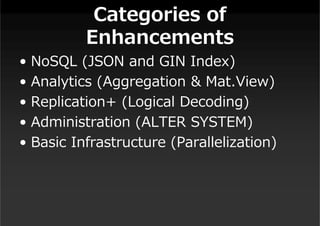
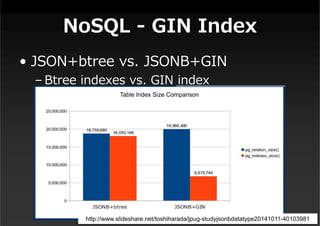
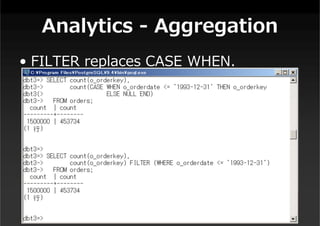
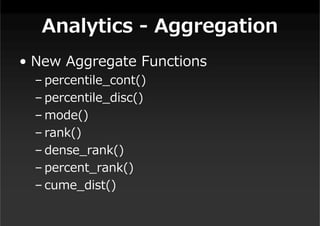
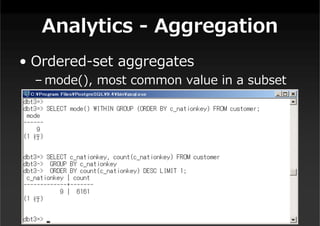
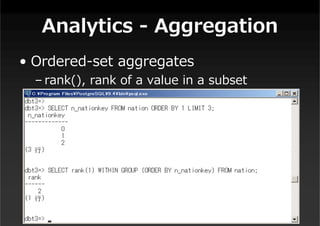
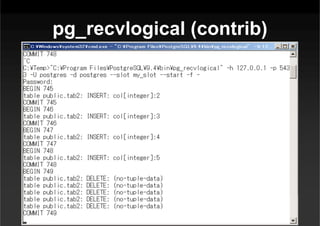
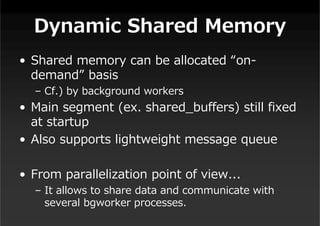
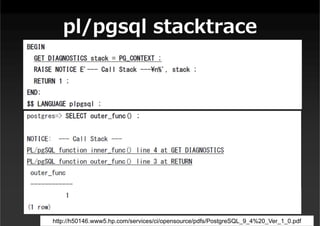
This document summarizes a presentation about new features in PostgreSQL 9.4. It discusses enhancements for NoSQL support with JSON and GIN indexes, analytics with new aggregate functions and materialized views, increased flexibility with logical replication, easier administration using ALTER SYSTEM, and improved infrastructure for parallelization through dynamic background workers and shared memory. The presentation provides an overview of the status of 9.4 and highlights some of the major new categories of features.