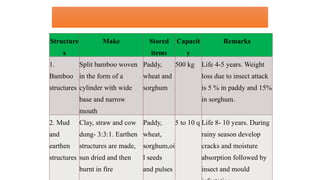
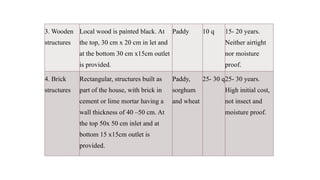
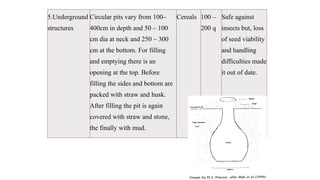
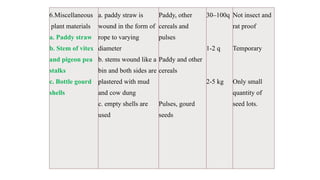
The document outlines precautions for the safe storage of grains to minimize post-harvest losses, particularly in India where storage losses are estimated at 6.58%. It details best practices for grain storage, including moisture levels, structural integrity, and protection against pests and moisture, and describes various types of storage structures such as bamboo, mud, wooden, brick, and underground options. The document emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate storage methods to ensure optimal grain preservation and public distribution.