The document discusses pointers in C++. It defines a pointer as a special variable that stores the address of another variable of the same data type. It provides examples of declaring and accessing pointers, pointer arithmetic, pointers as function parameters and return types, pointers and arrays, pointers and strings, and pointers and structures. Key topics covered include pointer declaration and dereferencing operators, pointer arithmetic, self-referential structures, and using pointers to implement linked lists.
![Prepared By : Rakesh Kumar D.A.V.Centenary Public School Chander Nagar
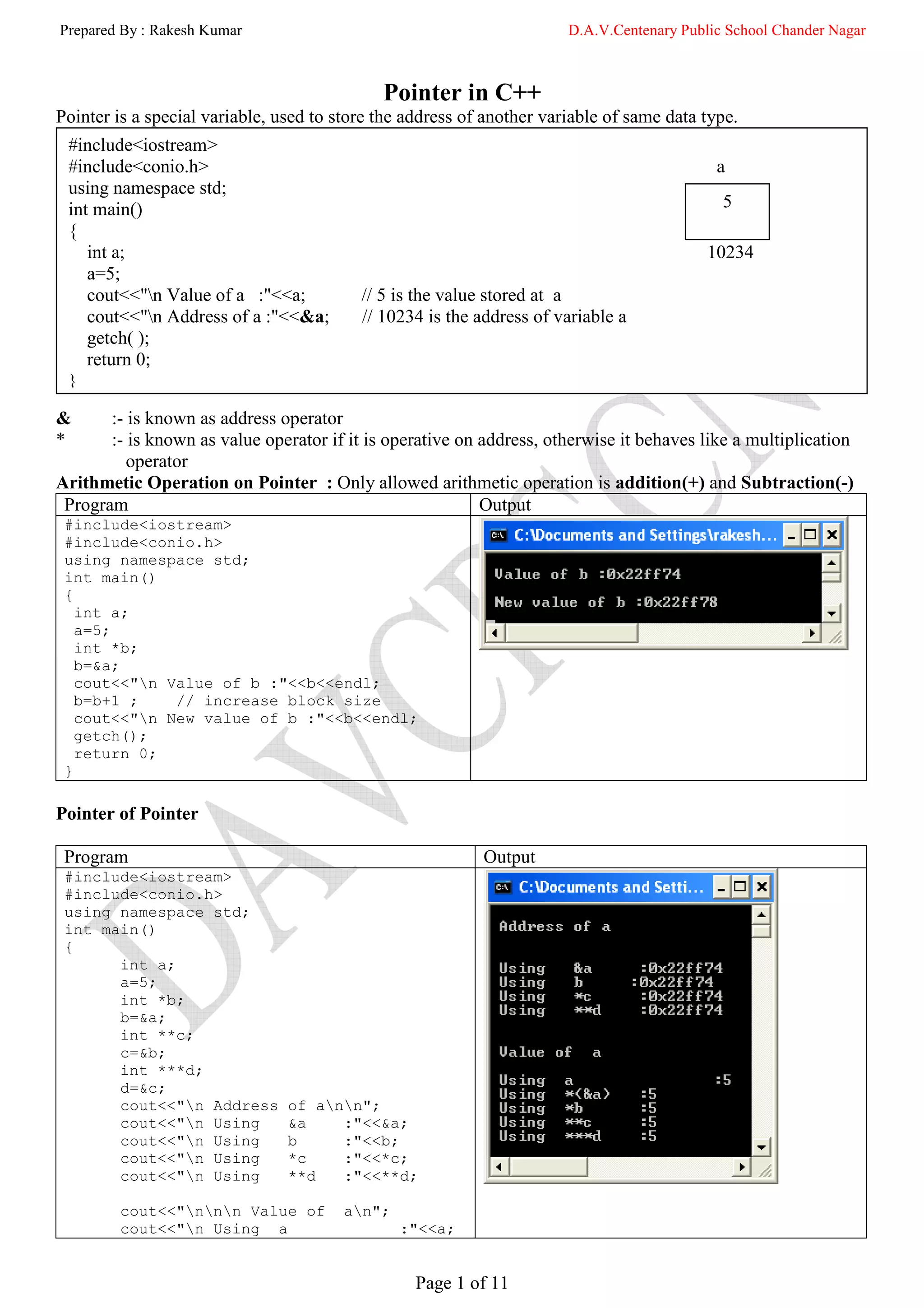
cout<<"n Using *(&a) :"<<*(&a);
cout<<"n Using *b :"<<*b;
cout<<"n Using **c :"<<**c;
cout<<"n Using ***d :"<<***d;
getch();
return 0;
}
Pointer as a function parameter
Program Output
// program to demonstrate call by pointer method
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
void change(int *a) // parameter as pointer
{
*a = *a+20;
}
int main()
{
int x=20;
cout<<"n Value of x before function call:"<<x;
change(&x); // passing parameter
cout<<"n Value of x before function call:"<<x;
getch();
return 0;
}
Pointer as a function Return type value
Program Output
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
int* read(void)
{
int a;
a=20;
return(&a);
}
int main()
{
int *res;
res = read(); // store retured address
cout<<"n Value of a :"<<*res;
cout<<"n Value of a :"<<*(read());
getch();
return 0;
}
Pointer and Array
When an array is defined like
int x[5]; // The memory block is as shown below
X
100 102 104 106 108
The address of 0th index block is called BASE ADDRESS and it can be obtained by the following
methods
Page 2 of 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-111219120235-phpapp01/75/Pointers-2-2048.jpg)
![Prepared By : Rakesh Kumar D.A.V.Centenary Public School Chander Nagar
(a) x -> 100
(b) &x[0] ->100
(c) x+0 ->100
(d) 0+x ->100
(e) &0[x] ->100
Processing array as a pointer without using any extra pointer variable
Program Output
// program to access array as
a pointer
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x[10],i;
// input phase
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
cout<<"Enter value :";
cin>>x[i];
}
// output
cout<<"n Output using as
a pointer:n";
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
cout<<setw(6)<<*(x+i);
getch();
return 0;
}
Processing array as a pointer using extra pointer variable
Program Output
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x[10],i,*p;
p= x; // assign base
address to p
// input phase
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
x[i]=rand();
// output
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
cout<<setw(6)<<*p;
p++;
}
getch();
return 0;
}
Page 3 of 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-111219120235-phpapp01/75/Pointers-3-2048.jpg)
![Prepared By : Rakesh Kumar D.A.V.Centenary Public School Chander Nagar
Accessing pointer as an array
Program Output
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
void change(int *x)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
x[i]=x[i]+20;
}
int main()
{
int x[10],i;
// input phase
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
cout<<"Enter value :";
cin>>x[i];
}
// processing phase
change(x);
// output phase
cout<<"n Modified List :";
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
cout<<setw(6)<<x[i];
getch();
return 0;
}
Pointer & String
String : it is an array of character, which always terminates with NULL (‘0’).
Char str[80]=”RAKESH”; // It’s allocation in stin is as follows
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ……………………………………………………..79
R A K E S H 0
101 102 103 104 105………………………………………………………………………… ………180
cout<<str; // Please note that only the base address of string has been given to cout
// and cout is here print the whole string not the base address
Result : RAKESH
Example 2.
char str[80]=”RAKESH”;
cout<<*str; // now compiler try to print value stored at base address
Result : ‘R’
Example 3
char str[80]=”RAKESH”;
cout<<*++str; // process nearest first
Result : ‘A’
Page 4 of 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-111219120235-phpapp01/75/Pointers-4-2048.jpg)
![Prepared By : Rakesh Kumar D.A.V.Centenary Public School Chander Nagar
Example 4
char str[80]=”RAKESH”;
cout<<++*str; // process nearest first
Result : ‘S’
Example 5
char str[80]=”RAKESH”;
cout<<++str; // print 101 address onward upto NULL
Result : AKESH
Pointers and Structure
Assigning and Accesssing structure type Pointers
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
int roll;
char name[30];
char address[60];
};
int main()
{
student s;
student *s1;
s1= &s;
//input phase
cout<<"n Enter roll no :";
cin>>s.roll;
cout<<"n Enter name :";
cin>>s.name;
cout<<"n Enter address :";
cin>>s.address;
// output - using pointer variable
cout<<"n Roll :"<<(*s1).roll; // s1->roll
cout<<"n Nane :"<<(*s1).name; // s1->name;
cout<<"n Address :"<<(*s1).address; // s1->address
getch();
return 0;
}
Page 5 of 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-111219120235-phpapp01/75/Pointers-5-2048.jpg)
![Prepared By : Rakesh Kumar D.A.V.Centenary Public School Chander Nagar
New ( ) : This function is used to assign memory to a pointer variable from the available memory heap. The
function is responsible to calculate no of bytes and types of data, required.
Delete ( ) : This function is used to release assigned pointer memory to memory heap
Accessing Pointer Variable using new( ) and delete ( ) function
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
int roll;
char name[30];
char address[60];
};
int main()
{
student *s;
s= new(student);
//input phase
cout<<"n Enter roll no :";
cin>>s->roll;
cout<<"n Enter name :";
cin>>s->name;
cout<<"n Enter address :";
cin>>s->address;
// output - using pointer variable
cout<<"n Roll :"<<s->roll;
cout<<"n Name :"<<s->name;
cout<<"n Address :"<<s->address;
delete(s);
getch();
return 0; }
Self Referential Structure: A structure which can have a variable of it’s own type inside it’s declaration,
then the structure is known as self referential structure.
Example
struct student
{
Int roll;
` student *s;
};
Example of link list
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int info;
node *ptr;
};
int main()
{
node *x,*y,*temp ;
x= NULL;
int choice;
do
{
system("cls");
cout<<"n 1. Add at beginning";
Page 6 of 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-111219120235-phpapp01/75/Pointers-6-2048.jpg)




