Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


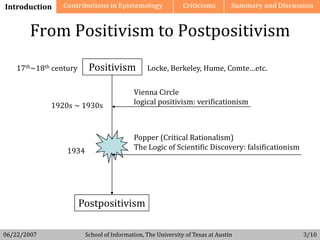





This document discusses the philosophy of Karl Popper and his contributions to epistemology. It outlines Popper's rejection of inductivism and verificationism, and his proposal of falsificationism as a criterion for scientific theories. Popper argued that a theory is scientific if it can be falsified, not verified, by empirical tests. The document also reviews criticisms of Popper's views from thinkers like Kuhn, Feyerabend and others.









