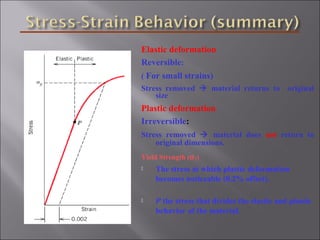
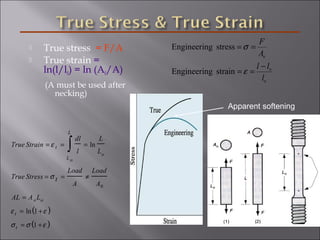
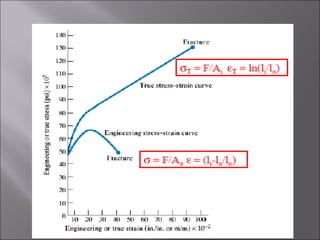
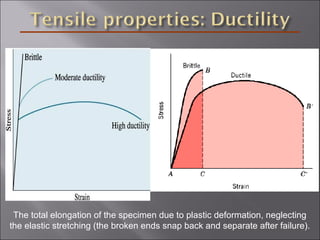
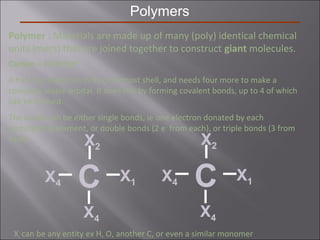
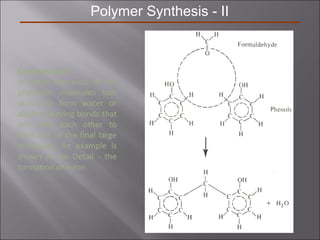
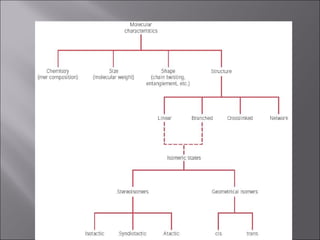
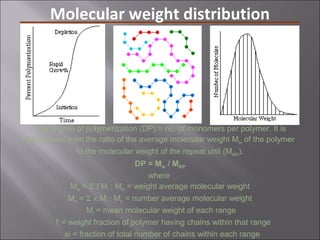
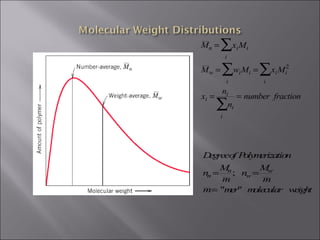
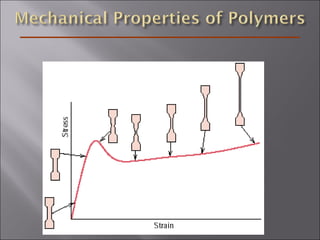
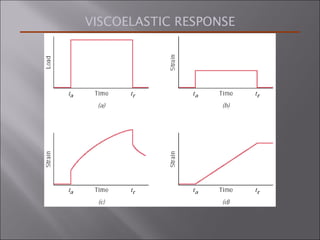
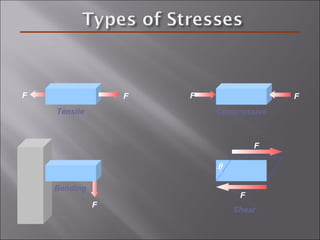
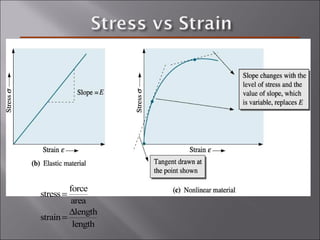
- Stress and strain are size-independent measures of load and displacement, respectively. Elastic behavior shows a linear stress-strain relation. Plastic behavior occurs when tensile stress reaches the yield strength (σy).
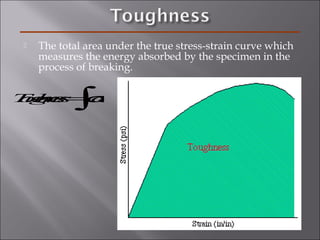
- The elastic modulus (E or G) and yield strength characterize mechanical properties. Materials with larger E resist deformation better. Toughness is the energy to break a material.
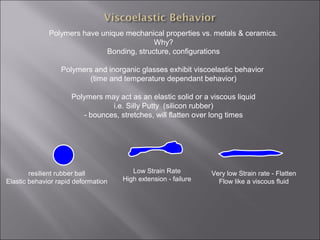
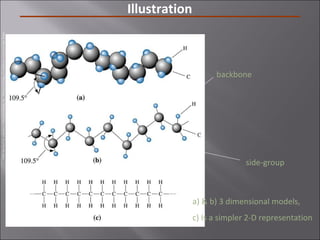
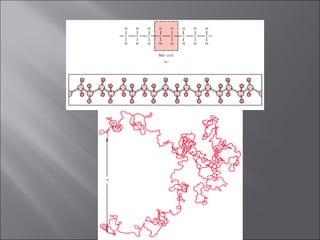
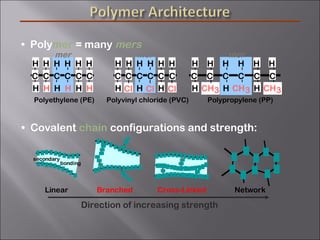
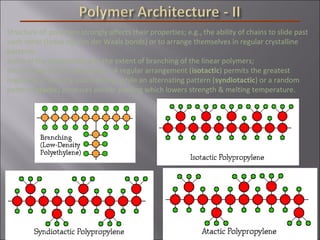
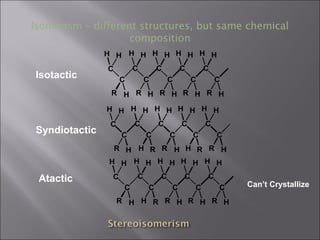
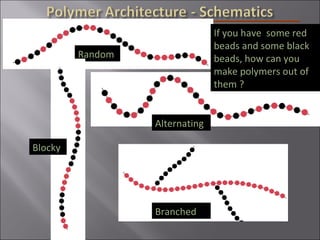
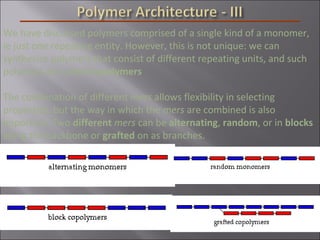
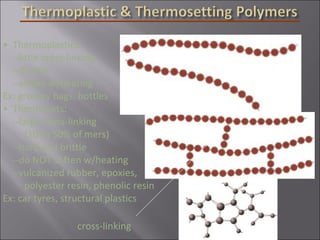
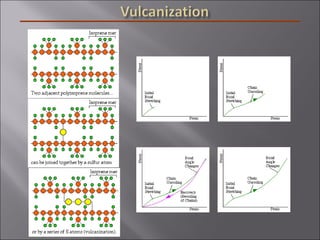
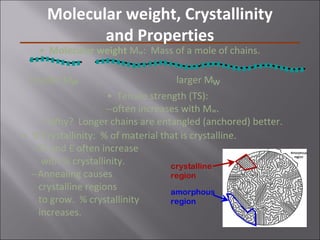
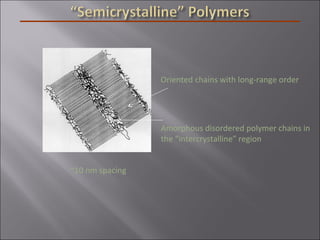
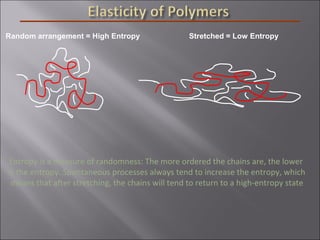
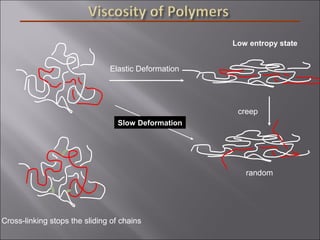
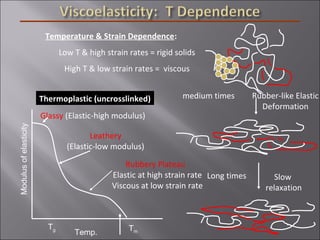
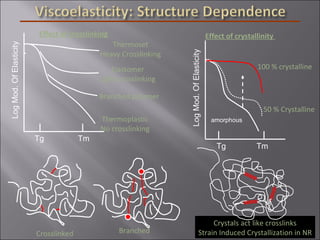
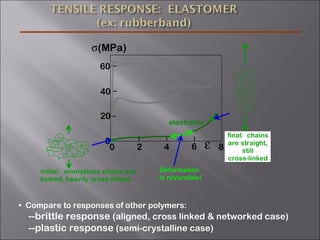
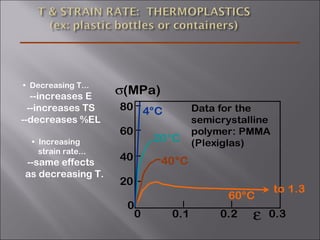
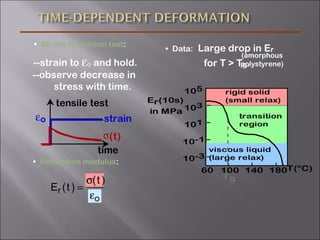
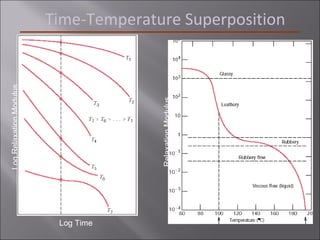
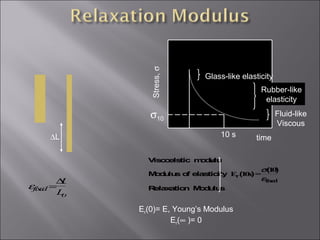
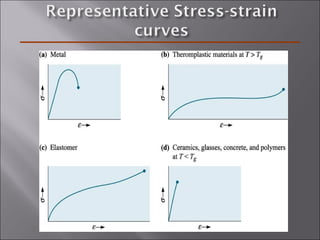
- Polymers have unique time- and temperature-dependent viscoelastic behavior compared to metals and ceramics. Their properties depend on bonding, structure, and chain configurations.

![ The slope of the stress-strain
curve in the elastic region.
Hooke’s law: E = σ/ε
A measure of the stiffness of
the material.
Larger the value of E, the
more resistant a material is to
deformation.
Note: ET = Eo – bTe-To/T
where Eo and b are empirical
constants, T and To are
temperatures
Units:
E: [GPa] or [psi]
ε : dimensionless](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymerproperties-170310073755/85/Polymer-properties-5-320.jpg)