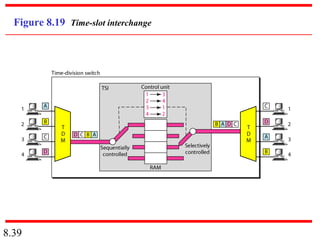
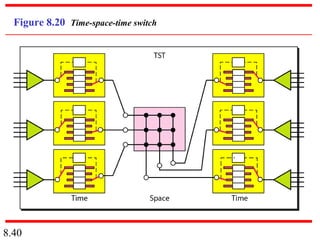
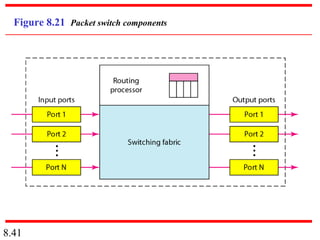
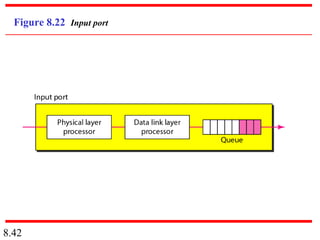
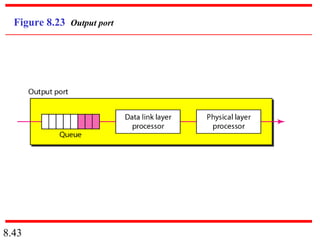
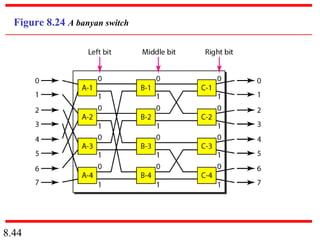
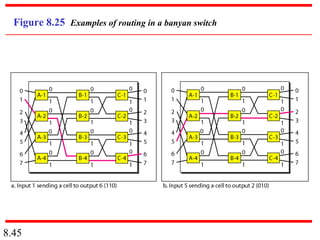
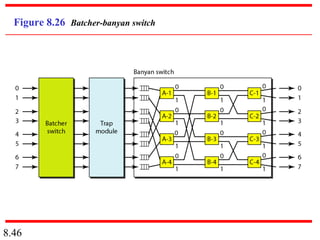
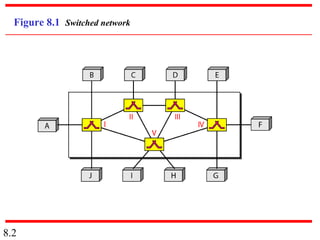
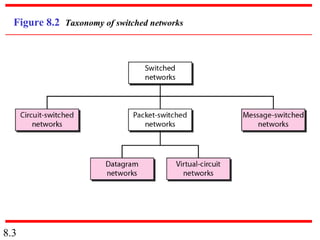
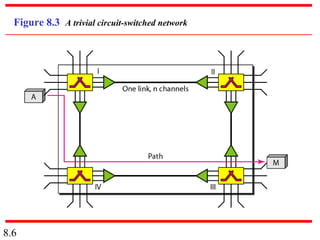
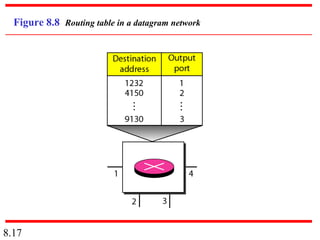
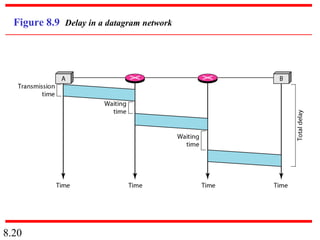
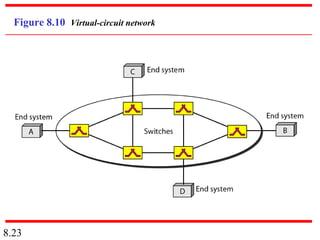
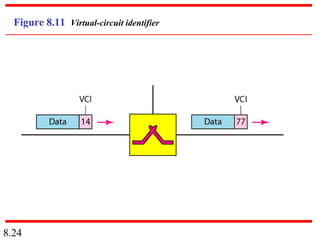
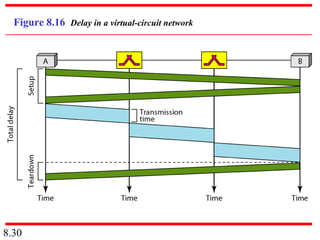
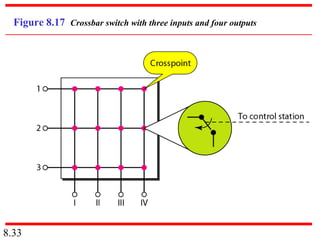
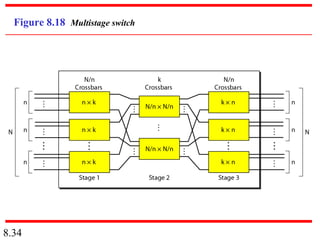
This document discusses different types of switched networks including circuit-switched, datagram, and virtual-circuit networks. In circuit switching, resources are reserved during setup and remain dedicated until teardown. Datagram networks allocate resources on demand without setup. Virtual circuits have aspects of both, reserving resources like circuits but packets may arrive out of order. The document also covers switch structures, comparing crossbar, multistage, and packet switches. Packet switches use buffers, queues, and scheduling at input and output ports.
















![Note
According to the Clos criterion:
n = (N/2)1/2
k > 2n – 1
Crosspoints ≥ 4N [(2N)1/2 – 1]
8.37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt0110-121003230516-phpapp02/85/Ppt-01-10-37-320.jpg)