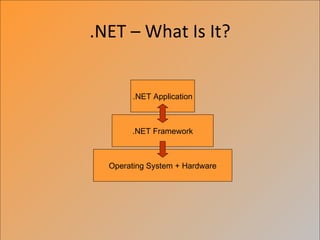
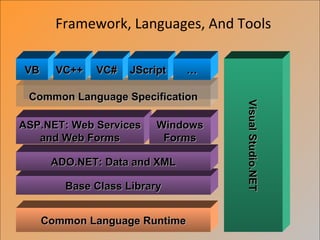
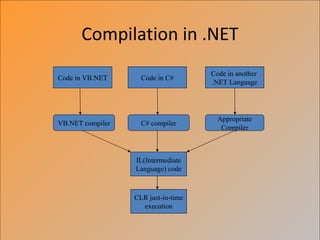
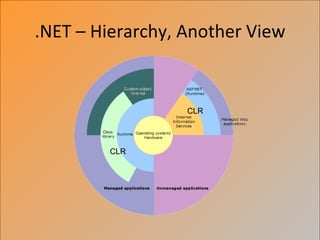
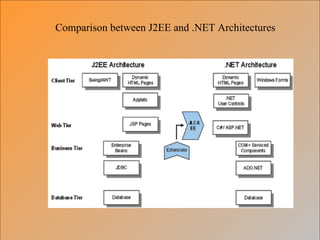
The document provides an overview of the .NET framework. It describes .NET as a software platform and language-neutral runtime that executes programs written in any compliant language. It discusses key aspects of .NET including the Common Language Runtime (CLR), support for multiple programming languages, and tools like ASP.NET and Visual Studio.NET. The conclusion compares .NET to the J2EE architecture.