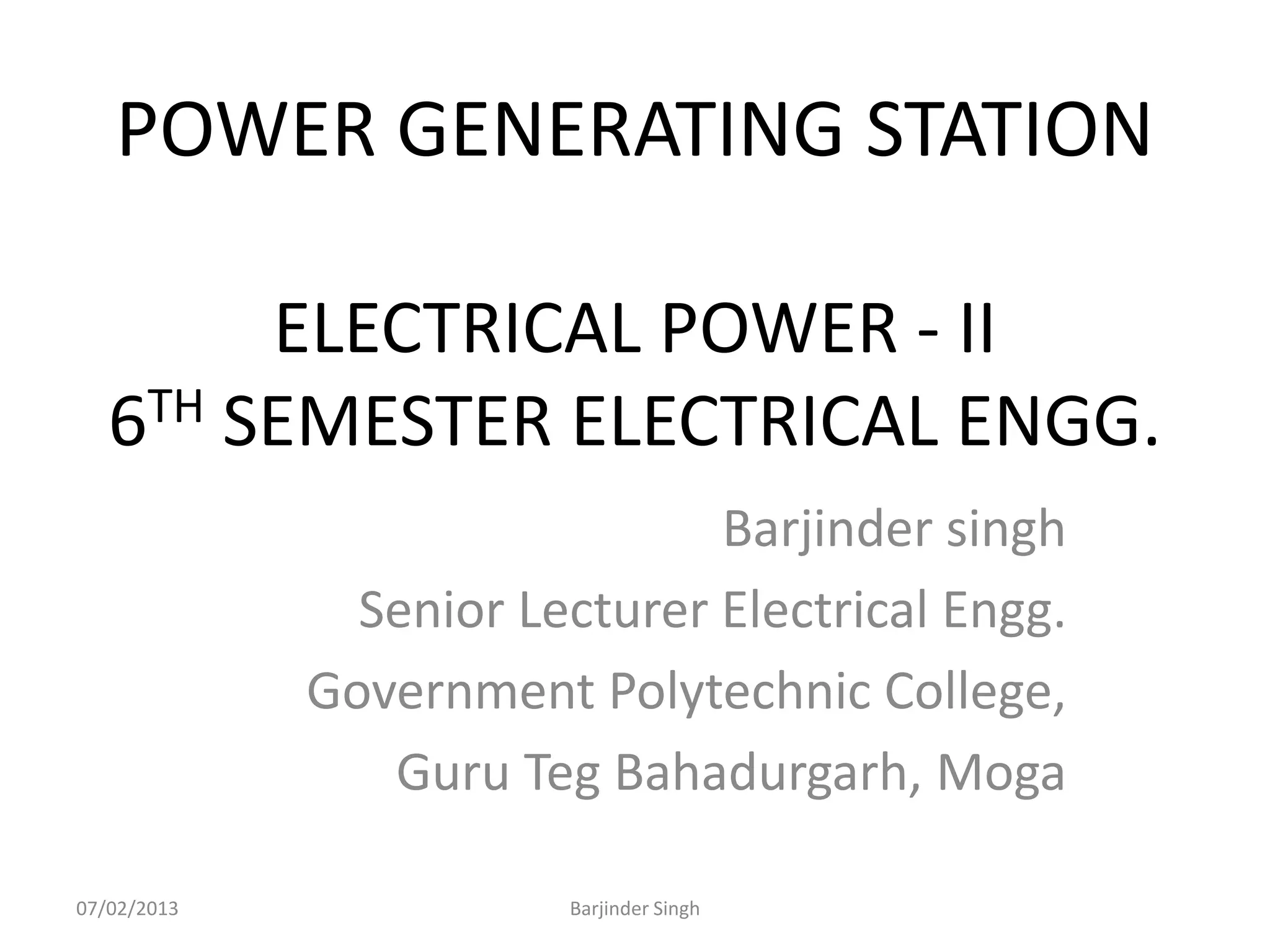
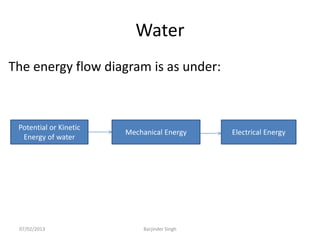
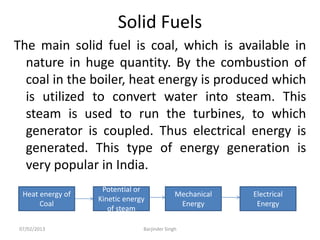
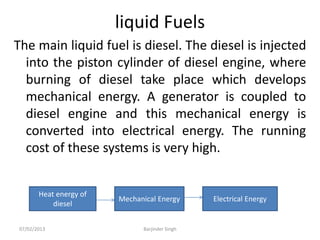
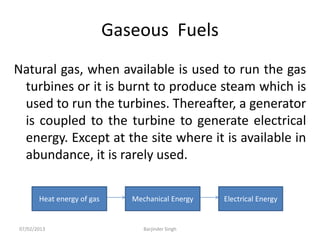
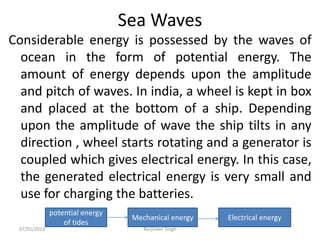
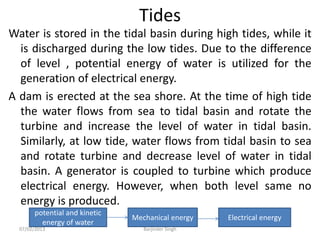
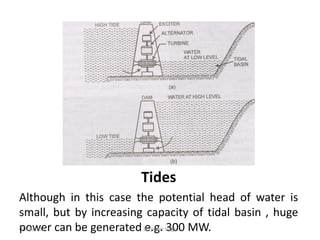
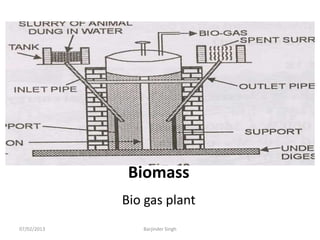
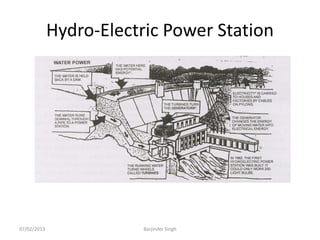
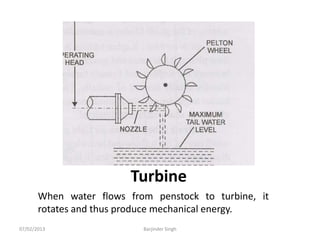
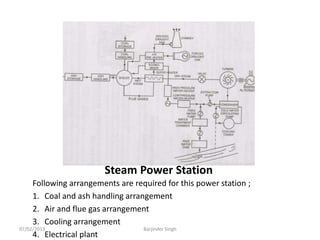
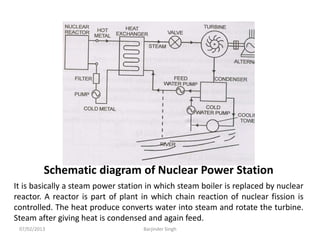
This document discusses various power generating stations and energy sources. It begins by introducing electricity and its importance. It then discusses advantages of electrical energy and various natural sources of energy including water, fuels, nuclear, sun, wind, tides, and biomass. It describes major power generating stations like hydroelectric, steam, diesel, and nuclear. It also discusses non-renewable and renewable energy sources and units of energy.