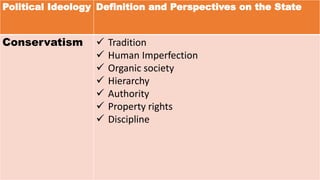
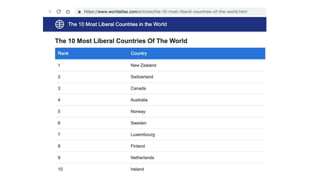
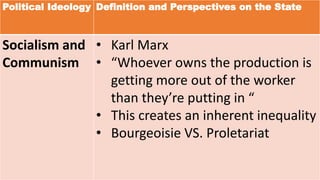
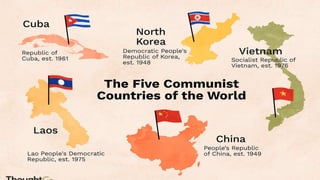
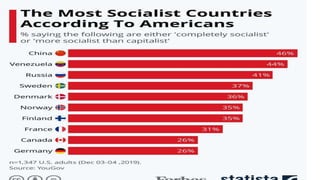
The document defines ideology as a set of beliefs and ideas that shape how individuals and groups view and interact with the world. It discusses political ideology specifically, defining it as a set of related beliefs about political theory and policy held by individuals, groups, or social classes. Political ideologies form the basis for how people view the world and the proper role of government. They aim to explain problems, provide visions for the future, and explain how to enact political change.