The document discusses logical decoding in PostgreSQL, detailing its process of extracting persistent changes from the database into a human-readable format through replication slots and output plugins. It covers how to enable logical decoding, the use of plugins for transforming data, and practical examples of consuming changes. Additionally, it touches on applications of logical decoding for auditing, replication, and migration tasks.



![Fun Things to do with Logical Decoding
Mike Fowler, mike@mlfowler.com mike.fowler@rantandrave.com
PGDayUK 2015
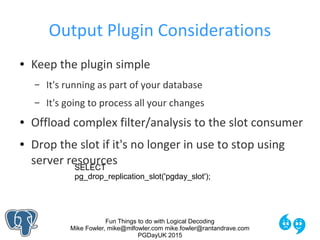
The Output from our Example
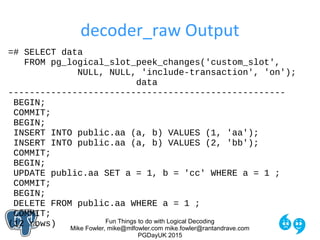
pgday15=# SELECT * FROM
pg_logical_slot_get_changes('pgday_slot', NULL, NULL);
location | xid | data
-----------+-----+----------------------------------
0/16C9ED0 | 723 | BEGIN 723
0/16C9ED0 | 723 | table public.sample: INSERT:
id[integer]:1
data[json]:'{"beverage":"coffee","temp":96}'
captured[timestamp without tz]:'2015-07-03 19:52:39.497161'
0/16CA000 | 723 | COMMIT 723
(3 rows)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/logicaldecoding-160630125806/85/Fun-Things-to-do-with-Logical-Decoding-18-320.jpg)


![Fun Things to do with Logical Decoding
Mike Fowler, mike@mlfowler.com mike.fowler@rantandrave.com
PGDayUK 2015
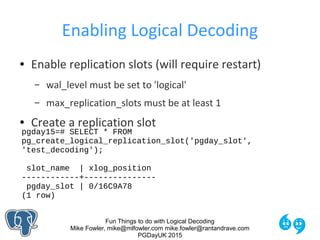
Limitations of test_decoding
● Only details the new/changed row
● No detail of a WHERE clause
● No timestamps in output to help cross reference
● Changed indexes don't make for easy reading
table public.sample: UPDATE: old-key: id[integer]:3 new-tuple: id[integer]:4
data[json]:'{"beverage":"coffee","temp":96}' captured[timestamp without time
zone]:'2015-07-07 00:07:56.305964'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/logicaldecoding-160630125806/85/Fun-Things-to-do-with-Logical-Decoding-21-320.jpg)