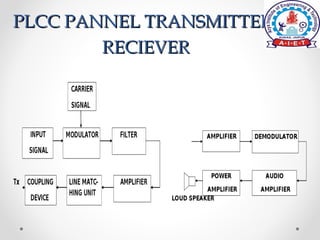
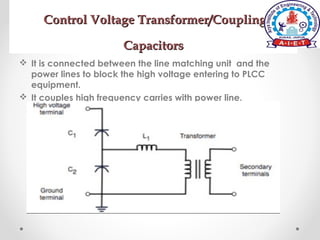
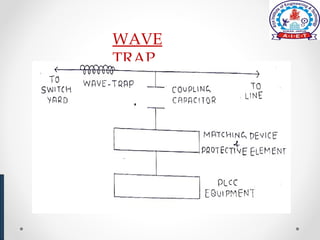
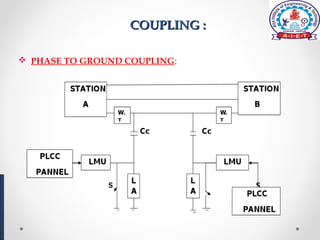
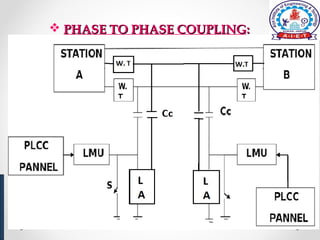
Power line carrier communication (PLCC) allows for telecommunication between electric substations using existing power lines. Data can be transferred at rates up to 9.6 kbps over many miles of cable. PLCC systems use coupling devices like capacitors and line matching units to connect communication equipment to power lines while preventing carrier currents from interfering with power equipment. Common PLCC equipment includes stations, line matching units, control voltage transformers, earth switches, lightning arrestors, wave traps, and coaxial cables. Wave traps are used to block carrier currents from entering power stations to avoid interference. PLCC offers communication without additional wiring but requires safeguarding equipment from high voltages and currents on power lines.