1) The document provides step-by-step solutions to 3 problems involving complex roots and factoring polynomials.
2) For problem 1, the technique of sum of cubes is used to solve the equation 27x^3 + 1 = 0, yielding solutions of x = -1/3, x = [1 + i sqrt(3)] / 6, and x = [1 - i sqrt(3)] / 6.
3) Problems 2 and 3 similarly use techniques like sum of cubes, quadratic formula, and substitution to solve the equations x^3 + 8 = 0 and x^4 – 2x^2 – 8, providing the techniques and solutions.

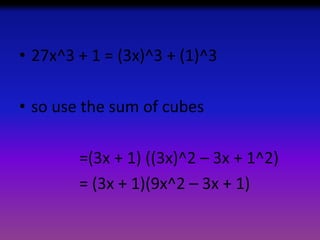
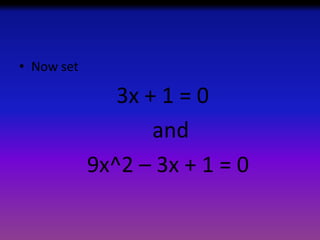
![• So x = -1/3
x = [3 +/ sqrt(9 – 4(9)(1)] / 18
= [3 +/- sqrt(-27)] / 18
= [3 +/- 3i sqrt(3)] / 18
= [1 +/- i sqrt(3)] / 6
• Technique: sum of cubes, quadratic formula](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicepowerpoint-131119014239-phpapp01/85/Practice-power-point-5-320.jpg)
![Solutions:
x = -1/3
and
x = [1 + i sqrt(3)] / 6
and
x = [1 - i sqrt(3)] / 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicepowerpoint-131119014239-phpapp01/85/Practice-power-point-6-320.jpg)


![x = -2
and
x = [2 +/- sqrt(4 – 4(1)(4))] / 2
x = [2 +/- sqrt(-12)] / 2
x = [2 +/- 2i sqrt(3)] / 2
x = 1 +/- i sqrt(3)
• Solutions: x = -2, x = 1 + i sqrt(3), and
x = 1 – i sqrt(3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicepowerpoint-131119014239-phpapp01/85/Practice-power-point-9-320.jpg)


