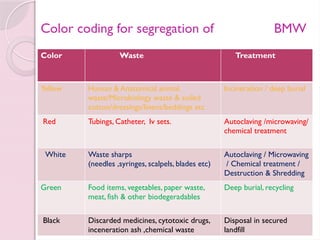
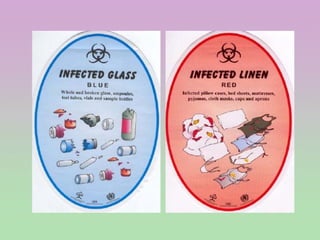
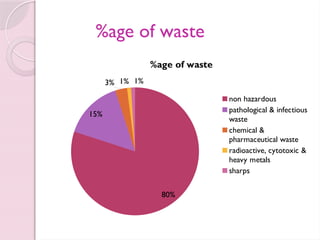
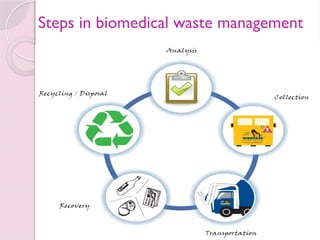
Biomedical waste, also known as infectious or medical waste, refers to any waste generated during the diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of humans or animals, and its management is governed by the Biomedical Waste (Management & Handling) Rules, 1998 in India. The document outlines the categories of biomedical waste, color coding for segregation, and steps for effective management, emphasizing the need for safe disposal to protect public health and the environment. It also addresses the principles for controlling hazards in healthcare settings, including staff training and proper housekeeping.