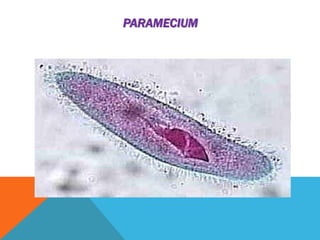
The document describes the nutrition process in the unicellular organisms Amoeba and Paramecium. It explains that Amoeba ingests food particles using pseudopodia, which are then enclosed in a food vacuole where digestion and absorption occur. Undigested waste is ejected from its cell when needed. Paramecium uses cilia around its mouth to sweep in food particles from surrounding water. Both organisms then digest, absorb, assimilate the food before ejecting waste.