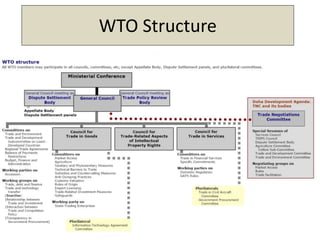
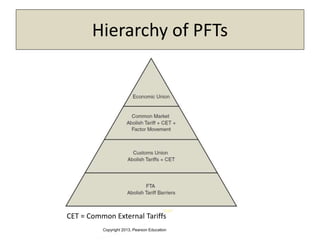
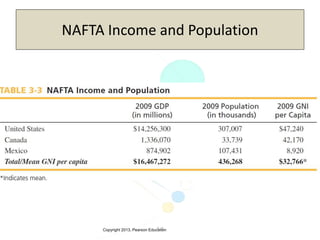
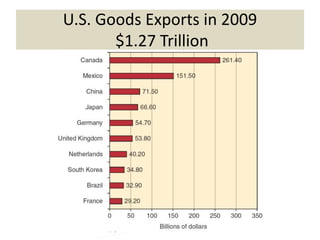
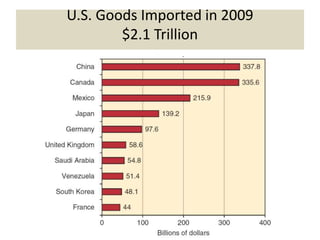
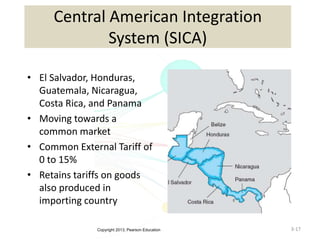
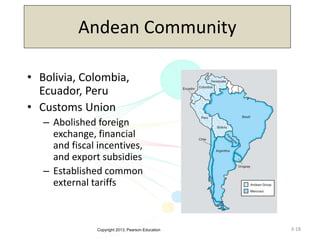
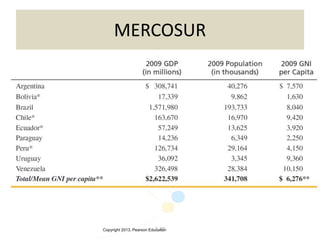
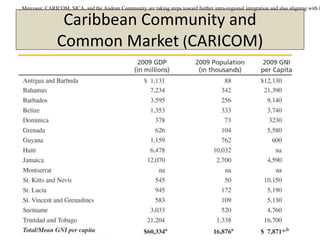
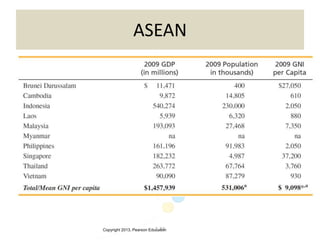
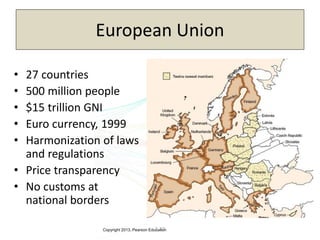
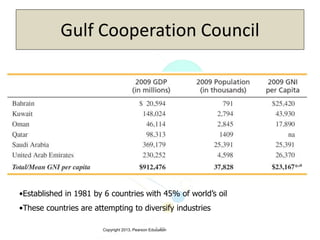
The document discusses the evolution of international trade agreements from GATT to the modern World Trade Organization (WTO). It then describes different types of preferential trade agreements (PTAs) that exist, ranging from free trade areas with no common external tariffs (like NAFTA) to full economic unions with a single currency and coordinated policies (like the European Union). Several existing regional trade blocs are also outlined, such as ASEAN, MERCOSUR, and the Gulf Cooperation Council.