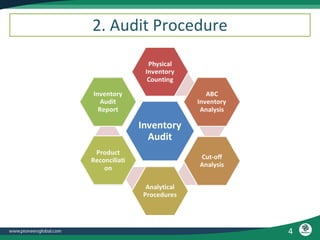
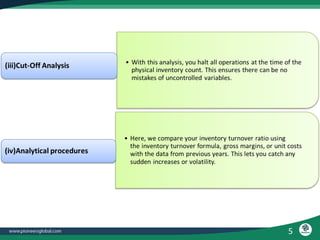
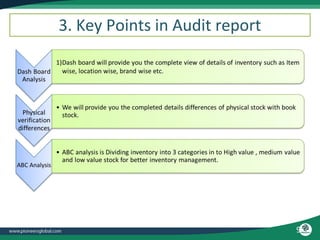
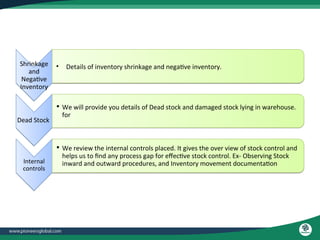
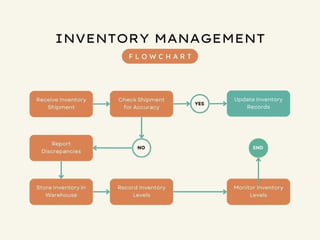
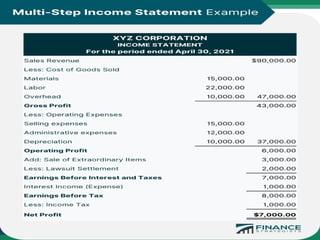
The document discusses the process and importance of inventory audits, which involve physically checking inventory against recorded financial records. It highlights the benefits of identifying inefficiencies, managing inventory levels, detecting theft, and improving budgeting. Additionally, it covers various types of audits and their purposes in ensuring accuracy and compliance within financial and operational processes.