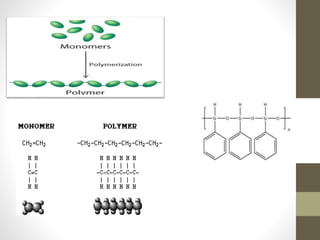
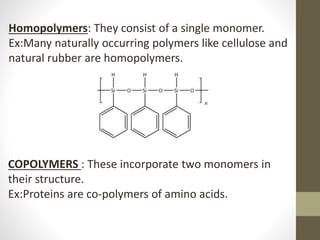
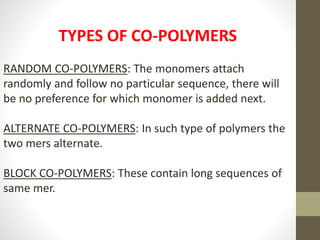
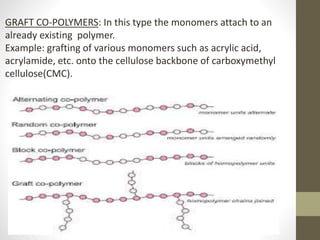
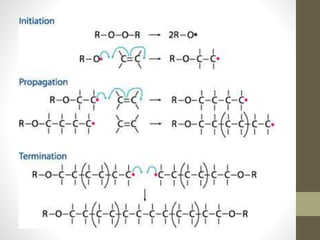
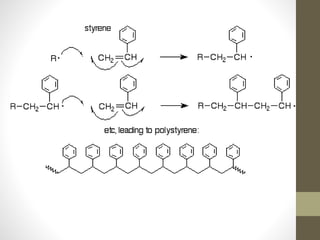
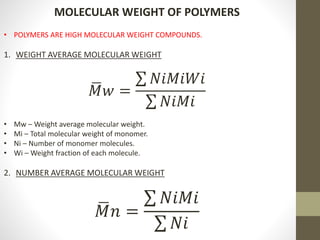
Polymer science is the study of polymers, which are large molecules composed of many repeating units called monomers. Some key points:
- The first synthetic polymer was celluloid in 1845, while Bakelite in 1872 was one of the earliest plastics. Many common polymers like polyethylene and PVC were invented in the 1930s.
- Polymers have a wide array of applications, from insulation coatings to automotive parts to pharmaceutical packaging and coatings. They are used to stabilize emulsions, thicken liquids, and control drug release.
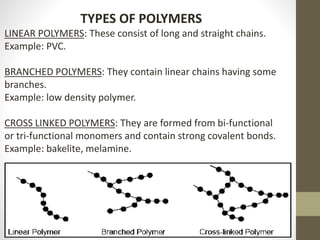
- Polymers can be classified by their structure (linear, branched, cross-linked), origin (natural vs synthetic), and properties (therm