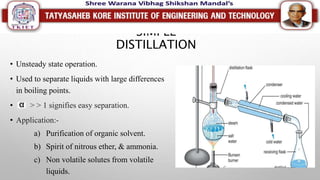
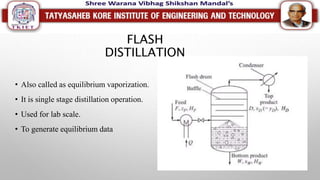
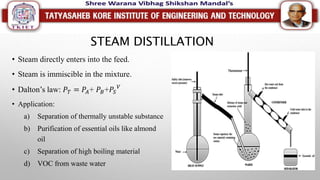
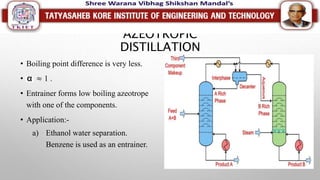
This document discusses different types of distillation processes. Distillation is defined as the preferential separation of components in a mixture based on differences in boiling points. There are several types of distillation including simple distillation, flash distillation, steam distillation, vacuum distillation, azeotropic distillation, and extractive distillation. Each type is suited for different applications depending on factors like boiling point differences, heat sensitivity of materials, and the ability to form azeotropes.