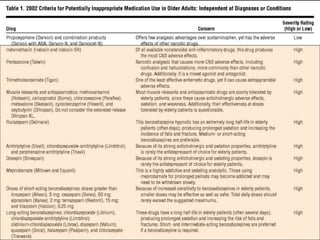
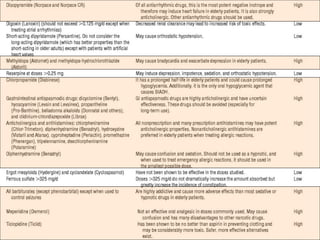
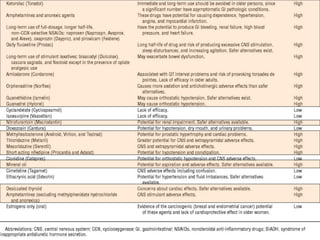
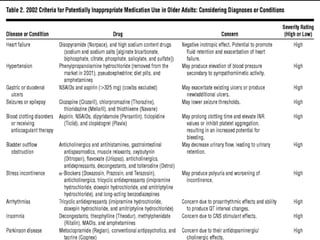
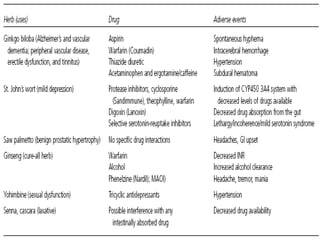
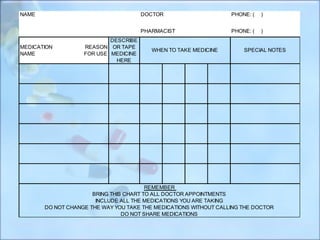
This document discusses polypharmacy in the elderly, defined as using more than 5 medications. It notes that polypharmacy prevalence increases with age, reaching 50% in those over 65. Consequences can include adverse drug reactions, reduced quality of life, and increased healthcare costs. Pharmacokinetic changes in aging like decreased liver and kidney function must be considered. The Beers Criteria provide guidance on inappropriate medications in elders. Interventions to reduce polypharmacy risk include regular medication reviews, educating patients, and using a personal health record.