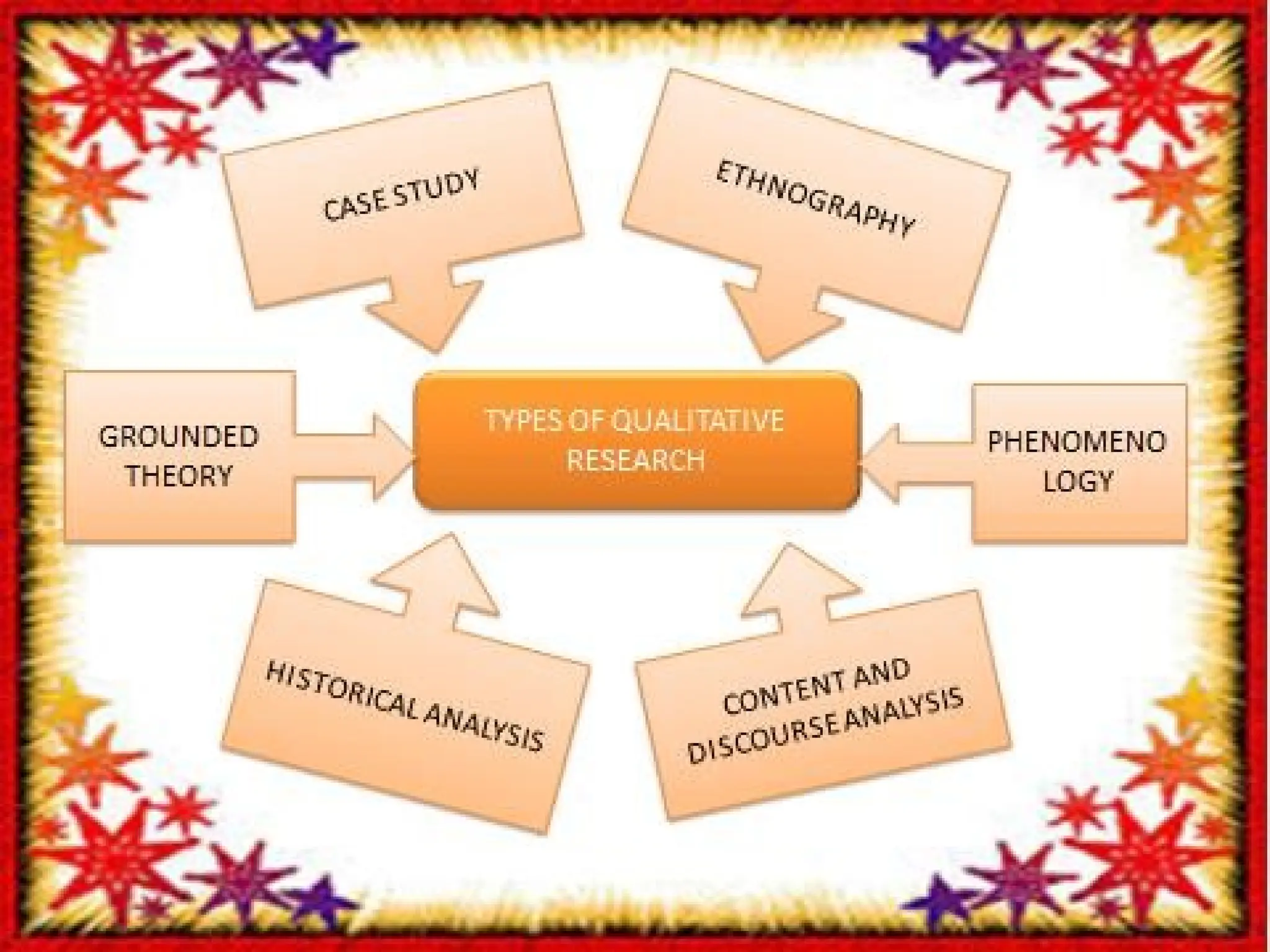
This document outlines various qualitative research designs, emphasizing the characteristics and applications of different types, such as historical, experimental, case study, and descriptive designs. It highlights the importance and value of descriptive research in providing factual knowledge, observing behaviors, and informing policy formulation. The document also details types of descriptive designs and encourages collaborative brainstorming for appropriate research methodologies.