The document provides an introduction to the .NET framework, including:
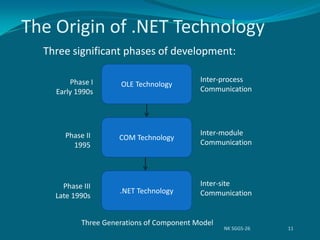
1) It discusses the origins of .NET technology and how it evolved from OLE and COM technologies.
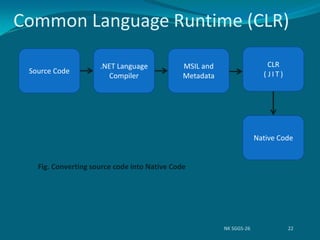
2) The .NET framework provides a common language runtime (CLR) that allows applications written in multiple languages to run on different operating systems and devices.
3) The CLR handles tasks like memory management, security, and code execution to provide a cross-language, cross-platform environment for .NET applications and services.